What are AI agents & how do they work? | AI in business

AI is getting better at making decisions. Too many tasks need constant human attention. Combine the two, and you get AI agents – artificial intelligence that can handle surprises (more or less).
In fact, the technology of AI agents hold so much potential that Gartner expects this innovation to reach mainstream adoption within just 10 years.
So, what are AI agents, how do they work, and can their benefit your business?
AI Agent development
What are AI Agents?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents are systems capable of performing tasks autonomously by perceiving their environment, reasoning through data, and taking purposeful actions to achieve specific objectives.
These agents extend human intelligence, blending utility-based reasoning, reflexive responses, and adaptive learning.
Unlike static software, AI agents can evolve over time, making them especially valuable in dynamic business environments. For instance, they can predict customer preferences or optimize supply chains based on real-time data analysis. Their ability to continuously adapt positions them as a cornerstone of modern innovation.
Types of AI Agents
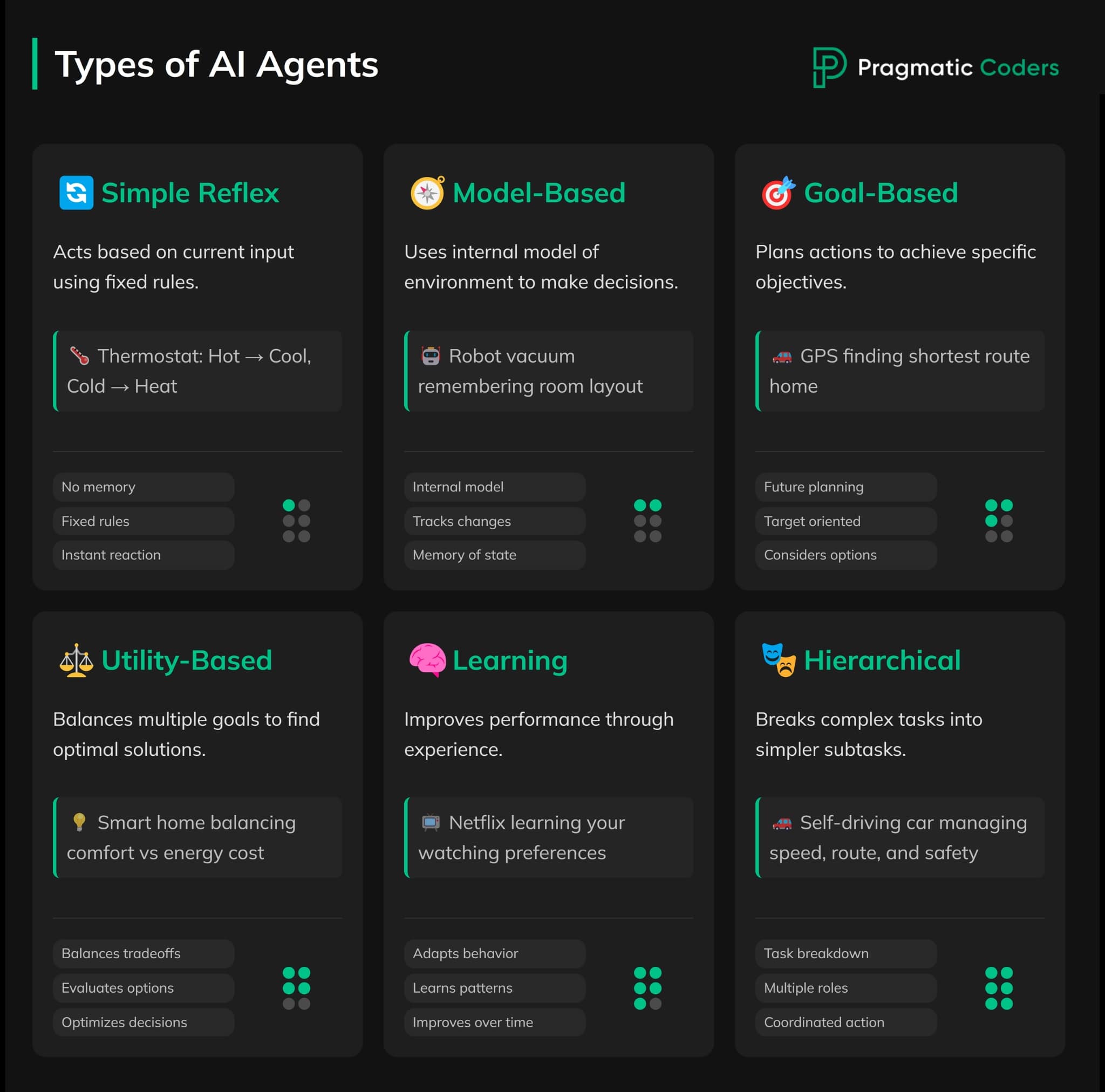
AI agents can be classified based on their functionality and complexity.
Some are straightforward, relying on predefined rules, while others are advanced systems capable of learning and reasoning autonomously.
- At one end of the spectrum are simple reflex agents, which operate solely on pre-programmed rules. For example, a thermostat that adjusts temperature based on predefined settings is a simple reflex agent. These agents cannot adapt or consider the broader context of their actions.
- Conversely, model-based reflex agents incorporate an internal representation of their environment. This enables them to assess how their actions might influence outcomes. For example, a robotic vacuum that uses sensors to navigate obstacles relies on model-based reasoning.
- Goal-based agents take functionality a step further by focusing on achieving specific objectives. They evaluate various scenarios to determine the most effective path to success. For instance, a logistics AI that plans delivery routes to minimize fuel consumption exemplifies this category.
- In contrast, utility-based agents aim to maximize a predefined utility function, balancing competing priorities such as speed, cost, and accuracy. Their adaptability allows businesses to manage complex operations, like optimizing inventory levels based on fluctuating market demand.
- Lastly, learning agents and hierarchical agents represent the pinnacle of AI adaptability. Learning agents evolve through experience, improving their performance over time. Hierarchical agents, meanwhile, break down complex tasks into manageable layers, making them ideal for intricate operations like manufacturing automation.
AI agent architecture
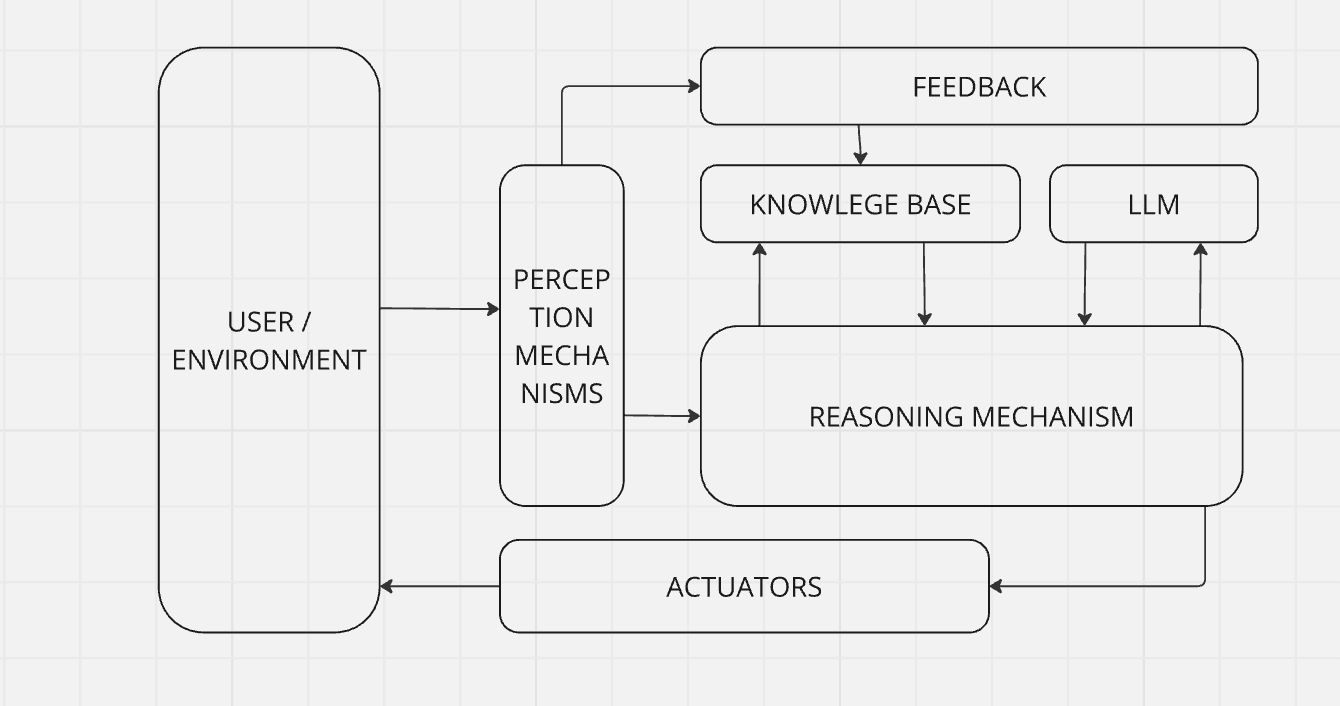
The architecture of an AI agent determines its functionality and efficiency. Key components include:
- Actuators: These are the tools or mechanisms that enable the agent to interact with its environment, such as robotic arms or APIs.
- Perception Mechanism: This component collects data from the environment, whether through sensors, cameras, or other inputs.
- Knowledge Base: A repository of relevant information, the knowledge base allows the agent to reason and make informed decisions.
- Reasoning Mechanism: This system is the brain of the agent. It evaluates data, predicts outcomes, and determines the best course of action.
- Feedback System: Ensuring adaptability, feedback systems monitor the outcomes of actions and refine future behavior.
- Foundation Models (LLM): Pre-trained systems, such as large language models, provide a robust starting point for reasoning and problem-solving.
These elements combine to create a cohesive system capable of tackling tasks ranging from simple automation to complex decision-making.
How AI agents work
AI agents operate through a continuous loop of perception, reasoning, and action.
First, they collect data from their environment through sensors or external inputs. For example, a customer service chatbot might analyze user queries in real time.
Next, the reasoning mechanism evaluates the data to determine possible actions. The agent identifies the most effective response using internal models and utility functions. For instance, a recommendation engine might analyze purchasing history to suggest relevant products.
The agent then executes the chosen action via its actuators. A self-driving car, for example, might adjust its speed or direction based on road conditions. Finally, the feedback mechanism assesses the outcome, ensuring the agent can adapt and improve over time. This cyclical process enables AI agents to function effectively in ever-changing environments.
AI Agents in business
AI agents are already reshaping industries. In customer service, virtual assistants provide 24/7 support, handling routine inquiries and escalating complex issues to human agents.
They optimize inventory levels, reduce operational costs, and predict demand fluctuations. Marketing teams use AI tools to analyze customer data and create highly personalized campaigns. Similarly, IT departments leverage AI agents for routine tasks like system monitoring and software updates, freeing up resources for strategic projects.
AI agents have the potential to connect every facet of game development, going well beyond single-task tools. They can link version control, asset libraries, documentation, and even live data sources—coordinating large-scale asset management, proposing code merges, and triggering automated tests. By gathering context from multiple channels, AI agents can adapt their plans in real time and refine outputs as the project evolves.
But there’s still more: Finance benefits from AI-driven fraud detection and risk assessment.
HR can leverage AI agents to automate repetitive tasks like resume screening, interview scheduling, and employee onboarding, freeing up time for strategic initiatives. Additionally, AI agents can provide real-time support for employees through chatbots and analyze workforce data to improve retention and engagement.
In manufacturing, AI agents optimize production, monitor machinery, and enable predictive maintenance. The automotive industry leverages AI for self-driving cars and automated drones, while robotics and multi-agent systems improve industrial automation.
While much attention has been given to AI diagnosing patients, the true AI revolution in healthcare is unfolding in back-office operations. Major tech companies like Microsoft, Oracle, and NVIDIA, along with startups like Quadrivia, are developing healthcare AI agents that automate administrative tasks, streamline workflows, and reduce documentation burdens—so that medical professionals can focus on patient care.
- Learn more: AI in healthcare: Key use cases & benefits
Benefits of AI agents
Implementing AI agents offers numerous advantages. They are available 24/7, ensuring uninterrupted service across various time zones. Another key benefit is scalability; AI agents can handle increasing workloads without proportional cost increases. Their ability to provide personalized interactions improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Moreover, AI agents excel at delivering data-driven insights. They uncover trends and patterns that inform strategic decisions by analyzing vast datasets. This results in significant efficiency gains, as repetitive tasks are automated, allowing human employees to focus on higher-value activities. Finally, their capacity for learning and adaptation ensures continuous improvement and long-term value.
Challenges of AI agents
While promising, the adoption of AI agents comes with challenges. Data privacy and security are paramount concerns, particularly in industries handling sensitive information, such as healthcare. Computational complexity and resource demands can strain existing infrastructure, requiring significant investment.
Ethical considerations, including bias and fairness, pose additional challenges. Ensuring that AI agents make equitable decisions is essential for maintaining public trust. Finally, real-time monitoring and oversight are crucial to prevent unintended consequences, such as erroneous decisions in critical applications.
- Must-read: How to build AI software right
Best practices for AI agents
To ensure effective and responsible deployment of AI agents, organizations should follow key best practices.
- Human oversight is essential—AI agents should operate within a human-in-the-loop framework to prevent errors and biases.
- Maintaining activity and conversation logs helps track performance, ensure compliance, and improve decision-making.
- Managing multi-agent dependencies and optimizing learning/knowledge base systems enable AI to adapt and improve over time.
Future and trends of AI agents
What’s the potential impact of AI agents on industries and society? And how will it influence businesses? Here are 3 potential consequences:
- As AI agents make rapid business decisions, companies will need to operate at both human and AI speeds. This means balancing quick automated choices with thoughtful human strategy and planning.
- People who are skilled at directing and optimizing AI systems will become increasingly valuable in organizations. Success will depend heavily on how well a company can coordinate its AI tools and have them work effectively with other companies’ systems.
- The interconnected nature of business AI systems creates new risks – problems can quickly spread between companies. Organizations will need new ways to protect themselves from both their own AI issues and problems that start in other companies’ systems.
- AI isn’t just changing how businesses operate—it’s reshaping entire industries. As AI agents take over more decision-making, businesses might find themselves in a world where software isn’t bought or subscribed to, but simply plugged in as needed. That’s a huge shift from the traditional SaaS model. Curious about what this means for the future of AI-driven businesses? Check out our article: “SaaS is dead? How AI agents reduced SaaS to just an API”.
Conclusion
AI agents are revolutionizing businesses’ operations, offering unparalleled efficiency, scalability, and adaptability.
Organizations can harness these tools to drive innovation and achieve competitive advantages by understanding their architecture, functionality, and applications. However, thoughtful implementation, addressing technical and ethical challenges, is essential for unlocking their full potential. With the right approach, AI agents can become invaluable partners in navigating the complexities of the modern business landscape.