What is innovation strategy? Lessons from Elon Musk

Ever wondered what separates a short-term fad from a long-term success story?
In this guide, we’ll explore the concept of innovation through the lens of Elon Musk’s visionary leadership. We’ll examine his approach at Tesla and SpaceX, and uncover 4 key factors that contribute to their immense impact.
This guide, inspired by real-world experience, equips you to innovate and achieve long-term success with your own app.
Agile software development
What we’ll cover in this guide
This article consists of two parts:
- How Elon Musk’s companies operate and what innovation lessons you can learn from them. It’s based on our talk with Joe Justice – a TEDx speaker, pioneer in Agile hardware development, adopter of Agile methodologies for big tech, the founder of WIKISPEED, and the man who operated Agile at Tesla.
- How to innovate with your product.
Hopefully, this article will serve as a valuable source of insight into designing and building your own businesses and products.
You can see the full interview with Joe on Pragmatic Talks’ YouTube channel or below.
What is innovation?
Are you building a digital product that addresses an unsolved problem? Or, maybe you’ve noticed there are solutions to a challenge people face everyday but they could be improved? Then you’re most probably innovating.
Innovation is the successful implementation of new ideas that create value.
This can involve creating new products or services, or improving existing ones. It’s not just about coming up with fresh ideas, but also about making those ideas a reality and bringing value to people.
Types of innovation strategy. Innovation strategy examples
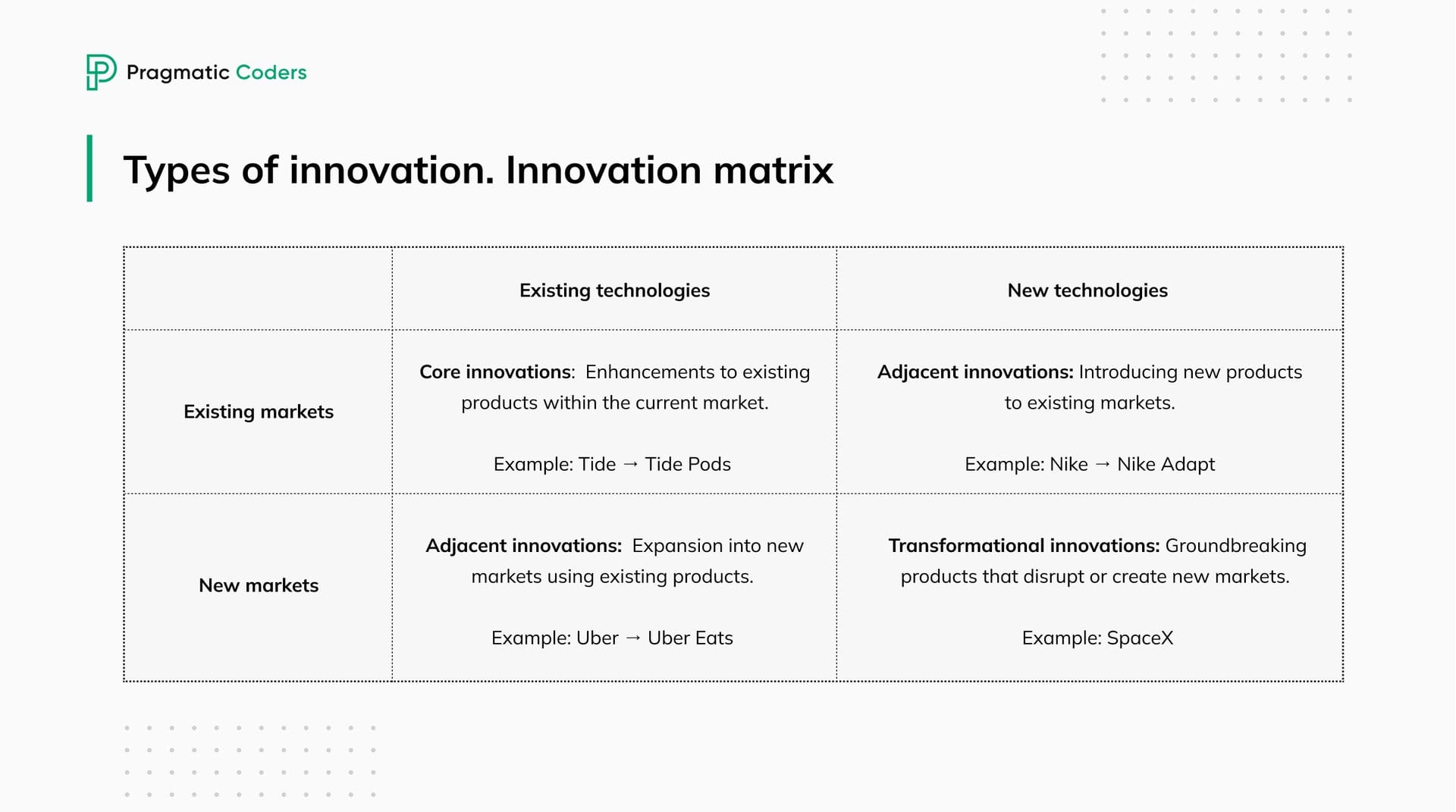
Core innovations
Core innovations are improvements to existing products, services, or processes within the current market. Goal: sustain competitiveness and meet current customers’ needs more effectively. Core innovations are typical for more mature businesses that focus on enhancing the product they have to retain their market share.
- Example. Procter & Gamble reinvented the laundry detergent with their pre-measured pods. They operated within the same market, but improved their product by making it more convenient to use.
Adjacent innovation (new market + existing technology)
In this case, innovating means expanding into new markets or segments using existing technologies, capabilities, or products. This often involves applying the company’s current strengths in a new context or to a different customer base.
- Example: Uber Eats. Uber used their existing ride-sharing technology to enter the food delivery market. This way, they expanded their service offerings to a new customer segment.
Adjacent innovation (existing market + new technology)
Another type of adjacent innovation (introducing new technologies, products, or business models to existing markets) might include expanding a product line or incorporating new tech into existing offerings.
- Example. Nike Adapt. Nike introduced self-lacing shoes that combine new technology with existing markets. This leverages new technology to enhance a traditional product and attract customers within the existing sportswear market.
Transformational innovations
Finally, transformational innovations (also known as breakthrough innovations) are the most innovative type of innovation. It’s the development of groundbreaking products, technologies, or business models that create new markets or disrupt existing ones. These are high risk but offer potentially high rewards.
- Example: SpaceX’s development of reusable rockets has been a game-changer for space travel. By significantly reducing mission costs, it’s opened the door to a new era of affordable space exploration and commercial spaceflight.
Innovation types by impact and approach
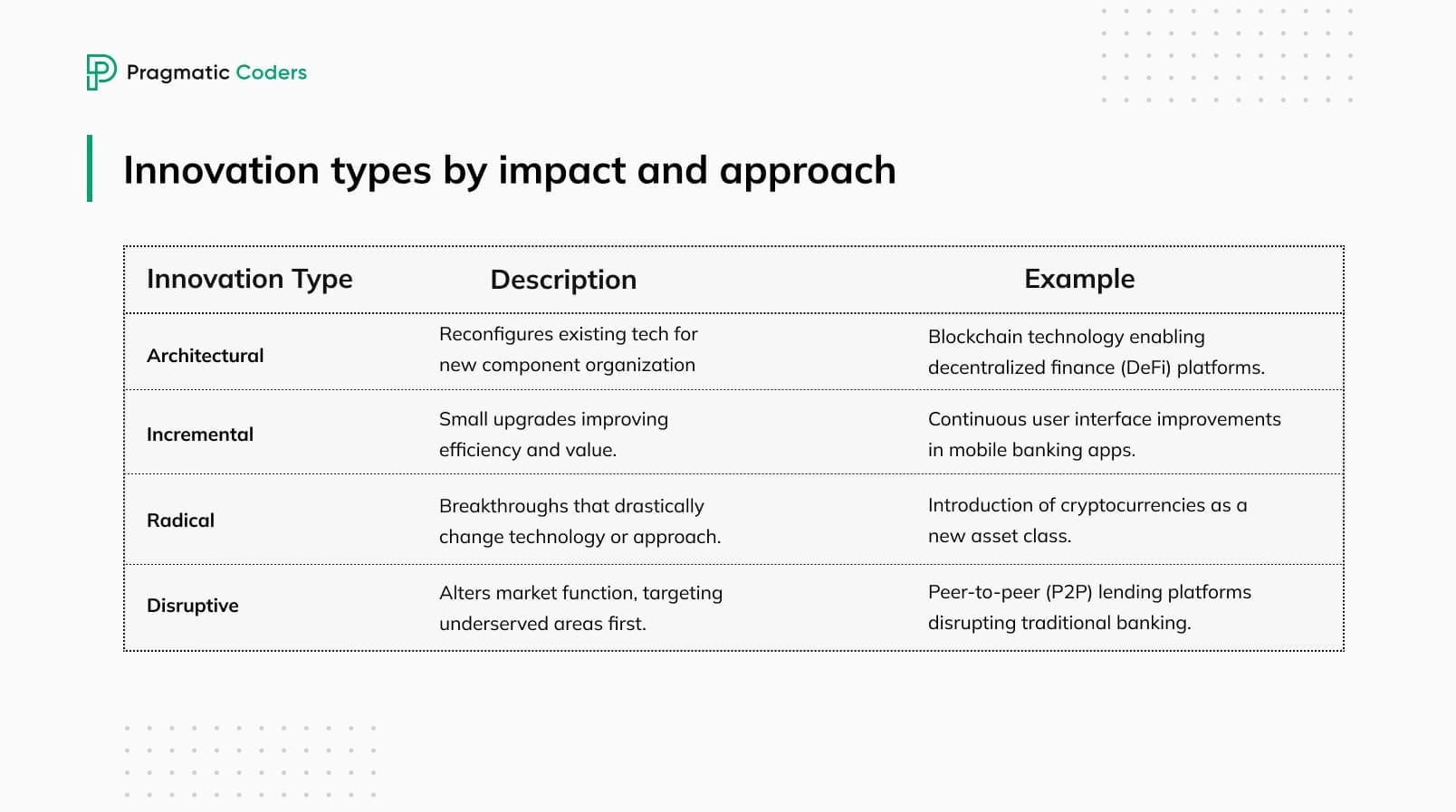
The innovation matrix is just one way of thinking about innovation initiatives. Other popular classification involves four innovation types: architectural, incremental, radical, and disruptive.
- Architectural innovation: Reorganizes existing tech to create new products/systems (e.g., the shift from desktop computers to laptops).
- Incremental innovation: Small improvements to existing products/services (e.g., updates to smartphones).
- Radical innovation: Breakthroughs that offer entirely new approaches (e.g., the internet).
- Disruptive innovation: Creates new markets or challenges incumbents with simpler/cheaper options (e.g., a digital camera that initially targeted low-end consumers).
Why is innovation important?
Innovation – continuously improving and adapting your digital product – is crucial for businesses, especially startups, for two main reasons.
First of all, you need it to stand out from the competition. The market is full of similar products, so innovation is essential to create something that will give you the competitive advantage, something so unique and valuable that users will choose it over existing options.
Secondly, user preferences and technological capabilities are constantly evolving. If you innovate, you can anticipate and meet these changing needs. This way you retain your existing users (because they keep being satisfied with your solution) and improve the chances of attracting new audiences.
4 factors that drive successful innovation across Musk’s companies
Our conversation with Joe shed light on the forces that drive innovation across Elon Musk’s companies. Let’s delve into the four key factors fueling this culture of groundbreaking ideas.
- North-Star goals
- Flatten your organization’s structure
- Data is your boss, automate what you can & use AI at scale
- Agile, iterations, modularity & short budgeting cycles
North-Star goals
The first principle you might want to incorporate in your innovation efforts is thinking goal-oriented. You should:
- Create an inspiring, high-level, long-term goal that will guide through all your decisions.
- Prioritize goals over money. Name what you want to achieve, and adjust the path that will lead to achieving it accordingly.
A 1,000-year goal
Musk’s companies are driven by overarching, visionary goals that transcend typical business objectives, that not only set the course for company development, but are also extremally inspiring.
What all those companies seem to do is they have a thousand-year goal like colonize other planets, orf spread the light of consciousness out among the stars, Joe says.
His advice to business owners is: If this person or group of people can choose the goal of the company that actually prioritizes where the money is spent, making that a worthwhile, inspiring goal would be the thing. I mean, that’s it. Let’s colonize another planet, let’s have a higher bandwidth communication pathway to AI, which is what Neuralink is about. Let’s solve quadriplegic problems, which is the near-term goal of Neuralink.
Of course, not everyone will be able to align their goals with funding – but there are other things you can do to develop a successful innovation strategy.
1,000-year goals provide long-term direction and inspire progress even if the full achievement is unlikely in our lifetimes. We at Pragmatic Coders have such a goal, too: “To become the most productive software development agency in the world”.
Goals over money
It’s [Tesla] the only company I’ve been in, aside from my own company, WIKISPEED, where decisions are made in favor of the goal over money.
When you prioritize the goal, you need so many fewer meetings because you’re not trying to protect different people’s ‘kingdoms’ and optimize budget allocations in different ways.
Instead, you’re simply trying to make the most efficient, safest, most lovable, and fast car. That’s a clear goal that is actually the only goal. Well, then it’s easy to know if you have an idea that will make the door weigh a gram less and it doesn’t cost any more and is actually a little safer—do it already. You don’t have to ask for approval, which is part of the self-management aspect that I experienced there.
Flatten your organization’s structure
Minimizing hierarchical barriers creates an environment where every employee contributes directly to the mission.
The [Musk] companies are very nearly completely flat.
There’s Elon as your administrator, and then you’re sort of in an open-world role-playing game where your only job class is engineer. […] Elon acts like the admin, so I assume if the rule system is wrong enough, Elon will reboot it. But it’s kind of like there’s not really any hierarchy at all. I actually do think Elon is a genius, but anyone is allowed to say which KPI is bottlenecking for SpaceX.
Apart from that, Joe encourages to start using AI to handle queries typically directed at managers, and integrate AI more deeply into decision-making processes: Start asking any question that you would ask your manager… start also trying to ask that to some AI.
Data is your boss, automate what you can & use AI at scale
The concepts of data, AI, and automation are closely related. Data fuels AI, which powers automation – and these are another key factors behind Musk’s success.
A lot of people think the Musk companies are fast because people work so hard… but so much of it’s automated.
Elon would always say you have no boss; your boss’s data.
Making decisions based on data is crucial. Even if your data is limited, you should start using AI now with what you already have:
I think companies that aren’t using AI are behind, and those that aren’t using their own AI have missed the opportunity to start training it.
Once you start training your own AI, you see which types of data and datasets are most useful. This realization starts to change how you gather information and even change how you work to make it easier to gather information. They haven’t even started that learning curve yet.
In a Musk company, your work is essentially to indirectly, or even directly, train the robots.
I’ve spent a lot of time participating in training AI. I’ve heard from many company founders and CEOs, both here in Poland and abroad, that they are preparing for using AI. By preparing, they usually mean building data lakes and collecting data. But what you just said might not be enough because they don’t know how they should prepare the data for the AI.
They should actually start from using AI, even if they don’t have much data yet, just on a small dataset and feed the data. That’s the Agile mindset.
Agile, iteration, modularity & short budgeting cycles
One of the key aspects of their innovation processes is the iterative approach to design and development, closely mirroring principles from Agile methodologies. They focus on short cycles, rapid prototyping, constant testing, and refinement. This lets them develop and improve technologies at breakneck speed. The same approach allows you to quickly integrate new tech and upgrades into your own products.
It’s closely related to the concept of modularity – designing systems, products, or processes in distinct, separable components that can independently be created, modified, replaced, or exchanged.
By adopting a modular approach, Musk’s companies can quickly iterate on specific components without necessitating wholesale changes. The modular nature of the products allow you to make significant changes without a ripple effect to a larger part of the product.
The Agile mindset applies not only to software development, but maybe more importantly… budgeting.
Attempting to have a shorter budgeting cycle is crucial. […]
When I visit any other car company like Toyota, Mercedes-Benz, or aerospace companies like NASA, Lockheed Martin, or Boeing, they all have a multi-year planning and execution cycle. They are making a bet that 9 years from now, they’ll have a product that’s improved.
The Musk mindset is focused on today: how do you reduce time by a second?
Elon encourages everyone to spend money as fast as they responsibly can, and there are no budgets—no annual, weekly, or monthly budgets. What you’re encouraged to spend money on is anything that will increase that KPI faster. […]
If you have a nine-year budgeting cycle like the Volkswagen Group, and you learn something new, all the engineers get depressed because they can’t implement any of it on company time and definitely can’t sell any of it for 9 years on average. Try to make it eight years. If you’re at a one-year budgeting cycle, can you do quarterly?
The shorter the cycle for checking whether we should change the budget without penalty, right, without an elaborate change request process and penalty, the more Agile the financially backed change of the company is.
Fundamentally, this makes the workplace more exciting for people who like to innovate. If the pace of innovation is the only thing that matters, then the budget length becomes enormously important as a bottlenecking factor.
So, even if you can’t choose the company mission and you’re just making something uninspiring, at least try to make innovation possible by shortening the budget cycle.
Developing an innovation strategy
To sum up, let’s discuss how you can implement everything covered above to innovate with your product.
Innovation tips for when you have or don’t have a product

First, let’s talk about your needs. Startup founders with a product idea have different needs that business owners with existing products.
If you’re a startup founder, and you’re only shaping the product concept, you should focus especially on validating your ideas. In simple words: ask users for feedback ALL THE TIME. There more times have you tested your ideas, the smaller chance of failure there is.
On the other hand, if you have an existing product, you might want to focus more on improving or extending it, or entering new markets. You still want to ask users for feedback, but you’re doing it to further evolve and enhance your product that has already been validated with the market.
Not to say that if you have a grown product you should give up on breakthrough innovations, because you shouldn’t – but you can think of them in terms of these 1,000-year goals mentioned earlier.
How to Implement an Innovation Strategy
Implementing an innovation strategy means turning ideas into real, valuable improvements for your business. Here’s a simple step-by-step approach:
- Align Innovation with Business Goals: Make sure innovation supports your company’s mission and long-term strategy. If your goal is to reduce operational costs, focus on automation and AI.
- Build an Innovation Process: Set up clear steps for idea generation, testing, and implementation. Build in short, iterative cycles (Agile approach) – test small changes often and adapt fast.
- Prioritize the Right Innovations: Focus on projects with the highest impact using a focused innovation portfolio (balancing high-risk and incremental innovations). Use architectural innovation to improve existing systems rather than starting from scratch.
- Embed Innovation in Daily Operations: Make innovation a habit, not a one-time effort. Set an inspiring long-term goal that guides all decisions – this will make it easier to prioritize progress over short-term profits. Streamline internal operations so new ideas can be tested and adopted quickly.
- Measure & Adjust: Use systematic measuring to track progress and impact. Example: Define KPIs (e.g., revenue growth, cost savings, customer satisfaction) and review them regularly.
- Create a Culture of Innovation – flatten the hierarchy: Musk’s companies remove unnecessary hierarchy. There are no traditional managers, as every employee is encouraged to solve problems directly. What’s more, decisions are based on data, not opinions. Allow employees to experiment and take ownership – that’s the best way to create a culture of innovation and feedback.
Conclusions. The pace of innovation is the only thing that matters
One of the cornerstone philosophies of Musk’s leadership is the focus on pace of innovation as the primary metric of success.
As Joe summarized it, the pace of innovation is the only thing that matters in the long run.
Musk’s belief in innovation as a core driver of success leads to a culture where rapid prototyping, iterative feedback, and continuous improvement are not just encouraged but required.
Innovative product development
To translate Musk-inspired innovation principles into a successful digital product, you’ll need a team that excels in user research and Agile development. Partnering with the right development team can accelerate this process.
We’re here to help! Check our Agile software development services or hop on a call with our team now.