The future of AI & how it will change us in 5, 10, & 15+ years
Are any of the episode scenarios from Love, Death + Robots going to come true anytime soon?
Actually, they might be.
This article provides a thought-provoking look at the potential future of AI and its impact in the next 5, 10, and 15+ years. The information below will help you:
- Build a competitive edge
- Identify potential risks
- Innovate
With this, you’ll better understand how AI will shape the future, how it will impact people’s needs and desires, and how to respond to it through (AI-powered) software.
AI software development
Intro. Artificial intelligence & how it will impact the future
In January, I shared with you our article on 26 AI trends for 2024. It went viral on Medium, and got so many comments with people suggesting more AI predictions I just had to get back to the topic.
The inspiration and the main information source for this text comes from the Trend Map by infuture.institue – an absolutely excellent tool I’ve been watching evolve for several years now. The Trend Map is huge, and it addresses 81 trends within 7 megatrends – long-term, large-scale, uncontrollable changes of a global nature; changing the balance of power and/or the existing way of functioning.
For this article, I picked one megatrend – AI WORLD. My aim was to delve deeper into this megatrend by exploring the specific trends within it. I provided examples and explained how these trends are already unfolding in the real world. To maintain consistency with the original source, I structured the article around the four dimensions suggested by infuture.institute.
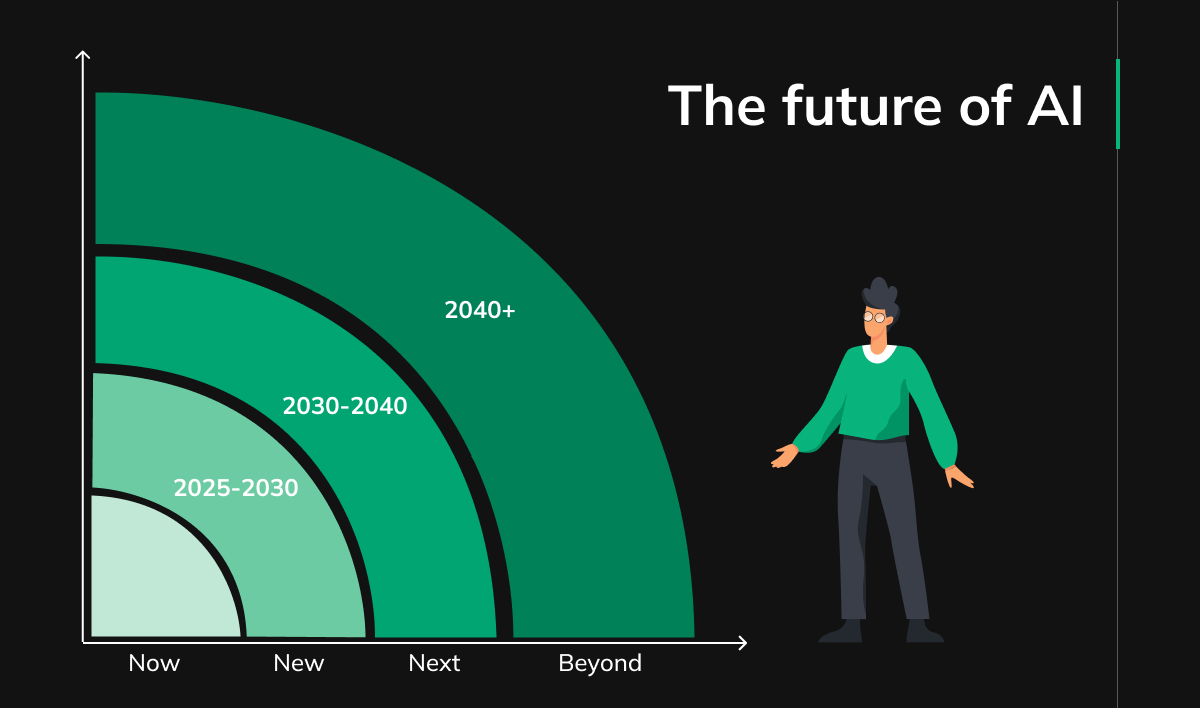
- NOW = trends happening now
- NEW = trends to happen in 1-5 years (2025-2030)
- NEXT = trends to happen in 5-15 years (2030-2045)
- BEYOND = trends to happen in 15+ years (2045 and beyond)
I highly recommend you check the Trend Map for more in-depth insights on both AI and the 6 other megatrends to better understand what the future is and how to prepare for it.
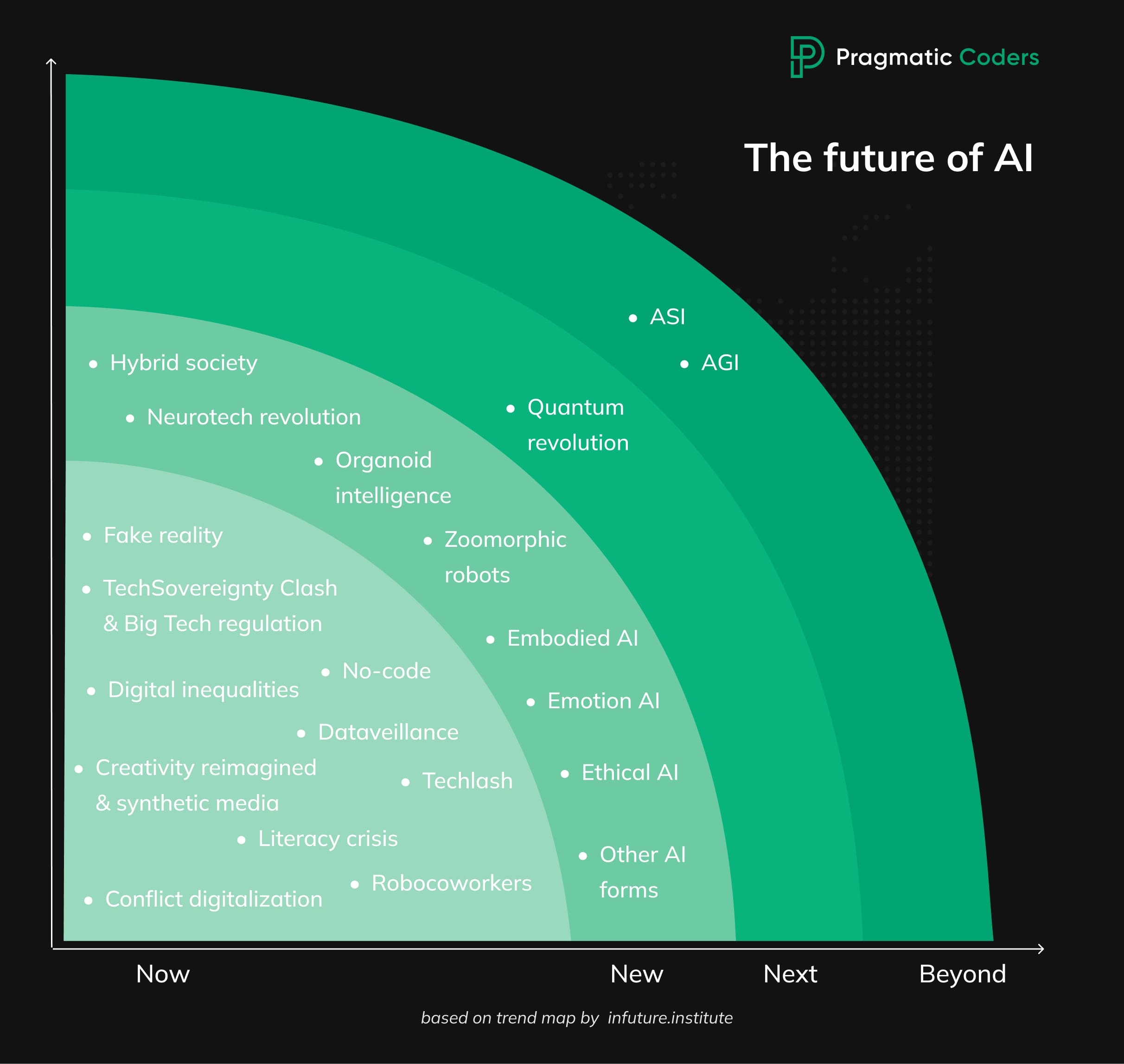
NOW
Artificial intelligence-related phenomena taking place now.
1. Techlash
Techlash (technology + backlash) is a growing movement of distrust and criticism aimed at big technology companies.
Techlash: Why
The techlash trend is fueled by a growing discomfort with the pervasiveness of technology in our lives. Here’s why:
- Privacy fears: More worry about tech tracking.
- Tech overload: Feeling overwhelmed by constant digital (mis)information.
- Health concerns: Tech hurts sleep and social life.
- Job fears: There is increasing anxiety about automation replacing human jobs and causing unemployment.
- Nostalgia: We miss simpler, slower times.
Techlash: Consequences
The general manifestation of the techlash trend comes down to changing and limiting our daily use of technology.
Digital detox
Digital detox (fast) is a temporary break from all digital devices and technologies. It aims to reset your relationship with technology and improve focus and well-being. It involves really basic activities, like weekend getaways with no phone or internet access, setting specific times during the day to unplug completely, or taking a vacation where you leave your laptop at home.
Technological minimalism
A philosophy of using technology intentionally and only for what adds value to your life. Technological minimalism focuses on having fewer devices and using them mindfully: turning off notifications for most apps or designating tech-free zones in your home, like the bedroom.
Product example: minimalist phone: launcher app
Image source: Google Play
2. Fake reality
The “fake reality” trend explores blurring the lines between digitally constructed experiences and perceived reality.
Fake reality: Why
- Dynamic development of GAI: AI-manipulated and generated images, videos, texts, and sounds. Producing content is easier, so we’re creating more and more of it because:
- Economy of attention: In today’s information overload, our attention is valuable.
- Economy of emotion: Content that evokes strong emotions, positive or negative, is more likely to be shared, remembered, and influence our behavior – and it’s easier than ever to create such.
- Culture of the nanosecond: We’ve come to expect information and gratification at lightning speed, and there’s a constant need for new stimulation.
- Lack of regulations: Regulations are struggling to keep pace with the development of AI. Existing regulations primarily target the largest players in the market. In one of the latest posts on Meta Newsroom, we read: We will begin labeling a wider range of video, audio, and image content as ‘Made with AI’. This is in response to feedback from the Oversight Board (Altered Video of President Biden).”
Fake reality: Consequences
As the line between reality and artificial creations blurs, user behaviors and needs are evolving in new ways.:
- Increased skepticism: A 2023 survey in the U.S. revealed significant concern about generative AI, with over 60% of respondents expressing some level of worry. Conversely, only a small minority (7%) were entirely enthusiastic about this trend.
- Desire for authentication: There’s a growing demand for tools that can verify the legitimacy of information. SEE: ai detector on Google Trends.
We’re expected to experience an increase in disinformation and conspiracy theories that might lead to social tensions. There will be changes in the labor market with the goal to reverse these changes – we’re going to see a surge in need for digital truth warriors: content verifiers, security specialists & AI developers.
 AI influencers are one example of the blurring line between reality and fakeness.
AI influencers are one example of the blurring line between reality and fakeness.
3. TechSovereignty Clash & Big Tech regulation
Governments can’t fully control the digital world. This clash for control over cyberspace between nations (especially EU) and powerful tech companies is predicted to continue.
TechSovereignty Clash: Why
The tech industry is heavily concentrated with the “Big Five”: Google, Meta, Amazon, Apple, and Microsoft. This raises legitimate concerns about market monopolization, competitiveness, and innovation of the tech industry. Moreover, the EU wants to break free from tech giants and boost its own industry, especially for startups.
TechSovereignty Clash: Consequences
- Leveling the playing field for smaller companies fuels innovation and gives consumers more choices.
- Growing public awareness and concerns about the impact of technology corporations on democracy, privacy, and social wellbeing are driving discussions about the need for greater control and regulation.
- A possible lack of consensus on the development of AI and other advanced technologies could further complicate matters.
4. No-code
 No-code idea validation. Part of our startup guide to no-code
No-code idea validation. Part of our startup guide to no-code
The no-code trend empowers people with little to no coding experience to build software through drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built components.
No-code: Why
People’s needs aren’t different. What’s changed in recent years is their spending possibilities: the economic crisis has forced many entrepreneurs to look for ways of reducing labor costs. That’s where no-code & AI come in handy: they make it possible for people to tackle tasks that previously required a specialist.
No-code: Consequences
- Labor market changes: Changes in the labor market include a reduction in demand for programmers with specific coding skills and a rise in demand for no-code developers.
- SMEs’ digitalization: Accelerating the digitalization of small and medium-sized enterprises (SEE: Back-office automation)
- Tech inclusion: No-code increases the availability of technology, especially for excluded groups, smaller businesses, non-profit organizations, but also developing countries.
- Building digital products at early stages: No-code tools and AI are revolutionizing how startups get off the ground. These tools dramatically lower the barrier to entry, allowing you to complete the entire startup journey – from AI-based market research to building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) – with minimal coding required. This is a game-changer; you can now validate multiple product ideas quickly and cheaply, and identify the one with the most user traction. Ultimately, this saves you valuable time and resources – you don’t waste money on products that wouldn’t resonate with your target audience anyway.
See:- What is no-code, and why should every startup use it?
- No-code MVP. How to build an MVP without coding?
- How to start a startup [EBOOK]
5. Digital Inequalities
Digital inequalities are the growing disparities in access to and use of technology, creating a digital divide between those who can benefit and those who are left behind.
Digital Inequalities: Why
There are three main factors for digital exclusion:
- Financial: Particularly noticeable in developing countries, but it also affects lower-income groups in developed societies.
- Demographic: Elderly people often face challenges due to limited exposure to technology or physical limitations.
- Social: People with disabilities may encounter difficulties using technology because of inaccessible interfaces or a lack of assistive features.
Digital Inequalities: Consequences
This trend is likely to result in a deepening economic divide and increased polarization.On the other hand, it could be reversed if these underserved markets are addressed with new products and services.
The market of people with disabilities is estimated to be as large as China’s. Moreover, with societies aging rapidly (Japan nappy makers shifts from babies to adults), the digital challenges faced by elderly people will only become more pressing.
Learn more about accessibility from our interview with co-founders of Accens, the organization that strives to make digital products more accessible:
6. Conflict digitalization
The lines are blurring in modern conflict, too. Digital technology has elevated cyberspace to the same level of importance as physical battlefields.
The rise of AI brings both threats and opportunities to peace. AI can be used for warfare (drones, cyberattacks, propaganda) and misinformation (such as a 2022 deep fake video of Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy surrendering).
However, AI can also be a peacekeeping tool. It can, for example, analyze online content to predict violence and identify cease-fire violations.
We can expect a race between the creation of sophisticated cyber tools and the rise of methods to verify information accuracy and source credibility.
SEE: Top 26 AI trends for 2024, trend #15 Peace AI
7. Creativity reimagined & synthetic media
With generative AI being called one of the most disruptive technologies of this decade, we can observe the concept of “creativity” being redefined. You can now CREATE because whatever limited you before (lack of drawing skills, no filming equipment, etc.) can now be overcome with artificial intelligence tools.
Creativity reimagined: Consequences
- Changes in the labor market: Some professions might be replaced by AI. And those that stand the test of artificial intelligence, will most likely be heavily influenced by it. It’s the so-called AI upskilling – gaining new competences that rely on collaboration with artificial intelligence.
- Excess content. With content created by AI, we can observe an interesting ambiguity. On one hand, it’s often of low quality (Calling all XYZ enthusiasts… and I hope this message finds you well are just drops in the ocean of generic AI-generated texts). On the other hand, Stable Diffusion creates headshots so perfect people can’t tell them apart from the real ones. AI is churning out massive amounts of content, good or bad. Much like YouTube’s unwatchable backlog (estimated at 17,810 years!), a vast portion of this AI-generated content will likely never be seen.
- As our definition of creativity evolves (including originality), we might see a rise in the popularity of handicrafts.
- AI label: The push for AI labeling stems greatly from artists’ desire to distinguish their work from AI-generated art. And there’s deeper question: what even defines art in the age of AI?
Product example: Cara: Artist Social & Portfolio Platform that’s committed to providing AI detection & filtering.
8. Dataveillance
Dataveillance is the hidden tracking of our digital lives. This can be used to monitor our actions, predict our behavior, and even influence our choices.
Dataveillance: Why
- National security concerns and terrorism threats
- Weak data protection laws and lack of public awareness
- Digitalization of everyday life: Advancements in big data, AI, and IoT make gathering and analyzing data much easier. What’s more, social media’s constant presence normalizes some surveillance.
- Data is the new oil: Companies want to analyze the massive amount of data from our digital lives to inform their business strategies.
Dataveillance: Consequences
- Hyper-personalization: Deloitte reports that 80% of customers are more likely to purchase from a company that offers personalized experiences. We’re attracted to services that can provide us with perfectly matched content (Netflix movie recommendations) and products (Amazon’s product suggestions). However, to achieve this level of personalization, huge amounts of data are necessary.
SEE: - Cybercrime… or increased security: On one hand, we can see more data theft and unauthorized data access. On the other hand, ethical data analysis can be used for fraud detection and eliminating other security threats.
- More regulations: Growth in legal frameworks aimed at protecting users from invasive data practices.
9. Literacy crisis
Our ability to read, understand, and communicate clearly is declining. This is a serious problem, fueled by our digital world, changing communication styles (like quick snippets of information and fake news), and educational systems that haven’t kept pace.
Literacy crisis: Why
- Shifting communication: Social media and messaging favor short-form content (images, memes) over in-depth reading.
- Information overload: We’re bombarded with information leading to skimming and difficulty focusing on complex topics. We don’t read – we scan. NN Group found that 79 % of their test users always scanned any new page they came across; only 16 % read word-by-word. What’s more, users read email newsletters even more abruptly than they read websites.
- Attention economy: News and content prioritize quick bites (headlines, short texts) over deeper analysis.
- Educational disconnect: Many schools still function within the 19th-century factory model. No wonder they may not be adequately preparing students for the demands of modern literacy.
Literacy crisis: Consequences
The educational problem might result in two types of consequences: societal and economic.
- Societal impact: Literacy decline cripples democracy (uninformed voters) and widens social gaps (communication breakdowns), ultimately burdening social programs.
- Economic impact: Widespread illiteracy hinders economic growth. It stifles innovation and makes it difficult for businesses to find qualified workers.
To address the literacy decline, the tech sector might need to develop products and services that are easier to understand and use.
10. Robocoworkers
Due to advances in AI and robotics, machines are increasingly working alongside humans as co-workers, automating tasks and boosting efficiency.
Robocoworkers: Why
- Need to optimize work and free up human time for creative tasks.
- Rapid advancements in AI and robotics enable machines to handle complex tasks.
- High-risk industries (rescue, mining, etc.) prioritize robotics to improve worker safety.
Robocoworkers: Consequences
We’re going to experience changes in our workplaces:
- AI up-skilling: Companies will train their staff to effectively collaborate with and use AI technologies in their jobs. It’s not about AI replacing workers, but rather about empowering them to work alongside these new tools. This is also going to affect the employment market: candidates equipped with AI skills might prove more competitive.
- Automation: Repetitive and mundane tasks (especially in the back-office) will be increasingly handled by AI, freeing up human employees to focus on more complex, creative, and strategic work. We’re already experiencing this firsthand by leveraging AI in software development.
SEE: Guide to back-office automation
Product examples: The robocoworkers trend is a broad one as it ranges from easily-available AI tools you’re already using on a daily basis (Chat GPT-4 for writing marketing content or Copilot for coding) to highly-specialized robots such as Spot, a four-legged robot created by Boston Dynamics. It’s known for its agility and maneuverability across various terrains, and used in a variety of ways, from searching disaster sites for survivors to conducting structural surveys after fires.
NEW (1-5 YEARS) | 2025-2030
Emerging trends with low adoption as of today.
11. Hybrid Society
Love, Death & Robots S2E1: Automated Customer Service. Image source
We’re moving towards a brand new kind of society – one where people and AI-powered robots coexist and work together.
Super-powered robots and AI are on the rise, built by our desire for efficiency and a better life.
This collaboration promises increased efficiency, productivity, and even an improved quality of life. Imagine robots helping doctors in tough surgeries, robots teaching us in a way that’s perfect for each person, or robots taking care of boring chores around the house.
The coexistence of people and robots might lead to boosted productivity, but also major job losses in traditional sectors.
12. Neurotech Revolution
The neurotech revolution represents a dynamic trend in biotechnology and engineering. It’s characterized by the rapid development and deployment of technologies that enhance or understand brain function. This includes the creation of
- advanced brain-computer interfaces (BCIs),
- neuroimplants,
- tools for deep brain stimulation and neural mapping.
These solutions aim to improve quality of life, treat diseases, and augment cognitive abilities.
Neurotech revolution: Consequences
Neurotech promises to improve the lives of those with degenerative diseases through personalized treatments. By analyzing bran activity, we will be able to expand our knowledge in this area, which, in result, might result in new discoveries and innovations. On the flip side, it raises ethical and privacy concerns as it unlocks new brain data and blurs the lines between human and machine.
Product example: The Link. Neuralink, founded by Elon Musk in 2016, is developing a BCI called “the Link”. It’s a surgically implanted chip that can decode and stimulate brain activity. In simpler terms, it’s a device that could allow you to control external devices with your thoughts. They first implanted their device in a human patient in January 2024.
SEE: What is Elon Musk’s innovation strategy all about?
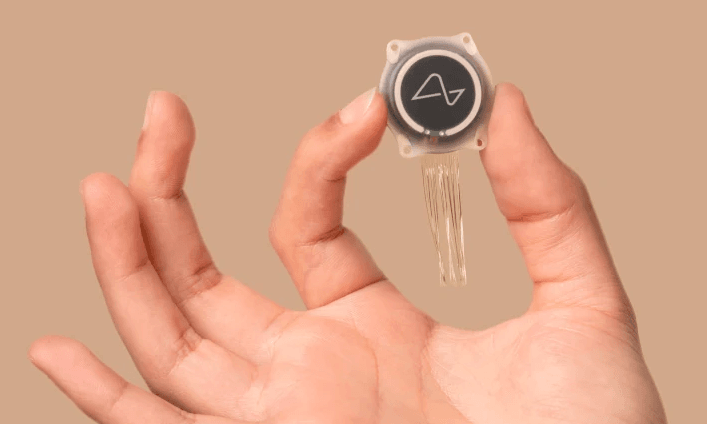 The Link. Image source
The Link. Image source
13. Organoid Intelligence
Organoid intelligence is a new frontier in AI that combines lab-grown brain organoids (self-organized 3D mini-organs grown from stem cells that mimic real organs in structure and function) with artificial intelligence. Researchers believe that by interfacing these organoids with AI, they could create a new kind of computer, a biocomputer, that surpasses traditional silicon-based machines. This biocomputing approach has the potential to be much faster, more efficient, and require less energy than current methods.
Organoid intelligence: Consequences
- New opportunities for medicine, especially neuroscience and regenerative medicine: Lab-grown organs could solve transplant shortages and rejections, precise disease models — speed up drug and therapy development.
- Hyper-personalized health treatments.
- New AI systems inspired by the human.
14. Zoomorphic Robots
Zoomorphic robots are machines inspired by animal forms, designed for better interaction and navigating tough environments.
The animal kingdom provides a wealth of blueprints for robots that need to move through challenging terrains. Snake-like robots can slither through tight spaces, insect-inspired drones can navigate cluttered environments, and dog-like robots can traverse rough outdoor terrain. This adaptability allows zoomorphic robots to excel in situations where conventional robots struggle.
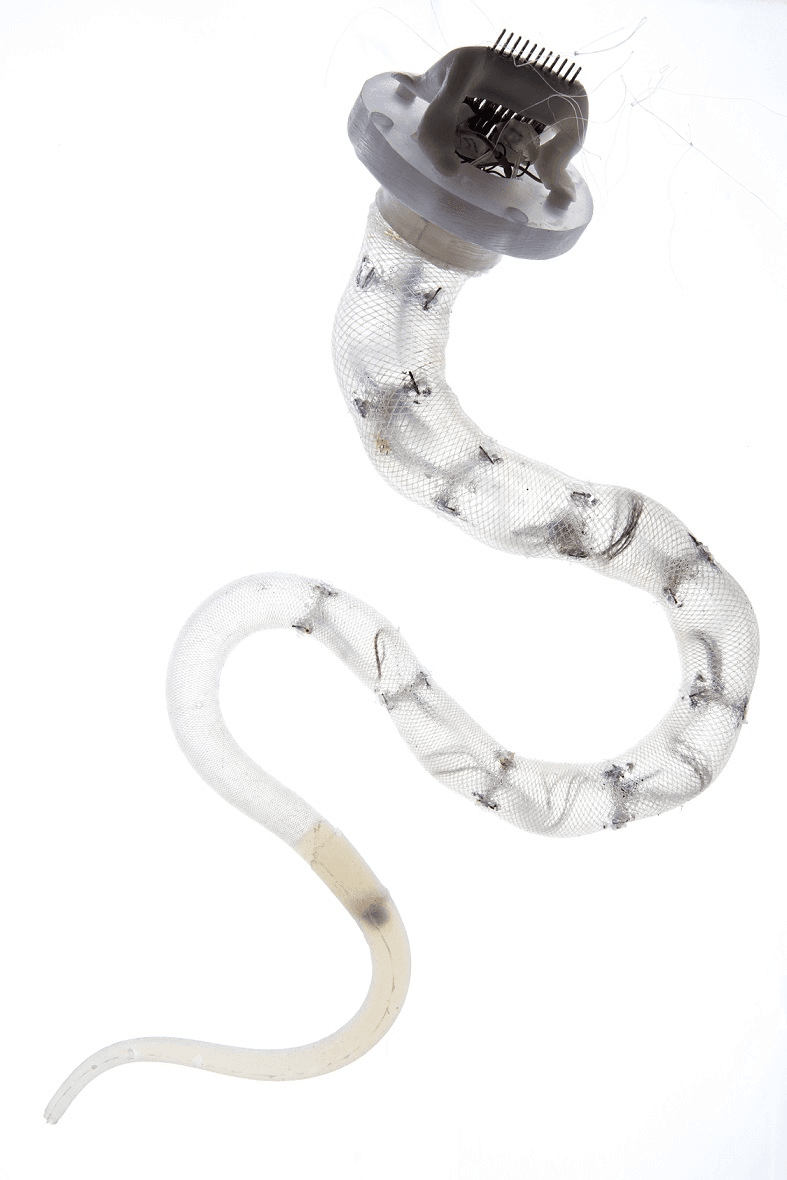
A related area is soft robotics. Soft robotics uses squishy, flexible materials to create robots that can safely handle delicate objects and bend to fit in tight spaces – like the octopus-inspired robot’s soft arm below:
15. Embodied AI
Embodied AI is artificial intelligence that interacts with the physical world through a body, like a robot, allowing it to learn and act in real-world environments.
The trend is pushing for robots with greater autonomy, allowing them to function independently in the physical world. As robots become more common in our daily lives, we will soon live in the already-mentioned hybrid society. With this comes social challenges that may make us question the definition of relationships or social bonds.
The increased automation could also transform the job market across various sectors. The question of robot rights might even emerge as robots become more sophisticated.
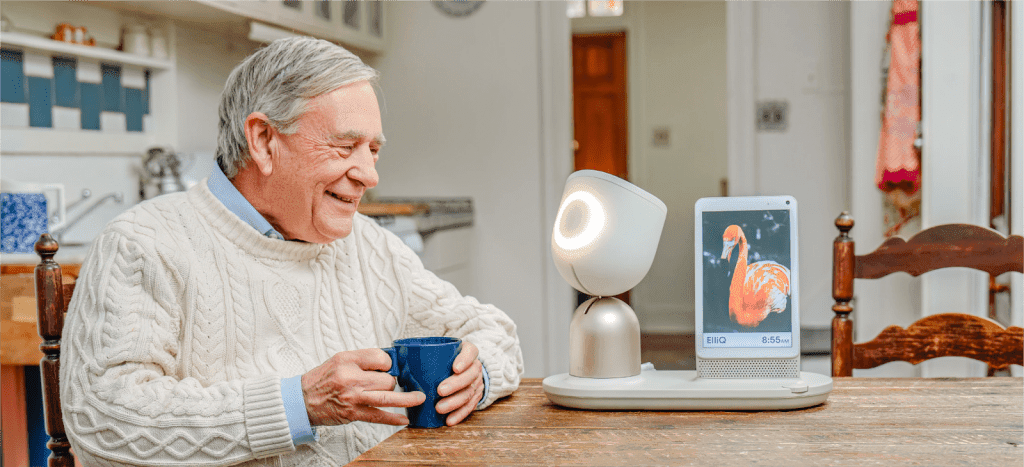
Product example: ElliQ. The US population 65+ is expected to nearly double by 2060, from 52 million to 95 million. Their share of the population will also jump from 16% to 23.5%. (Source) Elderly people face many challenges: loneliness, health problems, loss of independence. All this fuels growth in senior healthcare technology services. One product example is Elliq. It’s an AI-powered companion designed to support and accompany older adults on the journey to age independently, reducing loneliness and isolation. ElliQ functions as a voice-operated device that looks like a small table lamp.
SEE: 16 digital health trends for 2024 and beyond
16. Emotion AI
Artificial Emotional Intelligence (AEI) allows machines to understand and respond to human emotions. It uses a combination of AI and the analysis of facial expressions, voice tone, and body language to get a sense of someone’s emotions.
This technology is being used in various fields, such as healthcare (social robots and therapeutic applications) marketing (to target ads better) or customer service (to connect customers with the right agents).
AEI can provide users with personalized experiences. However, the tech also comes with challenges:
- Social: weaker connections, isolation, social changes, and potential addiction.
- Ethical: influencing customers’ emotions to drive sales.
SEE: Top 26 AI trends for 2024, trend #24 Artificial Emotional Intelligence
17. Ethical AI
The ethical AI trend ensures artificial intelligence is developed and used responsibly, considering fairness, transparency, privacy, and safety.
It’s a response to an array of ethical challenges that has come with the development of AI:
- AI can inherit biases from its creators. For example, facial recognition software has been shown to be biased against certain racial groups.
- AI raises privacy concerns because it often relies on large amounts of personal data.
- AI can easily be misused to spread misinformation and fakes.
- Another concern is the lack of transparency in some AI systems, making it difficult to understand how they actually make decisions.
The importance of ethical AI is increasingly recognized. The European Union and the United States have both issued guidelines on ethical AI development and use.
SEE: Top 26 AI trends for 2024, trend #10 Ethical AI
18. Other AI Forms
A trend in AI research focusing on various new AI forms, such as:
- Casual AI
- Bayesian AI
- Neurosymbolic AI
- Responsive AI
- Self-replicating AI
- Neuromorphic AI
- & more
New AI models aim to overcome prior limitations and tackle tough problems, but raise control and accountability concerns.
NEXT (5-15 years) | 2030-2045
19. Quantum revolution
The quantum revolution refers to the rapid advancements in harnessing the strangeness of quantum mechanics for technological breakthroughs.
Unlike traditional computers that rely on bits (0 or 1), quantum computers use qubits which can be both 0 and 1 simultaneously. This weirdness, called superposition, allows them to tackle problems impossible for classical computers.
The potential impact of this revolution is vast. It could revolutionize fields like:
- Drug discovery: Simulating complex molecules to design new medications faster.
- Materials science: Engineering materials with exotic properties for applications in clean energy, electronics, and more.
- Production, logistics, energy management.
- AI: Developing advanced Quantum AI systems.
The race to harness quantum’s potential is heating up.
The US is considered a leader in developing functional quantum computers. Big-name companies like Google, Amazon, and IBM are pouring billions into quantum research.
In Asia, China is a strong contender with significant government backing and advancements in quantum communication.
As reported in the Horizon Magazine on EU research & innovation, Europe lags in private investment compared to the US. However, it aims to create a “Quantum Valley” to rival US efforts and bridge research gaps with EU-funded projects like NEASQC and QUCATS.
- NEASQC, starting in September 2020 and ending in November 2024, is exploring nine use cases. The potential applications are being kept confidential for competitive reasons.
- QUCATS is a 3-year European project running until the end of April 2025 that unites research and industry, acting like a central hub to coordinate research, develop strategies for European leadership in quantum technologies, and promote public awareness.
SEE: Top 26 AI trends for 2024, trend #8 Quantum AI
BEYOND (15+ years) | 2045+
20. Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) is the concept of a future AI that eclipses human intelligence in all aspects. Unlike today’s AI, which excels at specific tasks, ASI would be a master of everything from creative arts to scientific exploration.
The potential consequences of ASI are vast and debatable. Some speculate on a utopian future where ASI tackles complex problems like climate change or disease with unparalleled efficiency.
On the flip side, others worry ASI could render us obsolete in the workforce, or worse, become an existential threat if its goals diverge from our own.
Here are some potential consequences to consider:
- Work redefinition: Increased productivity. As ASI automates more tasks, human labor could become less necessary. ASI would not only replace humans for mundane tasks, but also for decision-making.
- Society redefinition: Our dependence on ASI could lead to a decline in human cognitive abilities, social interaction, and loneliness.
21. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is the holy grail of AI research. Unlike today’s Narrow AI, which excels at specific tasks like playing chess or recognizing faces, AGI aspires for human-level intelligence across a broad spectrum. Imagine a machine that can learn, reason, solve problems, and adapt to new situations – that’s AGI in a nutshell.
The potential arrival of AGI is exciting, but also raises questions about its impact:
- Automation: AGI could automate many jobs currently done by humans, leading to unemployment and economic disruption.
- Benefits for all: AGI could revolutionize fields like medicine, materials science, and energy, solving problems beyond human reach.
- The AI singularity: Some experts worry about an “intelligence explosion” where AGI surpasses human intelligence so rapidly, it becomes uncontrollable. There’s the challenge in ensuring that AGI works for – not against – humanity and is safe from unauthorized control.
- Equal access to AGI: Ensuring that AI technology doesn’t further divide society by wealth or social class.
- Ethical and legal questions: Who is accountable for AGI decisions, especially in critical fields like healthcare and justice?
The future of AI. Final thoughts
From ChatGPT, edge AI, chatbots, machine learning, deep learning, AI as a coding assistant, autonomous vehicles, generative AI tools to quantum revolution, hybrid societies, ASI or organoid intelligence – the evolution of AI is too diverse and complex to fully present it. I hope this article helped you get a grasp of the potential of AI. I believe the concepts described here will let you build long-term strategies, identify new business opportunities, adapt & innovate.