AI agents for healthcare [2025 guide]

While everyone’s been focused on AI diagnosis, the real healthcare revolution might be happening in the back office.
Let’s skip the usual AI healthcare revolution headlines.
While everyone’s talking about AI chatbots diagnosing patients (spoiler alert: they’re not), something more interesting is happening in healthcare.
Major tech players (Microsoft, Oracle, NVIDIA) and startups are taking a different approach: AI agents that tackle healthcare’s back-office challenges.
This article is for healthcare professionals and decision-makers seeking to understand how AI agents are transforming back-office operations. Explore five key applications & discover how to implement them in your organization.
Build your AI agent
The healthcare AI agent revolution
Did you know that healthcare professionals spend nearly 35% of their time on administrative tasks? If your average visit takes 15 minutes, the physician will spend 5 minutes and 15 seconds just taking notes and typing them into their computer.
It’s quite a problem, isn’t it?
There are more issues in the back-office of healthcare… yet in just the past month (as of November 2024), we’ve seen a wave of announcements that show where how AI can solve them:
- Microsoft unveiled tools for building custom healthcare AI agents
- Oracle released a Clinical AI Agent
- NVIDIA launched customizable AI workflows
Simultaneously, a new player has entered the field. Quadrivia, a startup backed by Swedish VC Norrsken, is developing what they call an “AI agent for healthcare.” What makes this interesting is its founder – Ali Parsa, the entrepreneur behind Babylon Health. After building one of Europe’s most prominent healthtech companies, seeing it reach a $4.2 billion valuation… and collapse in 2023, Parsa is now betting on AI agents (focusing on insurance triaging or back office automation, as sources suggest) rather than consumer-facing healthcare solutions.
5 key healthcare AI agent applications
Below, I’ll show you 5 examples of how AI agents are transforming specific areas or healthcare.
Yet, the one field where artificial intelligence is making the biggest difference is simply this: letting doctors be doctors, researchers be researchers, and patients be patients.
1. Clinical documentation
Oracle’s implementation at AtlantiCare tells the most compelling story: 41% reduction in documentation time, giving providers back 66 minutes each day.
Let’s put that in perspective:
- For a hospital with 100 providers, that’s 110 hours saved daily.
- Annually, that’s over 40,000 hours of physician time redirected to patient care.
- At an average physician cost of $150 per hour, this represents potential savings of $6 million annually just in time value.
As Dr. Patricia Notario from Billings Clinic says about Oracle’s solution, “Compared to previous models of AI documentation, this has been the most reliable and accurate. The notes are done almost immediately for my review, and it works just as well in Spanish as it does in English.”
But it’s not just about time savings.
Microsoft’s nurse-focused solution takes this further with ambient voice technology.
Ambient AI refers to an intelligent environment that uses sensors and AI to continuously and unobtrusively monitor patients’ health and surroundings. What’s more, it allows nurses to document while keeping their focus on patients. The system automatically drafts flowsheets and clinical notes, works in multiple languages, and integrates directly with electronic health records.
Why is this such a breakthrough?
The sad reality of many healthcare systems is that medical staff spend a significant portion of their working time on bureaucratic tasks. For example, in the US, clinicians spend up to 35% of their time on documentation tasks. Ambient clinical intelligence uses AI to listen in on doctor-patient conversations and automatically document the visit in electronic health records. Ambient microphones reduced documentation time from 2 hours to 15 minutes in some cases.
“I look forward to the day I no longer have to sit in front of a computer to treat my patient,” says Beth Kushner, CMIO at St. Joseph’s Regional Medical Center. “Instead, I’m able to just have a regular conversation with my patient.”
Learn more: Ambient AI for healthcare
2. Patient service and navigation
Healthcare organizations are rethinking patient interaction. Cleveland Clinic’s implementation of Microsoft’s AI agents shows how – patients can navigate services, schedule appointments, and get health questions answered without staff intervention.
NVIDIA’s approach includes AI-powered avatars that handle everything from appointment scheduling to prescription management. These aren’t just chatbots – they’re full-service digital front doors that understand healthcare context.
Meanwhile, Quadrivia, Ali Parsa’s new venture, appears to be focusing on insurance-related patient interactions, suggesting the industry sees significant opportunity in streamlining these high-friction touchpoints.
Learn more: Intelligent automation in healthcare
3. Medical research and drug discovery
NVIDIA’s impact here is particularly striking. Their platform turns what used to be hours of computational work into seconds. The system can:
- Screen millions of potential drug compounds virtually
- Predict protein structures accurately in minutes
- Extract insights from vast databases of research papers
- Match patients with relevant clinical trials
The NCATS informatics team reported that with NVIDIA AI, processes that used to take hours on CPU-based infrastructure are now done in seconds.
4. Medical imaging
Microsoft’s working on new imaging foundation models. Here, AI agents can transform radiology workflows:
- Automatic routing of scans to appropriate specialists
- Quick abnormality identification
- Automated draft reports for chest X-rays
- Pre-surgery organ mapping
- 3D CT image segmentation
There’s a lot of excitement about AI agents in radiology because they could really shorten the time it takes to get your MRI report, which is a serious problem. For example, statistics for Poland show:
According to data from the Alivia Oncology Foundation, the average waiting time for a report has more than doubled in the last 3 years. In 2021, patients waited 14 days for an MRI report and 11 days for a CT scan under normal conditions. Currently, the waiting time for an MRI report has increased to 31 days, and for a CT scan to 22 days. And these are national averages. In some regions, patients are forced to wait much longer, for example, in the Lesser Poland region – up to 53 days.
5. Clinical workflow and data analysis
Here’s where everything comes together.
Oracle’s Clinical AI Agent doesn’t just handle documentation – it suggests clinical follow-ups, integrates with coding systems, and tracks patient outcomes. Microsoft’s platform analyzes everything from geographic distribution of patients to satisfaction metrics.
These tools are creating what Oracle’s Seema Verma calls “the ability to overcome long standing industry challenges.”
Learn more: What is back-office automation? (for non-technical people)
What this means for healthcare organizations
The market is moving fast. Microsoft, Oracle, and NVIDIA have shown their cards. New players like Quadrivia are entering the space. Yet, the real goal is not to jump on the AI agent bandwagon, but actually understand where these tools can deliver value.
Smart healthcare organizations are already asking the right questions:
- Where do our staff waste time on tasks that don’t need human intelligence?
- Which processes cause the most frustration for patients and providers?
- What could our specialists accomplish with an extra hour each day?
Learn more: 19 key digital health trends for 2025
Implementation realities & challenges
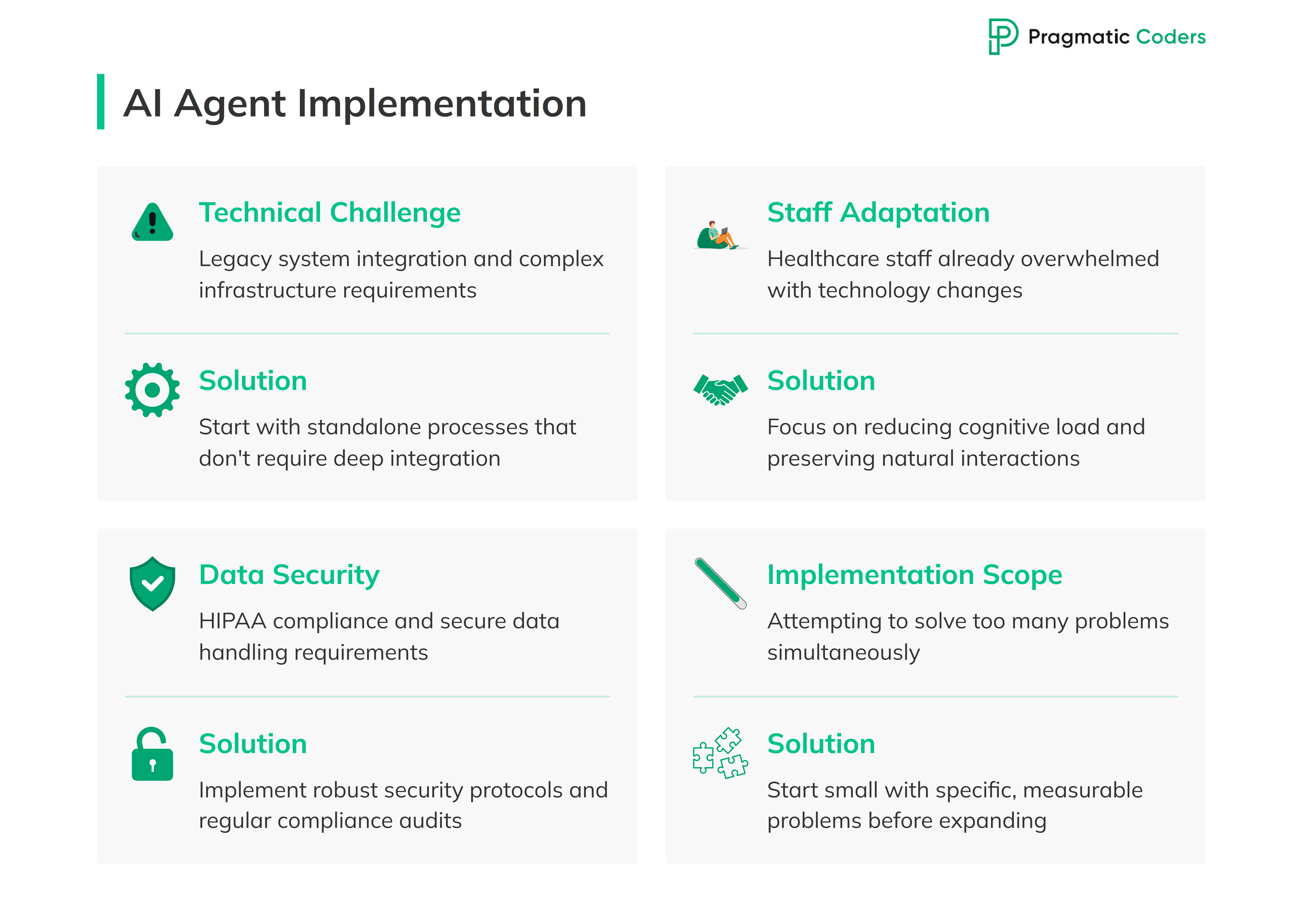
Healthcare organizations implementing AI agents face a complex set of challenges. However, we’re starting to see what works best.
Technical integration of AI agents
The first challenge isn’t AI capability – it’s infrastructure. Healthcare systems run on a complex web of legacy software, often decades old. Any new AI system must work within this reality. The technical requirements are substantial:
- Multiple system integrations
- Real-time data synchronization
- HIPAA-compliant data flows
- Reliable backup procedures
But healthcare organizations are finding ways around these obstacles. The key? Starting with standalone processes that don’t require deep integration with critical systems.
Organizational adaptation
The human side of implementation proves more challenging than the technical. Healthcare staff are already overwhelmed with technology changes (not to mention 49% of practicing physicians experience burnout weekly). Adding AI agents to the mix requires careful change management.
Successful organizations focus on:
- Reducing rather than adding to cognitive load
- Preserving natural patient-provider interactions
- Building trust through transparent results
- Starting with willing early adopters
What actually works
The pattern among successful implementations is clear: start small, prove value, then expand. Organizations seeing the best results choose specific, measurable problems to solve first. A single department, a specific workflow, a clear metric of success.
The most effective approach follows three principles:
- Target high-friction, low-risk processes first
- Measure concrete results (time saved, errors reduced, satisfaction improved)
- Let staff experience the benefits before expanding scope
The key is focusing on areas where AI can reduce administrative burden without attempting to replace clinical judgment.
Making AI agents work in healthcare: A practical guide

Where to start
The most successful implementations begin with processes that are:
- High volume but low risk
- Time-consuming but relatively simple
- Frustrating for staff but not critical for patient safety
- Easy to measure in terms of time saved or efficiency gained
Documentation is an obvious starting point – it meets all these criteria. But there are other entry points: appointment scheduling, insurance verification, or routine patient follow-ups.
Implementation strategy
Smart organizations follow a three-phase approach:
- Pilot Phase. Choose a department that’s both willing and representative. Give them real support, but let them face real challenges. Their experience will reveal your organization’s specific hurdles.
- Evaluation Phase. Look at both hard metrics and soft feedback. Time saved matters, but so does staff satisfaction. Watch for unexpected benefits and problems. Let the pilot group become your internal experts.
- Expansion Phase. Roll out to other departments gradually, using lessons and advocates from your pilot. Each new implementation should be easier than the last.
Avoiding common pitfalls
Experience shows several recurring mistakes, such as trying to solve everything at once or focusing on technology instead of workflows.
For healthcare organizations considering AI agents, the roadmap is becoming clear:
- Start with operational efficiency, not clinical decision-making
- Build on proven use cases rather than pioneering new ones
- Focus on staff empowerment rather than replacement
- Measure everything, but be patient with results
What to watch for
Several developments will shape this space in the coming months:
- Integration standards between different AI agent systems
- Real-world performance data from early implementations
- Regulatory frameworks catching up to the technology
- New players entering with specialized solutions
For healthcare organizations, the question isn’t whether to adopt AI agents, but how to implement them in ways that deliver measurable value. The technology is ready. The business case is clear. Now it’s about smart execution.
Note: Some information about upcoming products and features is based on announcements and press releases. Actual implementations may vary.
Looking for more content on AI Agents? Check out our article about AI agents in game development!

![AI agents for healthcare [2025 guide]](https://www.pragmaticcoders.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/C__Users_Ewelina_Downloads_healthcare-ai-infographic201.html.jpg)