All you need to know about Blockchain

In this article, we are going to tell you what is blockchain development. We want you to understand how blockchain works, what industries it can serve, and when it is worth developing one.
What is blockchain?
Basically, a blockchain is a specific type of database in a form of a digital, distributed ledger which is continuously growing. It’s characterized by storing transactions in batches called “blocks” and each block is connected to the previous one by a hash, which is protection against revision and tampering. Together they form a chain of blocks that cannot be altered.
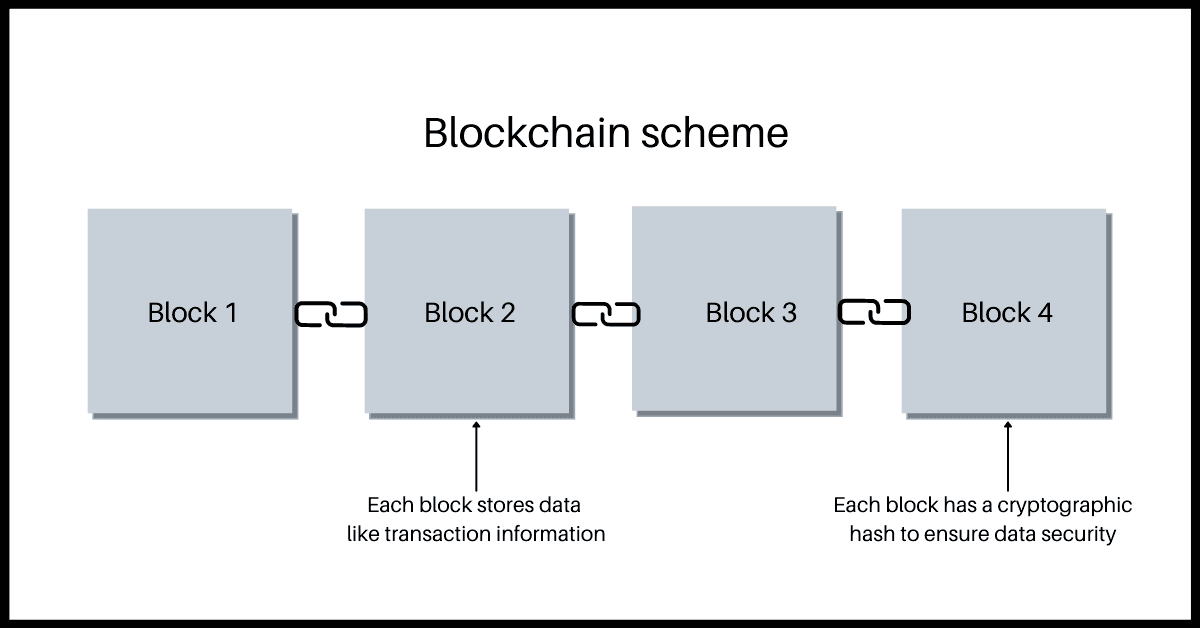
How does blockchain work?
As it was mentioned earlier, a blockchain is a continuously growing database consisting of blocks that store information about transactions. The most popular blockchains rely on consensus between users, called Proof of Work (POW). The new block is created by users, the so-called miners, or more precisely by their software. because such activity requires huge computing power. Why? Generally speaking, for security reasons.
Each block has a hash, which is computed out of it. It is usually a 256-bit number (sometimes also a 512-bit) that refers to the hash assigned to the previous block. In order to mine a new block, users must find the one correct hash that matches the previous block. This very activity requires tremendous computing power, just like making changes to a block, and the likelihood of a single user succeeding is negligible. And that’s because the number of possible combinations is unimaginably enormous.
The next term required to understand how blockchain works are nodes. A node can be any device connected to the blockchain. Most importantly, each node in the network can verify the correctness of the blockchain, and this, in turn, ensures security, because every time miners find a new block, algorithms check that all nodes match. So if a single blockchain user wanted to commit fraud and change some data, such as wanting to delete information about some transaction, they would be quickly detected because their copy would not match the copies stored on the other nodes.
History of blockchain development
Blockchain is not a new technology. We can define blockchain as a combination of proven technologies applied in a new way. It combines the Internet, asymmetric cryptography, and governing incentivization to eliminate the need for a trusted party. It makes a flow of value without intermediaries easy and secure. See what went into the creation of blockchain technology
- 1991 – that year Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta showed the world a solution for time-stamping digital documents so that they could not be backdated or tampered with. The solution used a chain of cryptographically secured blocks to store documents.
- 1992 – the technology was modernized by inventing a hash tree (also Markle tree). It made the system more efficient by allowing several documents to be collected into one block.
- 2004 – what is interesting about the technology originally created to stamp and secure documents is that it never came into use. The patent on it expired in 2004, so it has been at everyone’s disposal since then.
- 2008 – a man named Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper that outlined the general principles of a decentralized peer-to-peer network called Bitcoin. He used the concept created by Haber and Stornetta in which he improved the way to timestamp blocks.
- 2009 – Nakamoto launched the public Bitcoin network and issued the first block.
- 2014 – Ethereum technology, also known as Blockchain 2.0, has been released. It introduced to the blocks the possibility of launching so-called smart contracts.
What characterizes blockchain?
In the book The Real Business of Blockchain, the authors describe blockchain through its 5 features, an understanding of which is crucial to explain why blockchain is revolutionizing the market. The features are distribution, cryptography, immutability, tokenization, and decentralization.
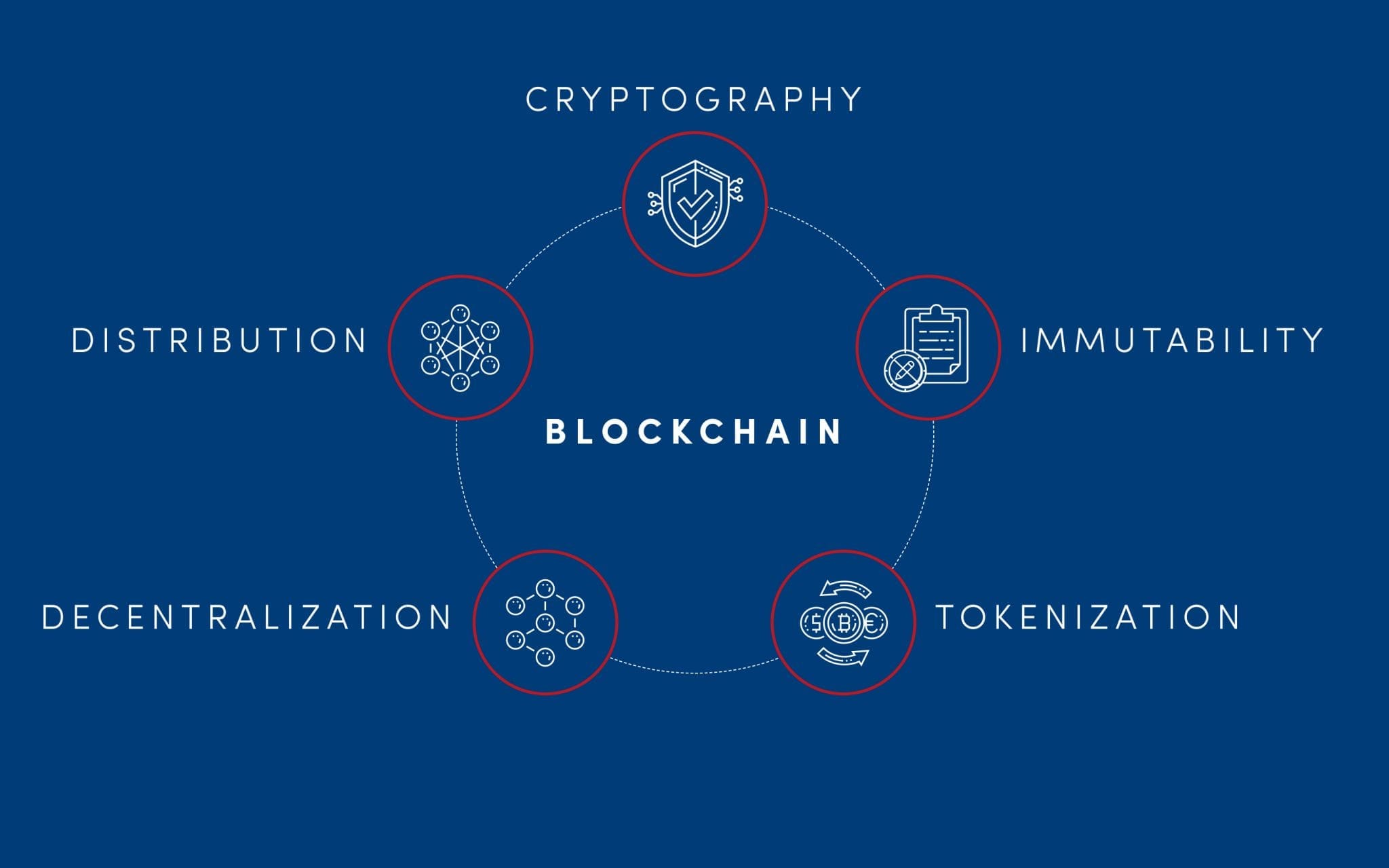
Distribution
Network dispersion guarantees stability. This means that once you “accelerate” a system based on the blockchain it won’t be easy to stop it. The network scales with each subsequent network user and all those who maintain the so-called Full node, store on their computers a full copy of blockchain history, which prevents accidental 😉 changes in history. In other words, servers and clouds are replaced by a vast number of “nodes” run by volunteers from across the globe. This provides resilience and trust without any central third party.
Cryptography
Cryptography, which is used in blockchain, mainly concerns digital signatures. Transactions sent between users are signed using asymmetric encryption. Thanks to the signature you can mathematically prove that the transaction was sent by a specific network user. Each network participant has one or many sets consisting of a private key (known only to him) and a public key (everyone can know it). The first allows you to sign the message and the second allows you to verify that a particular person has signed it. Remember not to share your private key with anyone – it may cause unwanted transactions to be published on your behalf.
Immutability
Once saved, data on the blockchain stays on it forever. Except, in special cases where history is artificially changed with the consent of the community or organization management, we cannot undo transactions. Each user is responsible for their own actions. As a conscious participant in the network, you need to know it again and keep an eye on your private key.
Tokenization
Blockchain was created, among others, to exchange values securely between users. Tokenization assumes that the system operates on one or many assets, and the ownership of them is recognized on the basis of tokens held reflecting the given asset. This opens up many possibilities and in combination with Smart Contracts, it becomes a powerful tool. When you introduce tokenization, transactions between users won’t be only an exchange of data but also of value. In addition, a blockchain with a native token provides itself a kind of “financing”.
Decentralization
A feature that is not obvious and is hard to measure. In fact, when talking about blockchain, we should talk about the scale of decentralization, not about whether it occurs. To describe it, let’s return to the first feature – distribution. It’s known that the network is based on many nodes but the fundamental question is how large groups of nodes are owned by a single person or organization? That is why we can only talk about the scale of decentralization because the problem described will always occur (unless it’s solved technologically). It’s also worth mentioning that many projects don’t have this problem by implementing a private blockchain, but such a choice is usually made for many reasons.
Is blockchain safe?
Blockchain is a safe solution because it doesn’t allow manipulation of the data stored in the ledger. And all because the ledger is not stored in a single location (like a server or cloud) or managed by any particular company. The cryptographic linking between blocks ensures data immutability. It is public and easily verifiable because it is hosted by millions of computers simultaneously. Anyone can maintain a copy of it and verify its correctness. In other words, servers and clouds are replaced by a vast number of “nodes” run by volunteers from across the globe. This provides resilience and trust without any central third party.
What can blockchain be used for?
Originally Blockchain has been developed along with Bitcoin which allows only peer-to-peer payments between its users. However, Blockchain proved to be highly useful in a large variety of applications beyond cryptocurrencies.
A most popular example of, a so-called Blockchain 2.0 solution, is Ethereum. It is an application platform that uses Blockchain as its storage and programmable Smart Contracts to execute its business logic. This combination proved to be highly disruptive and presents very promising perspectives for new technologies.
What are smart contracts?
Smart Contracts are a digital version of traditional contracts written in a programming language. They are programs that directly control the transfer of digital assets between parties under certain, programmed conditions. Once deployed they automatically and safely execute agreements between untrusted parties. The whole process takes place on the blockchain, therefore the execution is transparent, certain, immutable, and decentralized.
Industries we serve using blockchain development
We are working commercially on blockchain products since early 2017 whats makes us one of the very first companies that professionally played with blockchain products in the world. During those years we managed to deliver various blockchain solutions in different industry sectors. To name just a few of them, we have been working on blockchain products related to:
Investment
Payment processing
Internet of Things
Real estate
Insurance
Healthcare
Exchanges
Energy Management
Example blockchain use case
Below you can find a short description of a blockchain use case in agriculture that we recently analyzed and delivered to one of our clients.
Blockchain use cases in agriculture
The agricultural sector has been under a great deal of pressure as the planet struggles with climate change and its negative impact on the land and its productive capacity. Add to that the galloping rate of population levels and you’ve got a recipe for uncertainty.
Blockchain in Agriculture 10 possible use cases:
- Overseeing farm inventory
- Enhancing agricultural supply chains
- Modernizing farm management software
- AgTech IoT optimization
- Fair pricing
- Agricultural subsidies oversight
- Community-supported agriculture
- Mobile remittance for small farmers
- Great accountability for multinationals
- Incentivizing sustainable practices.
Blockchain aims to remedy that by eliminating food wastage and raising farmers’ income to keep them motivated. Thanks to its decentralized nature, blockchain can link food producers directly with consumers. As a result, harvests are sold quickly preventing spoilage, and middlemen are taken out of the equation lowering food prices.
Blockchain in agriculture is also bringing full transparency to the entire production cycle by documenting everything and keeping it open for verification by anyone. From how the food was planted or raised, what it’s been fed with, whether fertilizers were used, and so on, consumers can check everything from a ledger that’s tamper-proof. That takes away a lot of suspicions.
Cases in which you don’t need blockchain
Blockchain is a very trendy technology, however, it is not always worth using it at all costs. Below you will find a list of assumptions that may disqualify blockchain as a solution for you:
- There is no database in your project or data are changed very rarely.
- System users do not directly influence the data collected in the database.
- You supervise the entire system.
- Large amounts of data are stored in the system.
Want to know more? Read You ain’t gonna need a blockchain article.
Blockchain development – things you need to consider
You already know the strengths of blockchain technology and some examples where this technology will not be useful. This, in turn, should give you the answer to whether blockchain development is what you need. If so, read on, because we list things that have to be considered.
Your goal
The first point is not very revealing. Before you get in touch with a company that specializes in developing blockchain-based applications, think about product vision – what goals it fulfils, what problems the product solves for users, and how it should stand out from other applications of this type.
The most common reason startups fail is a lack of market demand, so your mission is to make sure your product will fit the market.
Design
Usually, the competition between startups is very high. What can convince users to your product is the ease of use, so an exceptional UX/UI. Don’t hesitate already at the stage of sketches and mockups to ask potential users for their opinions and whether such a designed product would be useful for them.
Starting from scratch?
You need to know that developing a blockchain-based application can take a good few months if you want to make it from scratch. Fortunately, it is possible to create a blockchain from already ready and proven components that companies have used for other such projects. We wrote about this in a separate article about creating cryptocurrency exchanges. To sum it up briefly: in the vast majority of cases, it is not worth creating an application from scratch.
Decentralization
The main advantage of blockchain technology is decentralization, which provides security to users and protects against fraud. However, you need to consider that once you put your blockchain in the hands of users, you will lose full control over it. Therefore, before you do so, consider whether the time is right.
We think that the app development stage is too early to think about this. That’s when transparency matters instead. If you already have first users, but you are still working on the product, inform them about all changes, and share documentation and your plans for the future.