AI in Asset Management: Trends and Challenges in 2025

Artificial Intelligence is reshaping industries around the globe, and the financial sector is no exception. Generative AI, a subset of AI, is revolutionizing asset and wealth management by enhancing investment strategies, automating operations, and providing personalized client insights. Notably, AI has generated approximately $59 billion by managing assets in 2024. This staggering figure highlights how AI is not just a gimmick but a next-gen tool that revolutionizes the asset management industry. Recognizing this transformative potential, industry leaders are making significant investments to harness AI’s capabilities:
In December 2024, BlackRock’s COO, Rob Goldstein, emphasized the firm’s commitment to enhancing its AI capabilities to automate processes and improve data handling.
In this article, we’ll explore AI’s capabilities in asset management. We’ll delve into its integration into the industry, its numerous benefits, and the challenges of its adoption. We’ll also examine current trends and anticipate developments for 2025. Whether you’re a financial professional or simply curious about the future of asset management, this article will provide valuable insights into this evolution.
Key Points
|
What is Asset Management?
Here’s a definition:
|
Overview of AI Integration in Asset Management
Today, AI plays a pivotal role in asset management by enhancing investment decisions, portfolio management, and market trend forecasting. Key AI technologies include:
- Machine Learning: ML algorithms learn patterns and make predictions based on data. For example, an ML model can analyze historical stock prices to predict future movements, aiding asset managers in making informed investment decisions.
- Natural Language Processing: NLP is used for sentiment analysis. It scans news articles, financial reports, and social media posts to determine the market’s mood. For example, if Elon Musk tweets about Dogecoin again, NLP will analyze how the public reacts to it. Based on this, a more informed investment decision can be made.
- Predictive Analytics: This combines statistical methods and machine learning to forecast future market trends, enabling proactive investment strategies.
- Generative AI: Generative AI can analyze unstructured data, such as financial news and social media sentiment, to enhance trading strategies and provide deeper market insights.
- Quantum AI: While still in the research phase, this combination of AI and quantum computing promises a true revolution in asset management and finance as a whole.
The integration of AI into asset management has evolved over decades, with significant advancements in recent years. In the early 2000s, hedge funds began using simple algorithms for trading. As technology advanced, so did the sophistication of AI tools. By 2010, machine learning models were analyzing vast datasets for more accurate predictions. In 2017, AI made headlines when BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, began using AI to enhance its investment strategies.
Use Cases of AI in Asset Management
Here are the main advantages AI technologies bring to asset management, together with real-life examples:
Data Processing and Analysis
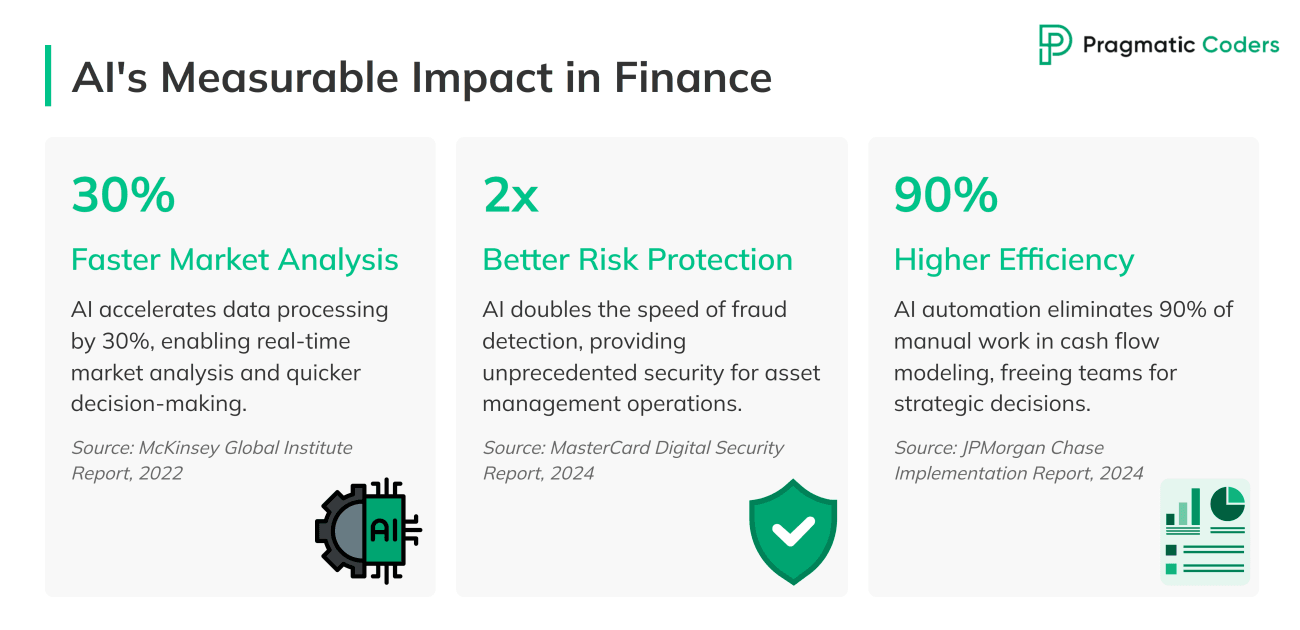
AI has revolutionized how asset managers process and analyze data. Traditional methods often struggle with the sheer volume and complexity of the task. AI, however, excels in this area. It can sift through vast amounts of data quickly and accurately. This allows asset managers to make more informed decisions. According to a report by McKinsey, AI could improve data processing efficiency by up to 30% as of 2022. And the tech vastly improved since then.
Predictive Insights and Forecasting
One of the most significant benefits of integrating AI into asset management is the predictive insights it can produce. This facilitates smarter decision-making. For instance, we can predict investors’ volatility and take preventive actions accordingly. Recently (April 2024), JPMorgan Chase sought to patent its predictive AI aimed at spotting overly aggressive investors.
Real-Time Risk Management and Fraud Detection
AI tools enhance risk management by identifying potential risks and fraudulent activities in real-time. This is crucial in the finance industry, where delays can lead to significant losses. AI systems can monitor transactions continuously, flagging suspicious activities and patterns that might indicate fraud. For example, Wells Fargo uses ML to detect unusual transaction patterns, helping prevent fraud and protect assets. AI is doubling the speed at which fraud is detected, MasterCard states.
Improved Decision-Making and Operational Efficiency
AI streamlines operations, reduces costs, and improves overall decision-making processes. By automating routine tasks, AI allows asset managers to focus on strategic activities. For example, robo-advisors like Betterment and Wealthfront use AI to manage portfolios, rebalance investments, and optimize tax strategies. As for efficiency; JPMorgan’s AI-aided cash flow model is said to reduce manual work by 90%.
While AI has boosted productivity in banks, monetizing these advancements remains a challenge. Institutions like Goldman Sachs and BNY Mellon have integrated AI into coding and risk management, yet direct revenue generation from AI is still evolving.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading is a big leap forward in AI-driven investment management. It uses complex algorithms to execute trades faster and more efficiently than human traders ever could. These AI-powered algorithms, especially those using machine learning and deep learning, analyze massive datasets, adapt to market changes in real-time, and make trades based on detailed patterns and trends. This boosts market efficiency, liquidity, and price discovery, allowing for quick adjustments and optimization of trading strategies. High-frequency trading (HFT) firms like Virtu Financial show just how effective this can be. They execute thousands of trades per second, taking advantage of tiny price differences. Here’s a recent example of AI at work in trading:
In October 2024, Qraft Technologies’ AI-driven AMOM fund increased its stake in Tesla, anticipating future gains. Despite Tesla’s underwhelming Robotaxi event that month, this strategic move proved advantageous. Tesla’s stock surged nearly 40% in November, significantly boosting the fund’s performance. Recognizing this momentum, the AMOM fund further increased its Tesla holdings to 7.95% in December.
Automation of Manual Administrative Tasks
AI-enabled digital platforms are transforming asset management by automating manual administrative tasks. Processes such as data entry, compliance checks, and client onboarding are now streamlined, enhancing operational efficiency. This automation reduces errors and frees up professionals to focus on strategic decision-making. For instance, AI can automate asset discovery, inventory management, and compliance reporting, allowing IT asset management practitioners to concentrate on forecasting, financial planning, and risk mitigation.
Key Trends in AI Asset Management in 2025
AI is driving significant changes in the asset management sector. Here are some key trends to watch in 2025:
Adoption of Generative AI
Generative AI is becoming a game-changer in asset management. A recent survey indicates that over 90% of asset managers are already using disruptive technological tools, including AI, big data, and blockchain, to enhance investment performance. This technology doesn’t just handle routine tasks; it also provides insights that can lead to better investment strategies. AI that reviews daily financial news and generates reports highlighting potential impacts on your portfolio is now a very real prospect. With such help, the investment process is more efficient and accurate. According to a study by Deloitte, using generative AI can improve the front-office productivity of investment banks by 27% to 35%.
Integration of ESG Factors and Sustainability
AI is also helping asset managers incorporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors into their investment decisions. Investors are increasingly looking to support companies that are not only profitable but also sustainable and ethical. AI can analyze vast amounts of data to assess a company’s ESG performance. This helps asset managers align their investments with their clients’ values. BlackRock, for example, uses AI to integrate ESG factors into its investment strategies, ensuring that its portfolios are both profitable and sustainable.
Active vs. Passive Management Strategies
The debate between active and passive management strategies is ongoing, and AI is influencing both approaches. Active management involves making specific investments to outperform the market, while passive management involves tracking a market index. AI can enhance both strategies. For active management, AI can identify market trends and opportunities faster than human analysts, making it easier to beat the market. On the other hand, AI can optimize passive strategies by automatically rebalancing portfolios to match the index closely. Vanguard makes it very clear that both management strategies can benefit from AI.
Note: Check this article if you’re interested in more trends from the banking tech sector.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI brings numerous benefits to asset management, it also presents several challenges and considerations. Here’s a closer look at some of the key issues:
Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
Using AI for the management of assets raises significant ethical and regulatory concerns. It’s often difficult to understand how AI models make decisions, which creates transparency issues. This lack of transparency can lead to mistrust among clients and regulators. There’s also the risk of bias. AI systems can unintentionally favor certain groups or make unfair decisions based on the data they’re trained on. Accountability is another concern. When AI makes a mistake, it’s not always clear who is responsible. For instance, if an AI system recommends a bad investment, who is to blame—the developer, the data scientist, or the asset manager? This “Wild West” is about to end, however, as regulators are taking notice. The European Union, for example, introduced the EU AI Act in 2023.
To mitigate these risks, robust governance and data protection measures are essential. An integrated, enterprise-wide approach ensures compliance with regulations and safeguards data privacy and security. This strategy fosters trust and promotes the responsible use of AI in asset management.
Trust in AI Models
Building trust in AI models is crucial for their acceptance. Asset managers and clients need to understand how AI systems work and why they make certain decisions. The above-mentioned transparency is key to building this trust. AI models should be explainable, meaning that their decision-making process should be clear and understandable. Some firms are already taking steps in this direction. For example, JP Morgan has developed explainable AI models that provide clear insights into their decision-making processes.
Data Quality and Management Issues
High-quality data is essential for AI systems to function correctly. Poor data quality can lead to inaccuracies and huge losses. Managing large datasets is another challenge. Asset managers need robust systems to store, process, and analyze vast amounts of information. This requires significant investment in technology and infrastructure. Moreover, data privacy is an issue (as it always is with AI systems). Client data must be handled responsibly and in compliance with regulations like GDPR.
Skill Gaps and Interdisciplinary Expertise
The integration of AI into asset management requires a blend of skills in finance and technology. Asset management firms need to understand data science and AI to use these tools effectively. However, there is often a skill gap. Many financial professionals lack the technical expertise needed to work with AI. On the other hand, data scientists may not fully understand the complexities of financial markets. Bridging this gap requires interdisciplinary collaboration. Companies need to invest in training and hire experts or work on the accessibility of data. For example, Goldman Sachs is making data more accessible to non-engineers via a special app.
Future Outlook: 2026 and Beyond
AI is set to continue transforming asset management. Here’s a look at what the future might hold.
Advancing AI Technologies
In the coming years, we can expect even more advanced AI technologies to impact asset management. One promising area is advanced machine learning models. Future models will be bigger and faster, able to process and analyze even larger datasets with greater accuracy. AI-driven predictive analytics will also evolve, providing asset managers with deeper insights and more precise forecasts. According to a report by PwC, AI could increase global GDP by up to 14% by 2030.
Asia-based hedge have already recognized this trend and invested in Chinese tech companies leading in AI innovation, such as Xiaomi and Baidu. These firms are developing AI products for a vast domestic market, presenting new growth opportunities.
Evolving Role of Human Advisors
Despite advances in AI, human advisors will still play a crucial role. AI can handle data and perform complex analyses, but it lacks the human touch and intuition. Moreover, statistics show that people don’t trust AI to make unbiased decisions. Thus, advisors will use AI tools to enhance their services, but AI won’t completely replace them. This partnership between AI and human advisors will lead to better, more personalized investment strategies.
Predictions for the Future
Looking ahead, AI will likely lead to new business models and investment strategies in asset management. One possibility is the rise of fully automated investment platforms that use AI to manage portfolios with minimal human intervention. These platforms could offer customized investment plans based on real-time data analysis, making investment management more accessible to a broader audience.
Additionally, AI might enable more dynamic and responsive investment strategies. For example, it could help create portfolios that automatically adjust to changing market conditions, optimizing returns and minimizing risks. This approach could lead to more resilient and adaptable systems, capable of thriving in various market environments.
Moreover, as AI becomes more integrated into asset management processes, we might see new regulatory frameworks to ensure ethical use and transparency. Governments and regulatory bodies will likely develop new standards for AI in finance, ensuring that AI systems are fair and transparent, and their creators accountable.
Conclusion
The continuous advancements in AI shape the future of asset management. Embracing them, while addressing the accompanying challenges, is crucial for maximizing their potential benefits. The synergy between AI and human expertise promises a transformative impact on how assets are managed, offering good prospects for 2025 and beyond.