Climate fintech: Ultimate guide [2025]

When 196 countries pledged to limit global warming at the Paris Climate Summit in 2015, we could only try to guess how much of an impact would this have on the financial sector. Initiatives linking financial innovation with climate action already existed, but the summit has started a real boom in climate fintechs.
We, in our fintech software development microscale, are observing it, too: there are more and more inquiries from clients wanting to build sustainable products, be it solar panel tokenization, carbon credit trading, waste management, AI in wind energy, or rewarding people for their eco-conscious decisions with tokens.
Green fintech is not just a trendy buzzword. It is a response to the urgent need to finance the green transition and engage consumers in the fight against climate change.
But what does actually hide behind the term?
What do climate fintechs do?
And is this revolution really changing the face of finance, or is it just another speculative bubble?
What is climate fintech?
Climate tech is an umbrella term for technologies that are designed to address climate change.
Key areas of climate fintech include green investing, carbon emissions tracking & ESG data reporting.
Why is climate fintech a key financial trend?
Fintech and climate change are a duo that’s been making waves lately.
Why do these two fields get along so well? And where did this sudden surge of startups dealing with sustainable finance come from?
- First, money has power. Finance is a tool that can strongly influence how we deal with climate. Changing the way we invest can bring significant effects in the fight for the environment. (That’s why a natural environment for green finance are banking apps.)
- Second, fintech likes data, and climate is a goldmine of it. New financial technologies excel at analyzing complex information, which is abundant in climate topics.
- Market demand. People get more sustainability-conscious, and want to make a change Sustainability is a major concern. For example, in 2020 McKinsey US consumer sentiment survey, over 60% of respondents stated they’d pay more for a product with sustainable packaging. NielsenIQ reported that 78 percent of US consumers say that a sustainable lifestyle is important to them. Consumers want to measure and lower their carbon footprint with responsible shopping, banking, or investing. Unsuprisingly, it’s the younger generations–Millenials and Gen Z–more likely to adopt sustainable buying habits. Fintech startups can respond to this demand faster than traditional financial institutions.
- New regulations matter too. Financial companies now have to report climate-related risks. Fintech offers tools that help meet these requirements. And then there’s scale – financial technologies can reach many people in a short time. This is an opportunity for quick changes in how money affects the climate.
- Finally, a report by CommerzVentures shows that climate-focused financial technology startups, or climate fintechs, are attracting more venture capital (VC) funding than other fintech startups, despite an overall decline in VC funding. Europe is leading the way, with climate fintechs there raising $1.4 billion compared to $881 million in the US.
Green landscape: Climate fintech startups
The green fintech market is expanding in various directions: Enduring Planet supports climate-focused startups, Arnie offers customizable 401k retirement plans focused on impact investing, and Veritree will help your company plant trees with blockchain. Below you’ll find the most important market niches along with startup product examples.
B2C impact investing platforms
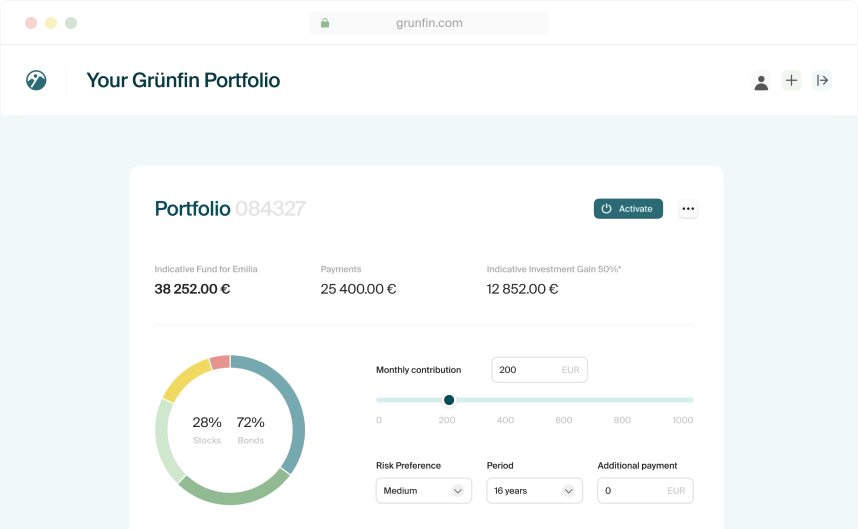
Image source: Grünfin
We can clearly see the numbers of individuals and businesses seeking to invest their money in a way that aligns with their environmental values keep growing. A 2022 Morgan Stanley survey found a whopping 90% of Gen Z investors prioritize ESG (environmental, social, and governance) factors, with 85% even willing to accept slightly lower returns to back companies that reflect their values.
Climate-focused fintech platforms don’t remain blind to these growing needs. They are providing new avenues for both individuals and institutions to support sustainable projects through green bonds, impact investing, and carbon offset programs.
- Grünfin offers personalized investment portfolios using sustainable exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that align with individual values and financial goals. The company is a certified B Corporation and provides investment plans for individuals, companies, and children, with assets protected under the European Investor Compensation Scheme.
B2B sustainable investing
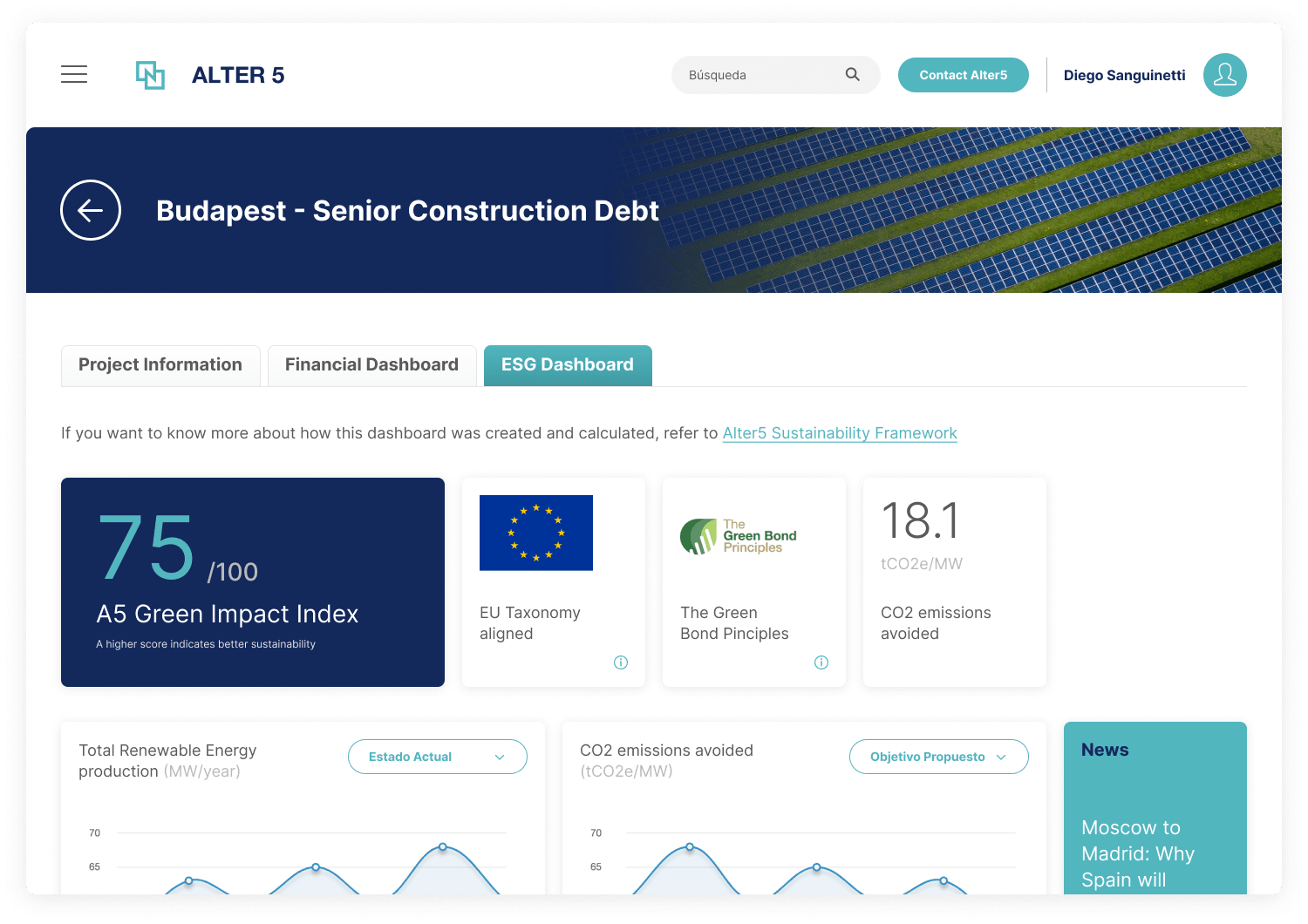
Source: Alter 5
B2B sustainable investing refers to the practice of businesses investing in other businesses with a focus on sustainability. This type of investing involves directing capital towards companies and projects that are committed to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria.
The goal is to promote sustainable business practices, reduce environmental impact, and enhance social responsibility while still achieving financial returns.
- Alter5 is a digital platform offering financing and M&A solutions for renewable energy projects. It enables developers to access financing and sales opportunities, while providing investors with direct access to debt and equity investments in green energy projects. The platform also includes a Luxembourg-based green bond issuance vehicle.
ESG reporting
ESG is a key concept in anything sustainability-related. It stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance factors used to assess a company’s sustainability and social responsibility.
Companies that specialize in ESG reporting help other businesses create reports on their environmental, social, and ethical practices. Their services usually include developing an ESG strategy, data collection and analysis, or report preparation.
- EcoVadis provides sustainability ratings for businesses, evaluating their environmental, social, and ethical performance. The platform helps companies manage risks, drive improvement, and foster transparency in their supply chains. By offering detailed scorecards and actionable insights, EcoVadis supports organizations in making informed decisions and improving their sustainability practices.
Sustainable pension
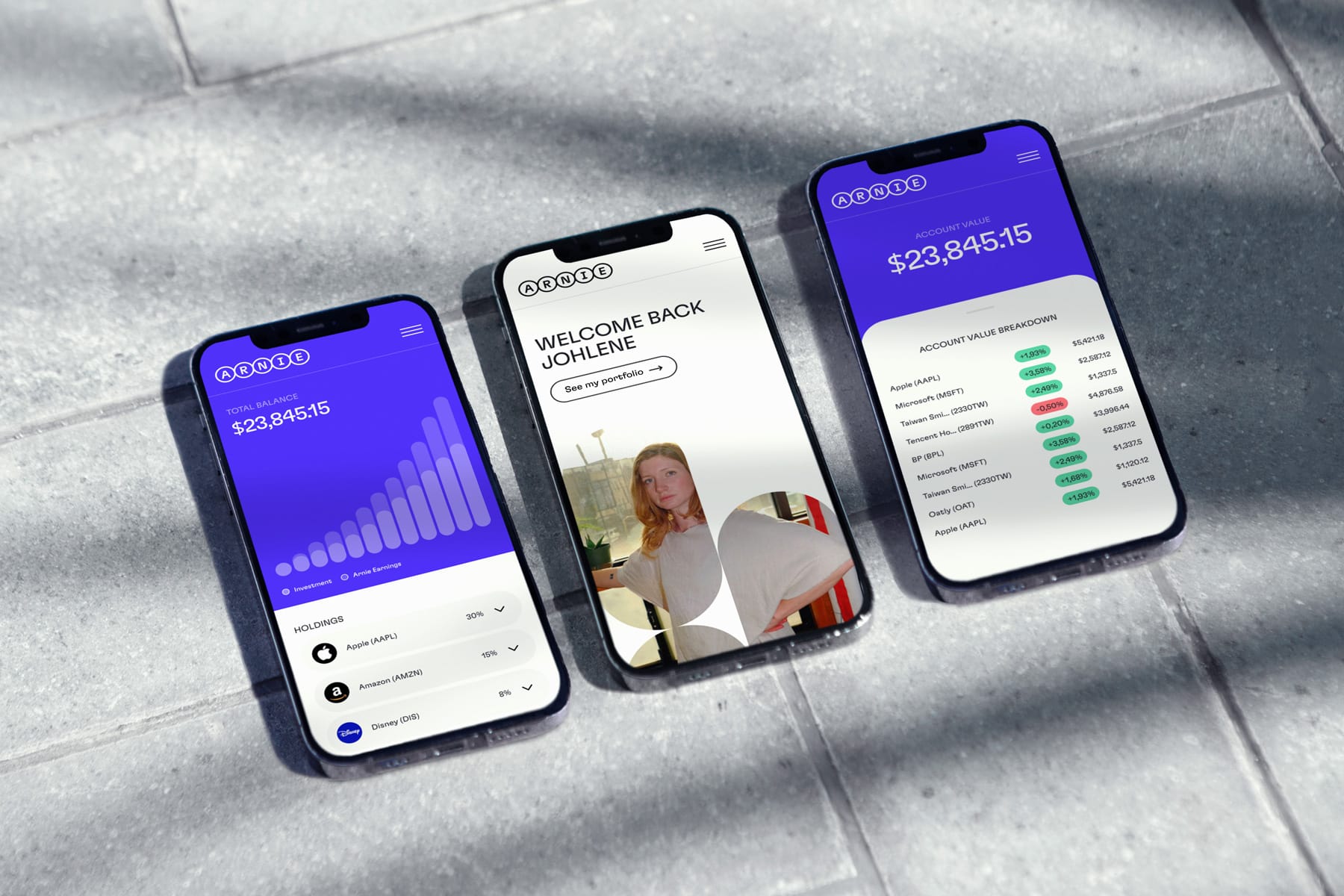
Source: soderhavet.com
Think of your traditional pension plan, but with a green twist.
Sustainable pensions are a type of retirement plan offered by financial institutions that specifically invest in companies with strong ESG practices and those contributing to a sustainable future. This allows individuals to save for retirement while aligning their investments with their values.
- An example of a sustainable pension tool is Arnie. The company specializes in customizable 401k retirement plans. They focus on flexibility, personalization, and impact investing. Their customers can create individual portfolios aligned with their values, such as avoiding fossil fuels and supporting equal pay. Arnie offers features like advanced risk management, access to alternative assets, and ESG-aligned investing.
Impact investing: financing for climate tech startups
Companies in this market segment act as financial bridges, connecting investors with a social and environmental conscience to innovative startups that are tackling climate change.
- Enduring Planet provides financial support and advisory services for climate-focused startups and small businesses. They offer founder-friendly working capital solutions, such as grant advances with minimal collateral requirements, and fractional CFO services tailored to the needs of climate entrepreneurs. Their mission is to support teams involved in climate mitigation, adaptation, and resilience by providing accessible financial resources and expertise.
Climate crowdfunding
Climate crowdfunding companies is a way to raise money for projects that fight climate change or promote environmental sustainability. It works by pooling resources from a large number of people, typically through online platforms.
- These are after small-scale, local initiatives, like energy-efficient cookstoves for Kenya or sustainable textile concept for the hospitality industry in Dubai you could support through Bettervest–a German crowdfunding platform founded in 2012.
Carbon tracking & offsets
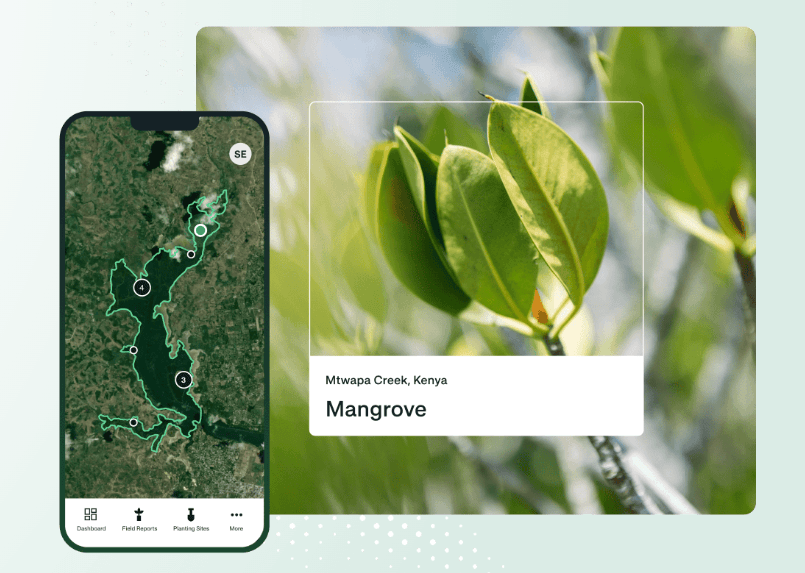
Image source: Veritree
Carbon tracking and offsets companies help organizations measure, reduce, and compensate for their carbon emissions. They offer services such as:
- Carbon footprint analysis: Assessing the total greenhouse gas emissions produced by a company.
- Reduction strategies: Implementing plans to lower carbon emissions through energy efficiency, renewable energy, and other sustainable practices.
- Carbon offsetting: Purchasing carbon credits to offset remaining emissions by investing in projects that remove or reduce carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, such as reforestation or renewable energy projects.
- Veritree connects businesses with verified tree-planting projects to help restore ecosystems, sequester carbon, and create local jobs. Using blockchain technology, Veritree provides transparency and accountability by digitizing and verifying the impact of these projects.
Sustainable banking

Image source: Tandem
Sustainable banking is a way for banks to consider the environmental and social impact of their decisions, alongside making a profit.
There are two main parts to sustainable banking:
- Green banking – This is where the bank looks to lessen its own environmental impact, for example by using less energy or investing in renewable sources.
- Sustainable finance – This is where the bank uses its financial products to encourage environmentally friendly behavior. This could involve things like offering loans for electric cars or investing in renewable energy projects (like Tandem Motor Finance program, for example).
Here’s a breakdown of the key ideas:
- Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG) factors: These are the things that sustainable banks consider when making decisions. Environmental factors could include a company’s carbon emissions, while social factors might include its labor practices. Governance looks at how a company is run, for instance, its transparency and accountability.
- United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Many sustainable banks are trying to support these goals, which include things like tackling poverty, protecting the planet and promoting peace and justice.
If you’d like to learn more, check our article on green tech and sustainability in banking.
Crypto for climate
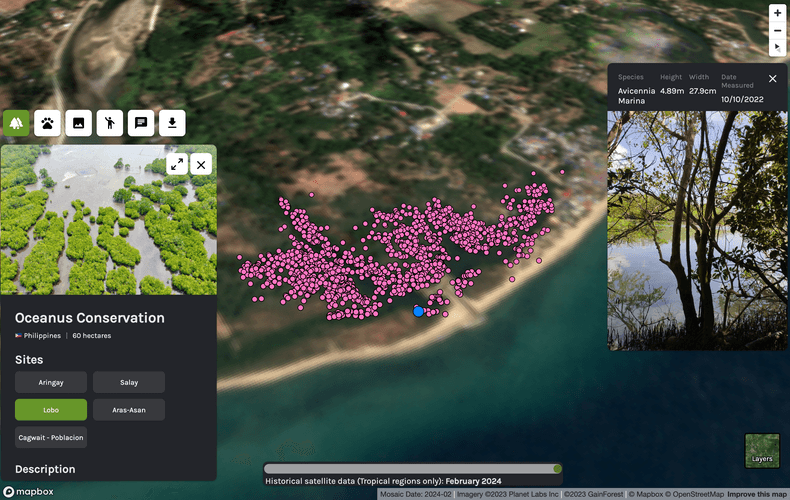
Image source: GainForest
“Crypto for climate” companies are those utilizing cryptocurrency and blockchain technology to address climate challenges. They take various approaches, here are some of the main ones:
- Carbon offsetting and tokenization: These companies create tokens that represent carbon offsets. Buying a token funds projects like tree planting or renewable energy. Example: GainForest is a non-profit that combats deforestation by rewarding local communities for conserving forests. Using artificial intelligence and blockchain, they track conservation efforts and ensure transparency. Donors can directly support specific projects and see verifiable proof of their impact.
- Green energy for crypto mining: Some companies aim to power crypto mining with renewable energy or develop more energy-efficient blockchain validation methods.
- Climate investments: Using crypto to create financial instruments for funding renewable energy projects or trading carbon credits.
Climate risk management (insurance)
Climate risk management companies help organizations prepare for climate change impacts. They assess risks using data and climate models, analyze future scenarios, and support regulatory compliance. They also assist with emissions reduction planning and climate risk reporting. Many provide specialized software for ongoing risk monitoring and offer training to build internal capacity. Some work with insurers to address climate risks in coverage options.
- Kita offers custom-made insurance solutions to safeguard your investments in carbon credits. They protect against events like natural disasters, scams, project failures, and even changes in carbon regulations. By minimizing risk and boosting confidence, Kita helps more money flow towards valuable carbon reduction projects.
Natural capital accounting
Natural capital accounting is a system for measuring the value of nature, a tool to put a price tag on nature’s services. It’s like a financial accounting system, but instead of tracking money, it tracks the health and benefits we get from ecosystems.
Here’s a breakdown of what it involves:
- Stocks and flows: It calculates the amount and condition of natural resources (like forests, fisheries) and the services they provide (clean air, water purification). This can be done in physical units (e.g., number of trees) or monetary terms (e.g., value of carbon storage).
- Decision making: This information is then used to inform decisions by governments, businesses, and individuals. By understanding the value of nature, we can make better choices about how to use and protect it.
- Standardized framework: There’s a global framework, called the System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA), that provides a common set of rules for measuring natural capital. This allows for consistent comparisons across different regions and ecosystems.
Example: Endangered Wildlife OÜ develops biodiversity strategies and implementation plans, using tools like the Biodiversity Valuator to assign financial values to biodiversity. They help businesses meet new biodiversity reporting standards, calculate environmental footprints, and support conservation projects by providing credible, accountable data and insights. Their goal is to integrate biodiversity into business decision-making and reporting processes.
Carbon credits trading
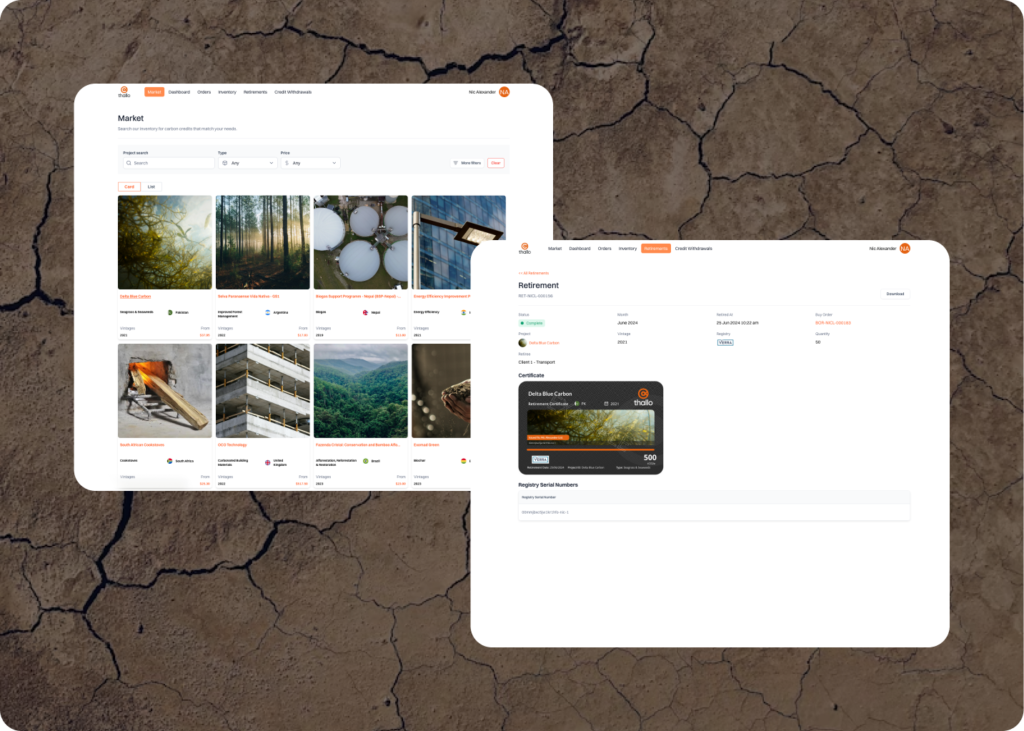
Image source: Thallo
Industrial CO2 emissions are driving climate change. Companies and industries urgently need to significantly reduce it. The problem is many industries face high costs in switching to cleaner practices.
Carbon credits offer a solution. These credits represent verified CO2 removal from the atmosphere and can be traded between companies.
That’s how the carbon credit trading market was born. It allows companies that exceed their emission reduction goals to sell their extra credits to those struggling to meet theirs. This creates a financial incentive for all companies to reduce emissions while providing flexibility.
- The carbon credit segment might not be the biggest one ($672M–compare it to sustainable banking $1.4B), but it’s growing, and there are fintechs trying to levarage this trend. Check Thallo (blockchain technology to revolutionize and democratize the way individuals and businesses buy, sell and trade carbon offsets) or Climate Impact X (global exchange and marketplace for high-quality carbon credits.)
Conclusions
Climate fintech faces many challenges. It must prove its effectiveness in having a real impact on the climate, ensure the security of user data, and meet increasingly stringent regulations.
One thing is certain – the combination of finance, technology and pro-climate actions is a trend that will shape the future of the financial sector. However, will climate fintech actually contribute to stopping climate change, or will it remain just a technological curiosity? This is a question that we will only know the answer to in the coming years.
Do you have a vision for a climate fintech app that can make a difference? We can help you navigate the challenges of climate fintech development and bring your green finance solution to life. Contact us >>