AML & KYC compliance: Guide for fintech app founders

When building a fintech app, one of the most critical areas to focus on is compliance with Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations.
These frameworks are designed to prevent financial crimes, including money laundering and terrorist financing.
Here’s what you need to know to launch a KYC/AML-compliant app in the US, EU, and UAE.
Fintech software development
What are KYC & AML?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws aim to prevent criminals from disguising illegally obtained funds as legitimate. Your fintech app must implement systems to detect and report suspicious activity.
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a regulatory requirement for financial institutions and payment services to verify the identity of their customers. It ensures that businesses know who they are dealing with and can trace the source of funds.
- KYC is a key component of broader AML programs. KYC procedures help verify customer identities and assess their risk profiles, which is crucial for effective AML monitoring.
Do you need KYC/AML compliance?
So, do AML and KYC apply in your case?
If your app will involve financial services, including but not limited to:
- Payments
- Banking services
- Cryptocurrency
- Peer-to-peer transactions
- Credit systems
- International transfers
- Investment platforms
Then, yes, KYC/AML compliance is required. You will need to follow specific regulations depending on the jurisdictions in which you operate (e.g., the US, Europe, or UAE).
KYC/AML vs. 3rd party providers
Even if your app doesn’t directly handle financial services, payment gateways or integrations with third-party providers (e.g., PayPal, Stripe) will require your app to comply.
Fortunately, providers like Stripe will handle much of the KYC compliance process for you, though you’ll still be responsible for providing accurate information and keeping it up to date.
Key AML & KYC practices
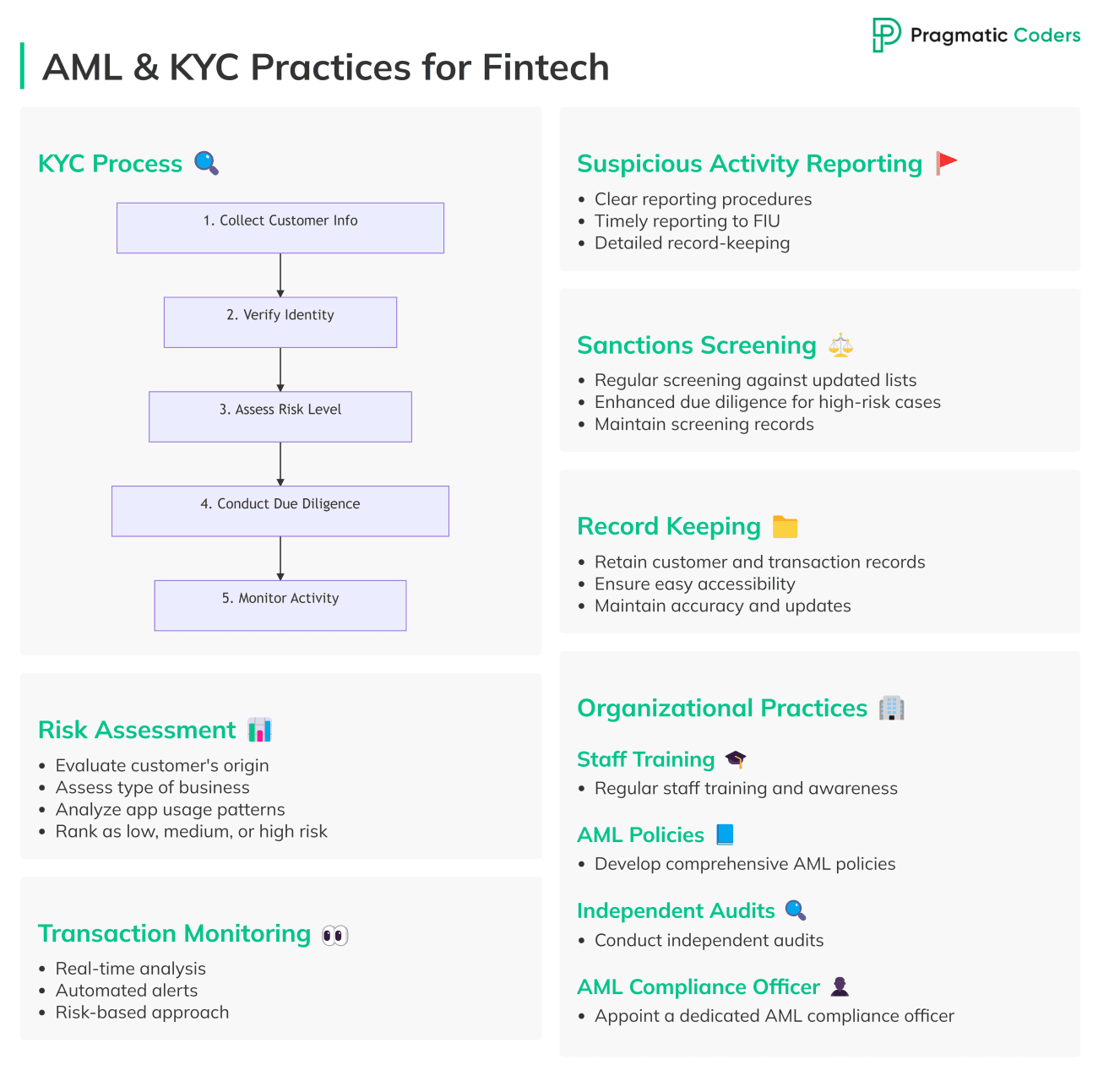
Now, here’s a list of things your fintech app should check off on to make sure it’s compliant with AML requirements.
Risk assessment
Risk assessment is about figuring out how risky a customer or transaction might be. You look at factors like:
- Where the customer is from (as some countries have higher risks of money laundering or terrorism financing)
- What kind of business they’re in (for example, high-risk categories might include politically exposed persons or non-profits, as they can sometimes be used for money laundering)
- How they use your app (some financial products are riskier than others, like high-value transactions or anonymous payment methods).
You then rank customers as low, medium, or high risk. This helps you decide how closely to watch them.
KYC
Know Your Customer is a process to verify customer identity and assess risks in financial services. KYC is a crucial part of the digital onboarding process.The KYC flow typically looks like this:
1. Collect customer information
This initial step involves gathering essential data about the customer, including:
- Personal information: Name, date of birth, nationality, contact details
- Proof of identity: Valid government-issued ID (e.g., passport, driver’s license)
- Proof of address: Utility bill, bank statement, or rental agreement
- Financial information: Employment details, income source, and net worth
2. Verify identity
Once the information is collected, the fintech app must verify the customer’s identity. This typically involves:
- Document verification: Checking the authenticity of the provided documents (e.g., using optical character recognition (OCR) or biometric verification)
- Data validation: Ensuring that the information provided matches existing databases or records
- Liveness check: Confirming that the person presenting the documents is a real, living individual (e.g., using facial recognition or video verification)
3. Assess risk level
Based on the collected information and verification results, the fintech app must assess the customer’s risk level. This involves evaluating factors such as:
- Jurisdiction: The customer’s country of residence or citizenship
- Business activity: The nature of the customer’s business or occupation
- Transaction patterns: The expected frequency and amount of transactions
- PEP status: Whether the customer is a politically exposed person (PEP)
4. Conduct due diligence
Depending on the assessed risk level, the fintech app must conduct appropriate due diligence. This can include:
- Standard Due Diligence (SDD): For low-risk customers, this may involve basic identity verification and source of funds checks.
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): For higher-risk customers, this may require more in-depth background checks, source of wealth verification, and enhanced monitoring of transactions.
5. Monitor ongoing activity
After onboarding the customer, fintech apps must continue to monitor their activity for signs of suspicious behavior or money laundering. This includes:
- Transaction monitoring: Identifying unusual or suspicious transaction patterns
- Sanctions screening: Checking against sanctions lists to ensure the customer is not subject to restrictions
- Adverse media screening: Monitoring for negative news or legal proceedings involving the customer
Remember: KYC is an ongoing process, not a one-time check. It’s crucial for maintaining a secure and compliant payment app across different regions.
Below: Monzo: Identity check flow as part of the KYC process
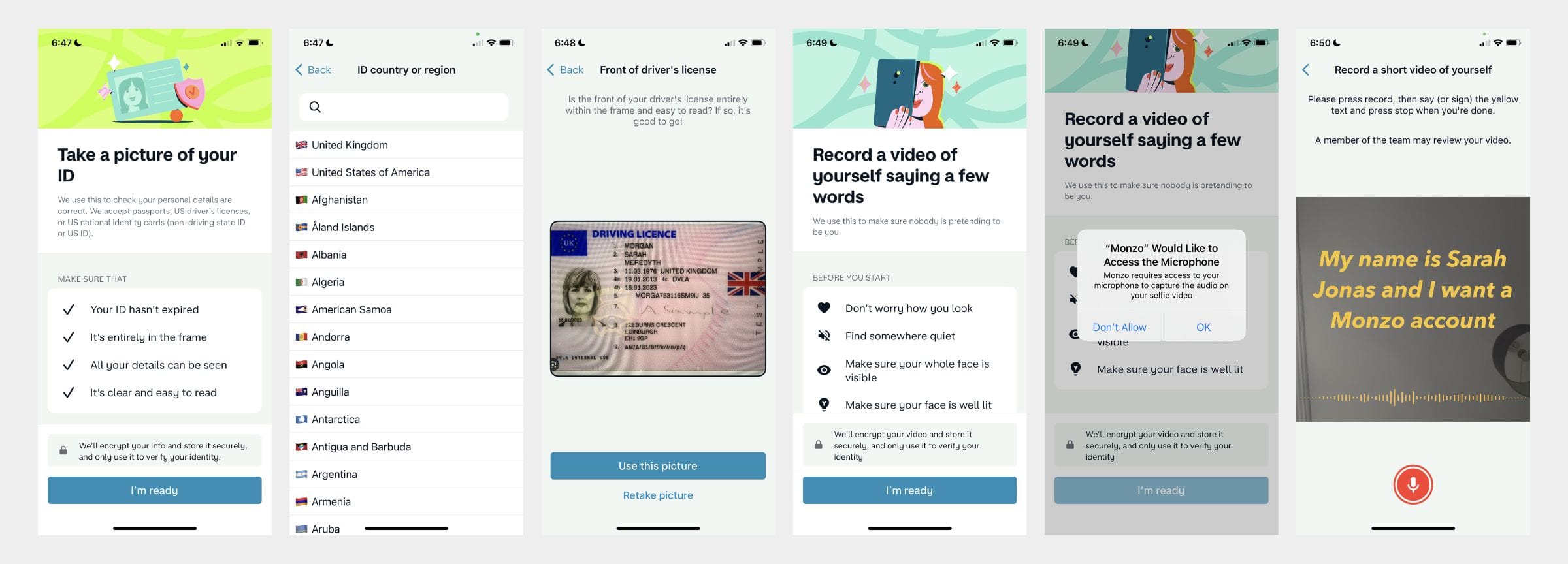
Transaction monitoring
- Purpose: To identify unusual or suspicious activity that may indicate money laundering or terrorist financing.
- Requirements:
- Real-time monitoring: Continuously analyze transaction data for patterns or anomalies.
- Alert systems: Set up automated alerts for suspicious activities, such as large cash transactions, unusual transfer patterns, or transactions involving high-risk jurisdictions.
- Risk-based monitoring: Prioritize monitoring based on the customer’s risk profile.
Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR)
- Purpose: To report suspicious activities to the relevant financial intelligence unit (FIU).
- Requirements:
- Clear reporting procedures: Establish guidelines for identifying and reporting suspicious activities.
- Timely reporting: Report suspicious activities promptly to the FIU.
- Record-keeping: Maintain detailed records of SARs filed.
Sanctions screening
- Purpose: To prevent transactions with individuals or entities on sanctions lists.
- Requirements:
- Regular screening: Screen customers and transactions against updated sanctions lists.
- Due diligence: Conduct enhanced due diligence for customers with connections to sanctioned jurisdictions or individuals.
- Record-keeping: Maintain records of sanctions screening activities.
Record keeping
- Purpose: To document compliance with AML/KYC regulations and facilitate investigations.
- Requirements:
- Retention: Retain customer information, transaction records, and compliance documentation for a specified period.
- Accessibility: Ensure easy access to records for regulatory reviews and investigations.
- Accuracy: Maintain accurate and up-to-date records.
If you can cover the essential AML elements, you’ve made a good start. However, you might still need to implement elements like training and awareness to ensure your staff understands the AML/KYC framework and can identify potential red flags.
Training and awareness
- Staff training: Regularly train employees about AML regulations, red flags, reporting processes, and their role in preventing money laundering.
- Continuous updates: Update training to reflect changes in laws and the company’s evolving risk profile.
AML policies and procedures
- Policy development: Create internal policies that comply with local and international AML regulations.
- Procedural guidelines: Clearly define how CDD, SAR, and sanctions screenings are to be carried out, including responsibilities of the compliance team.
Independent audit
- Third-party audits: Regularly conduct independent reviews of your AML program to ensure its effectiveness and compliance with regulations.
- Internal audits: Continuous internal monitoring to ensure AML compliance is being upheld across all processes.
Compliance officer
- AML compliance officer: Appoint a designated person responsible for overseeing the AML program, monitoring compliance, and acting as a liaison with regulators.
Geographical compliance. Regulatory frameworks in the US, UAE & Europe
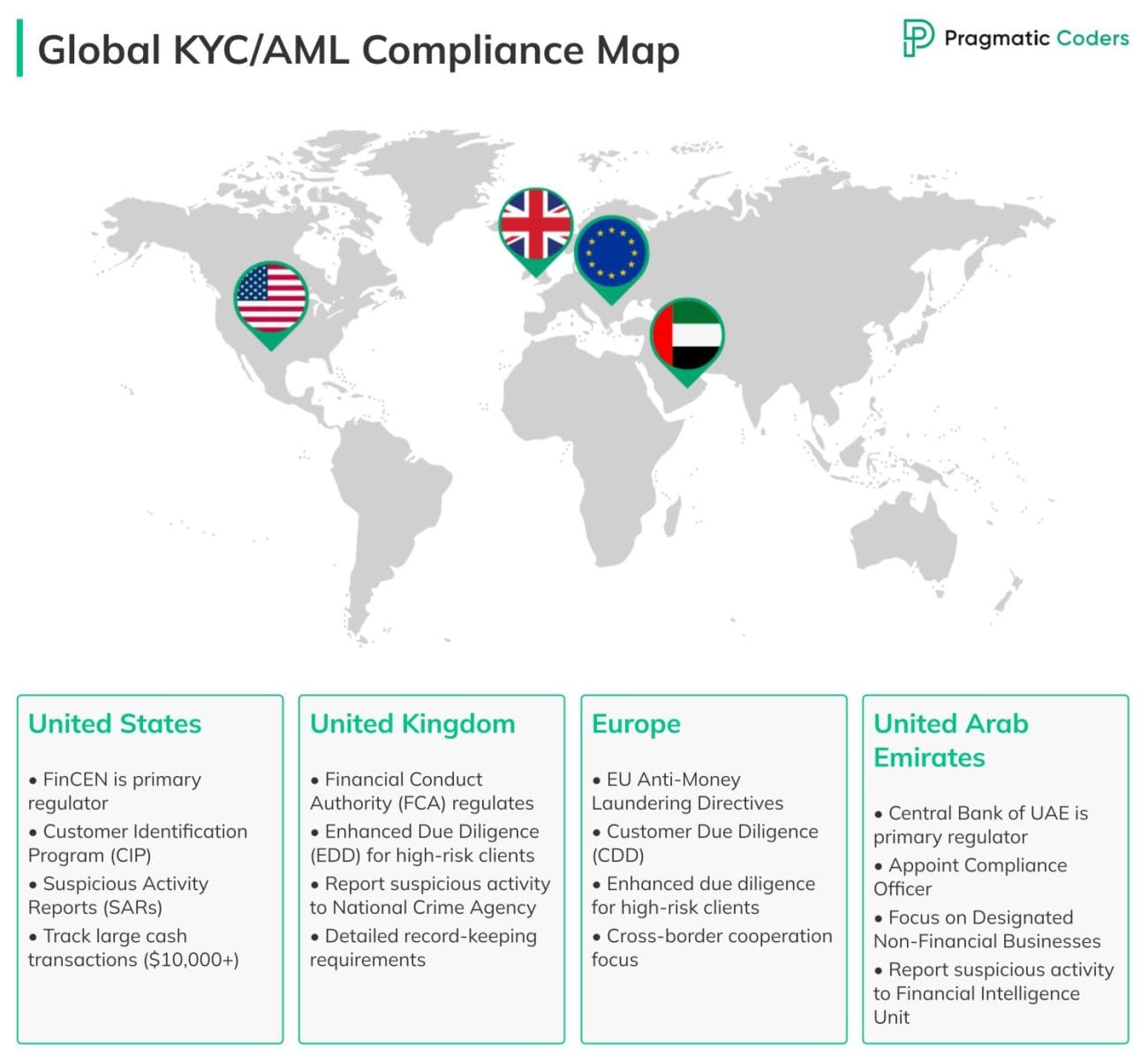
Let’s now review the most important AML regulatory frameworks for the US, Europe, and UAE. As you’ll see below, most requirements are universal, but there are subtle differences depending on the region.
KYC & AML in the United States
The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) under the U.S. Department of the Treasury is the primary regulator for KYC and AML compliance. Other laws like the USA PATRIOT Act and Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) also play significant roles.
Compliance requirements:
- Implement a Customer Identification Program (CIP) to verify customer identities. KYC documents for the USA are: Social Security Card, passport, driving license, and credit or debit card.
- Conduct Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and ongoing transaction monitoring.
- Maintain records of transactions and reports of suspicious activities.
- Financial institutions are required to monitor customers for money laundering risks and submit Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) when necessary
Unique requirements:
- The US focuses heavily on Customer Identification Programs (CIP) and mandatory reporting of suspicious activities through Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs).
- There is a strong emphasis on tracking large cash transactions (above $10,000) and strict ongoing monitoring requirements.
KYC & AML in European Union
In Europe, KYC and AML regulations are primarily governed by EU Directives like the 4th, 5th, and 6th Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AMLD). These directives provide a unified legal framework across all member states. Additionally, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) sets international standards for AML compliance, which are adopted and implemented by EU countries. Each member state also has its own national regulatory bodies to enforce compliance (e.g., FCA in the UK, TRACFIN in France).
Compliance requirements:
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): Businesses must verify customer identities and assess risks associated with each client. Enhanced due diligence is required for high-risk clients, such as politically exposed persons (PEPs).
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular monitoring of customer transactions to detect suspicious activities is mandatory.
- Reporting Suspicious Transactions: Firms must report any suspicious activities to the relevant authorities.
- Record Keeping: Organizations are required to maintain detailed records of customer information and transactions for a minimum of five years
Unique requirements:
- The EU has more harmonized KYC/AML laws across member states but allows flexibility for local implementation.
- Special focus on cross-border cooperation within member states to prevent money laundering, with uniform reporting and transparency standards.
KYC & AML in UK
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) regulates KYC and AML compliance in the UK. Compliance is also guided by the Money Laundering, Terrorist Financing and Transfer of Funds Regulations 2017.
Compliance requirements:
- Establish CIP and conduct Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for high-risk customers.
- Implement ongoing monitoring of customer transactions to identify suspicious activities.
- Retain records of customer identification and due diligence for at least five years.
- Reporting suspicious activity to the National Crime Agency (NCA) is mandatory.
Unique requirements:
- The UK requires Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for high-risk clients, such as politically exposed persons (PEPs).
- More detailed emphasis on record-keeping and transaction transparency due to the UK’s role as a global financial hub.
KYC & AML in United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The Central Bank of the UAE (CBUAE) is the principal regulatory body, supported by entities such as the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) and Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM).
Compliance requirements:
- Conduct risk assessments and implement necessary due diligence measures.
- Appoint a Compliance Officer to oversee KYC/AML programs.
- Maintain records of transactions and due diligence for five years and promptly report any suspicious activity to the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU).
- Financial institutions must ensure continuous monitoring of customer transactions and enhance due diligence for high-risk clients
Unique requirements:
- Strong focus on compliance officers and local regulation under entities like the Central Bank of the UAE.
- UAE-specific emphasis on Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs), such as real estate agents and legal professionals, which might not be as rigorously regulated in other regions.
Technology & tools for KYC compliance
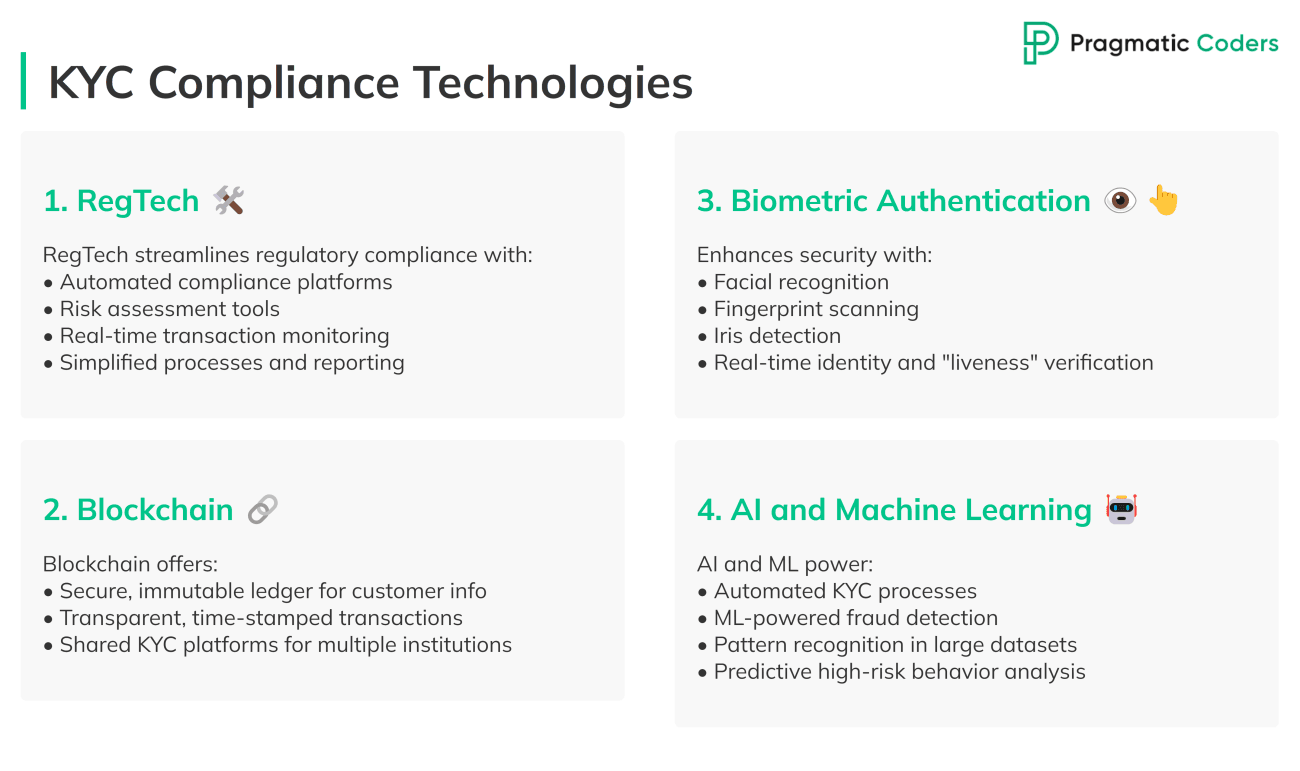
What technologies are key for AML compliance?
1. RegTech (Regulatory Technology)
RegTech refers to the use of technology to help businesses comply with regulatory requirements more efficiently. It includes automated compliance platforms, risk assessment tools, and real-time transaction monitoring solutions.
RegTech helps reduce the complexity of regulatory compliance by streamlining processes and providing real-time reporting and auditing tools.
2. Blockchain
Blockchain provides a secure, immutable ledger that can be used to store and verify customer information for KYC compliance.
Since every transaction on a blockchain is transparent and time-stamped, it offers a tamper-proof system for identity verification and monitoring.
Blockchain can also facilitate shared KYC platforms, allowing multiple financial institutions to access and verify customer data from a single source, which reduces duplication of effort and enhances efficiency.
3. Biometric Authentication
Biometric technologies, such as facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and iris detection, are used for real-time identity verification.
Biometric authentication adds an extra layer of security by verifying the “liveness” of the customer during onboarding or transaction processes, thus reducing the risk of fraud.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML play a pivotal role in automating the KYC process.
With ML-powered fraud detection, you can analyze large datasets to identify patterns of suspicious activity and even predict high-risk customer behavior. By continuously learning from transaction data, AI-powered systems can improve accuracy and reduce false positives in identifying potential financial crimes.
AI and ML tools are often integrated with other compliance platforms to optimize decision-making and reduce manual workloads.
Practical steps for your business
So what does it mean for your startup?
How do you cope with all this?
Dealing with complex KYC/AML requirements can feel overwhelming, but here’s what you can do to ensure compliance without building everything from scratch: use a ready-made solution.
RegTech platforms provide comprehensive tools that handle identity verification, document checks, and transaction monitoring for you. You can choose from several top platforms depending on your needs. For example, here are a few tools we integrate our client’s products with:
- Synaps–for a crypto project
- Jumio–for a trading project
- Shufti Pro–for a banking project
Integrate KYC/AML compliance tools into your app
If you’re looking to seamlessly integrate RegTech solutions like KYC/AML compliance tools into your app, Pragmatic Coders can be your perfect partner.
We have extensive experience integrating KYC/AML tools into numerous projects and can provide you with assistance in getting GDPR compliance.
With our deep expertise in fintech development we can help you streamline the implementation of identity verification, AML screening, and transaction monitoring within your platform.
Reach out to us–let’s discuss your project!
Sources: Guides to KYC requirements in the US, UAE, UK and globally by KYC Hub.








