Custom Software for Fintech
and Healthcare Leaders
We're here to become the world's most effective software company.
Custom Digital Health Software Solutions
Check Our ServicesWho We Are and How We Help
Since 2014, we’ve helped companies move from idea to production with speed, security, and clarity.
Learn how we work
Experts in building digital products
Since 2014, we have been developing solutions that address real problems. We have helped over 100 clients bring their software ideas to life, launching digital products that have reached millions of users.
What our clients say about working with us
I'm impressed by how flexible Pragmatic Coders is (...). Culturally, they're a really good fit for us, and the team is very responsive to feedback. Whenever I ask them to do something, they look at it, and they're not scared to push back. I've found it very easy to work with them — we have more of a partnership than a client-supplier relationship.

Pragmatic Coders pay attention to detail and understand the business domain correctly. They led us to a successful launch of our product this year. We’re happy with the effects of their work. Our team is still using the platform and building on top of it.

The entire focus was on the product and the customer, and I loved it. (...) The team was turning up with solutions to problems I didn't know we had.

It’s truly been a partnership. They have an in-depth understanding of our client base and what services we provide, anticipating evolving needs and addressing them by adding new features into our system. Their team also makes sure that there is a shared understanding so that what they deliver meets my organization's and our clients’ expectations.

(...) Pragmatic has highly skilled engineers available immediately but most importantly, passionate people who love what they do and learn new things very quickly. I recommend Pragmatic Coders to anyone who requires expert software development no matter the stage of their business.

They responded to our queries almost immediately, and they were consistently polite and professional in their interactions. If there was something even more impressive than their communication, it was definitely their transparency. We were well informed about every aspect of their work, including what they did, why they did it, and how long it was going to take (...).
Check successful businesses that worked with us and join them

















This is how we work
Deliver & Scale
- Product Development
- DevOps Architecture
- Continuous User Feedback & Delivery
Tony Kelly on working with Pragmatic Coders
“[…] Coming over here and having the team go, ‘We saw this, we think this is a better way of doing this,’ and you go, ‘Ooh. That’s 10x better than the way we were going to do it, and we didn’t even realize that was a problem.
That’s the kind of solution-oriented approach you want to have in a partner, right? “
Tony Kelly – Core Team Member at Common Wealth, Serial CTO, CPO and Founder

Key Cooperation Results:
- Just 11 weeks from idea to launch
- 63,000+ registrations on Common Wealth app in the first 3 weeks
- 1.64 million missions completed by users – that’s 3,291 missions/hour!
Case Study: How We Made Early-Stage Startup Investing Accessible to Everyone
Check our case studies
- Banking
- Fintech
- Digital Health
- Foodtech
- E-commerce
- Social media
- Blockchain
- Web3
Atom - an entirely new, remote team for the UK’s first fully digital bank
Read the case study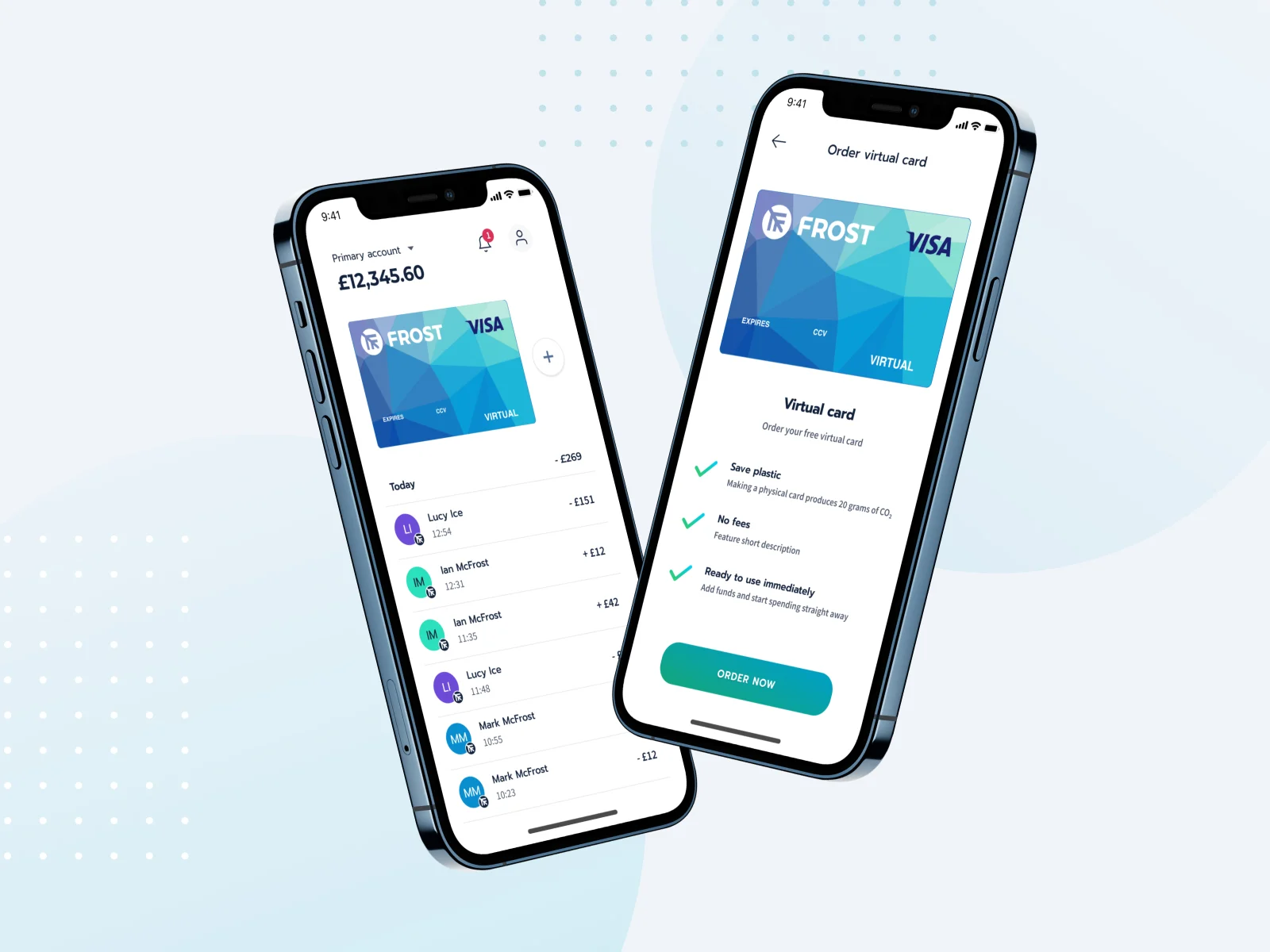
Frost - a digital account that helps people master their money sustainably
Read the case study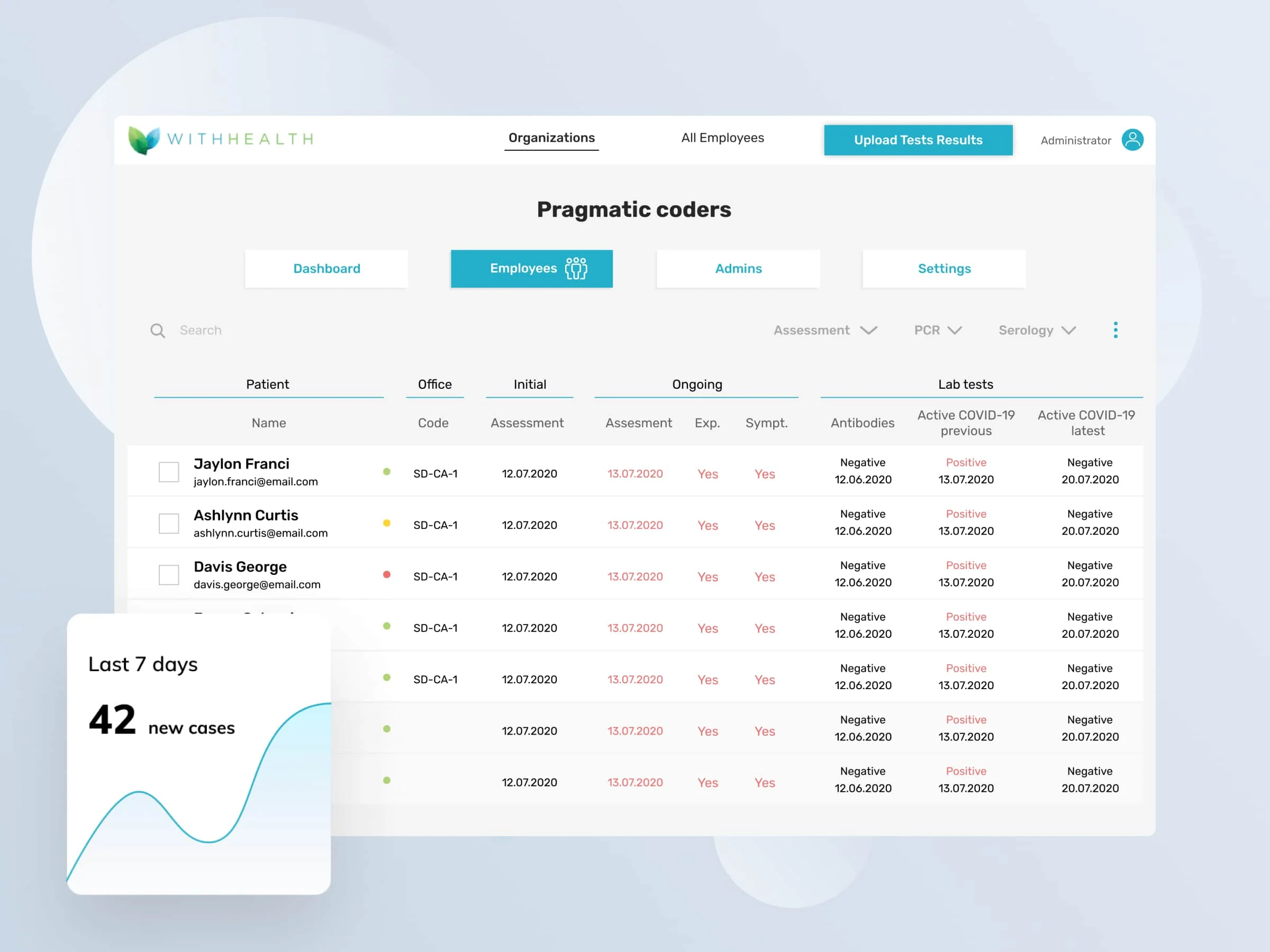
WithHealth - Releasing fully operational patient MedTech portal in just 6 weeks in response to COVID-19 pandemic
Read the case study
Kitopi - cloud kitchen unicorn startup from UAE
Read the case study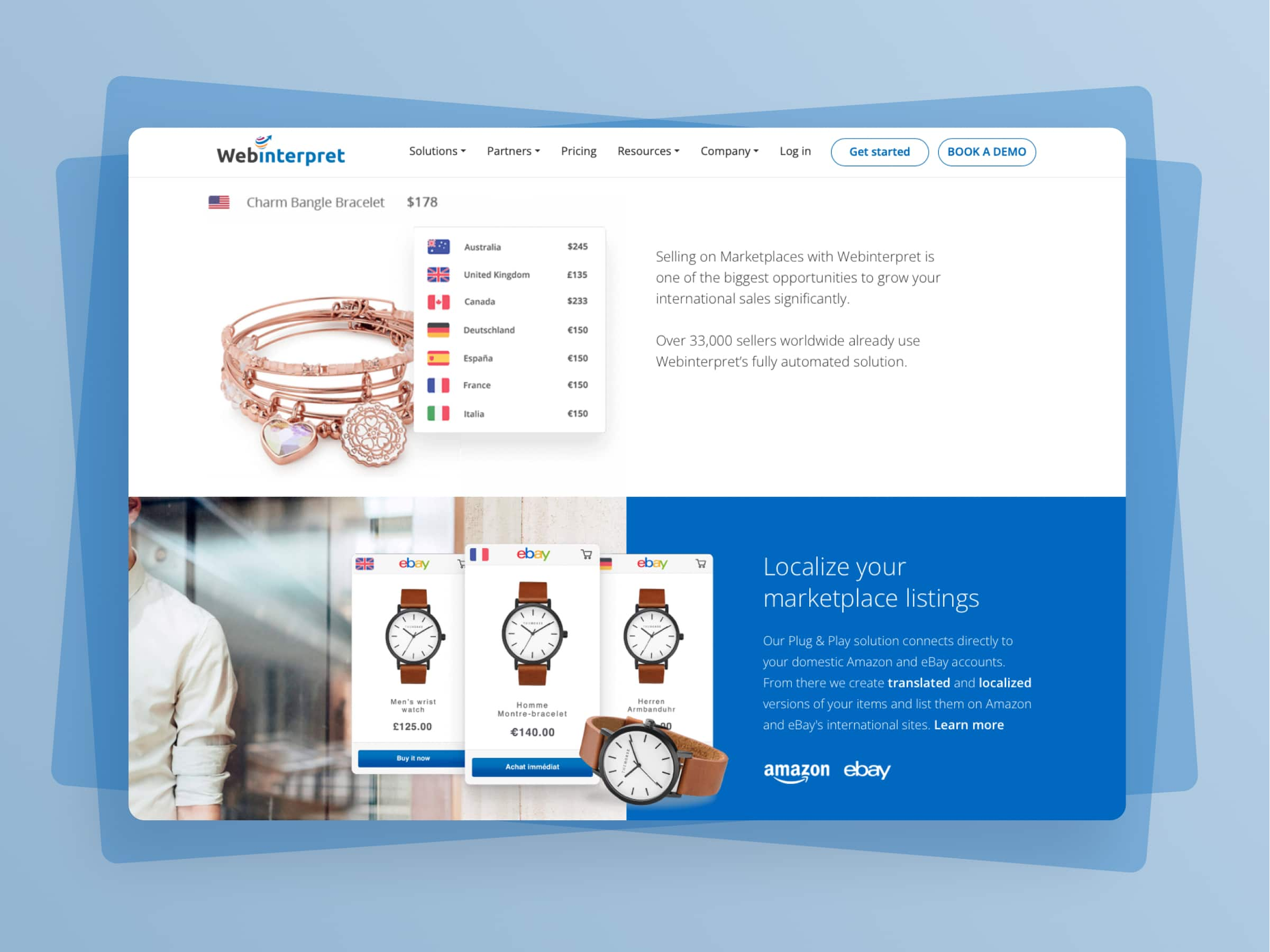
Webinterpret - Scaling up one of the largest multiplatform e-commerce listing and translation tool
Read the case study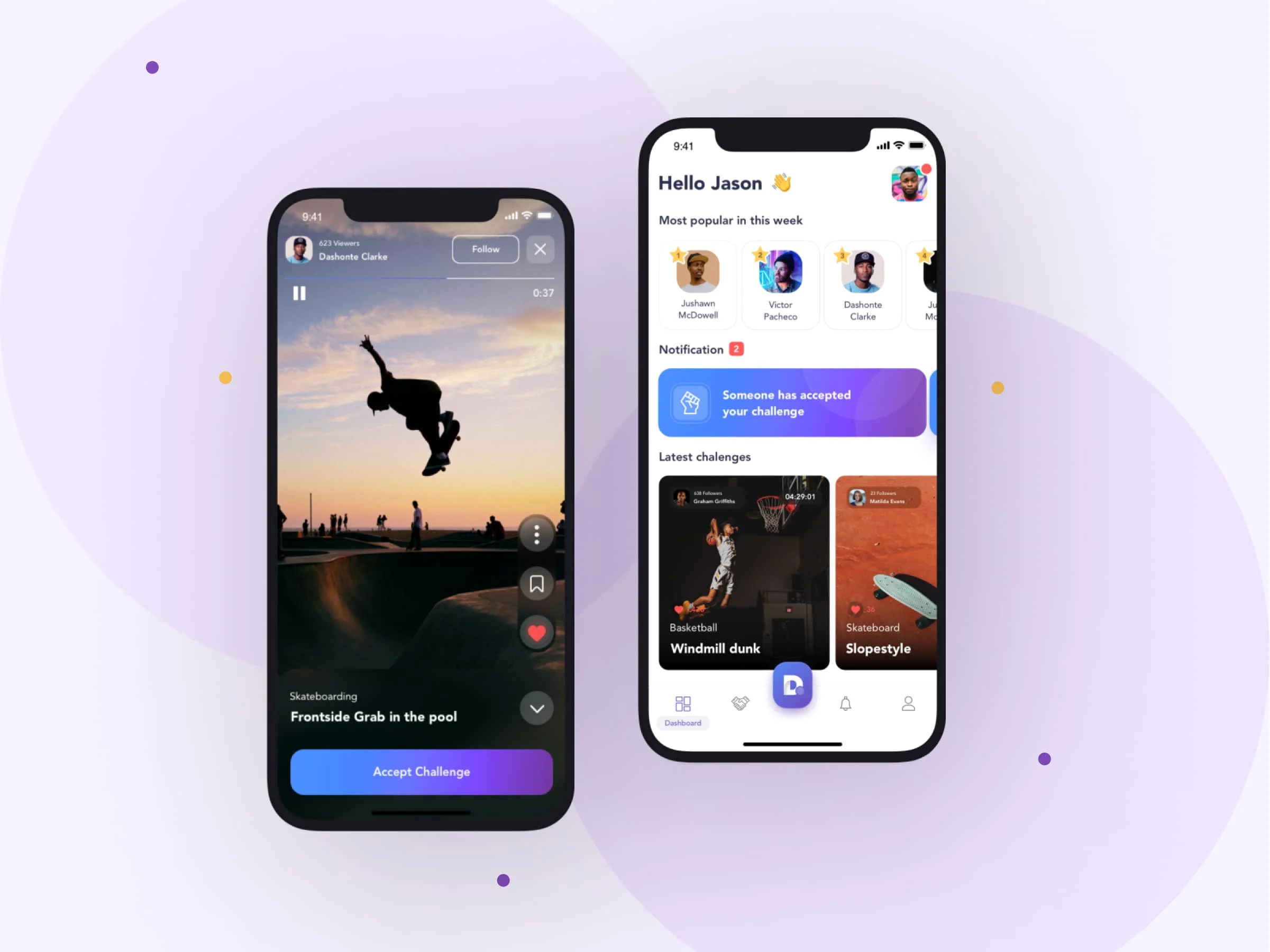
Duel - MVP for a challenger video social media app
Read the case study
EXCC - Creating a new PoS + PoW blockchain and crypto-exchanges
Read the case study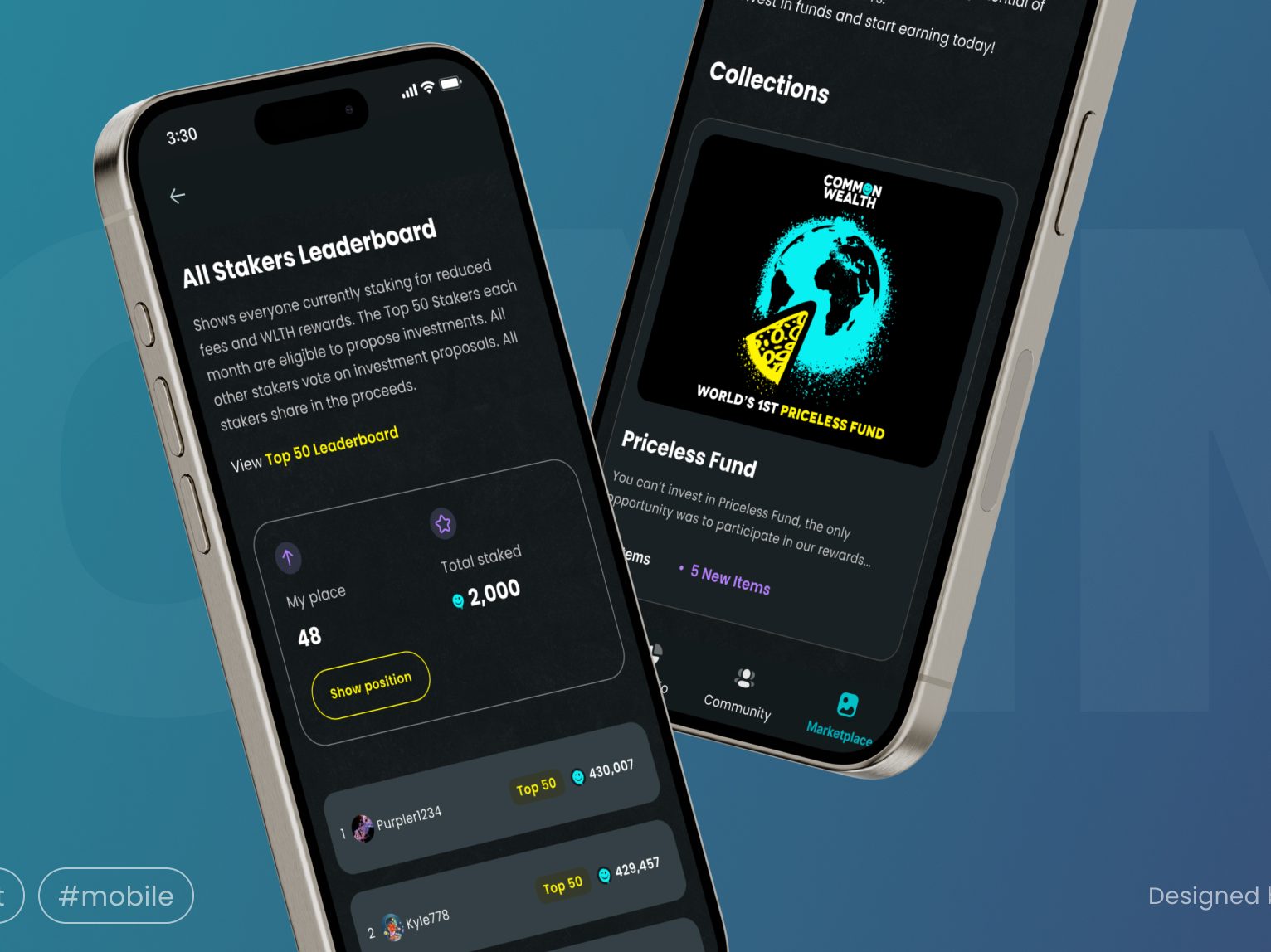
Common Wealth: Building a successful all-in-one Web3 investing platform, attracting 63k users in its first 3 weeks
Learn moreLet's talk
We’ve got answers on anything connected with software development.
Message us
Feel free to reach out using the form below, and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Schedule a meeting
You can also schedule an online meeting with Wojciech, our Senior Business Consultant.

founders who contacted us wanted
to work with our team.
Check our latest articles
Newsletter
You are just one click away from receiving our 1-min business newsletter. Get insights on product management, product design, Agile, fintech, digital health, and AI.













