The ultimate guide to insurance software development
Last updated: December 22, 2023

The insurance industry, once a realm of paperwork and phone calls, is undergoing a radical makeover thanks to the power of software.
Why?
- Firstly, gone are the days of filling out clunky forms and waiting for weeks to get insurance quotes. Today’s insurance customers want seamless and personalized experiences delivered through digital channels that fit their busy lifestyles.
- Secondly, companies need to implement cutting-edge technologies, like artificial intelligence and machine learning, not to be outcompeted by other players. It applies to the insurance sector as well.
The industry is no longer a sleepy old dinosaur; it’s a sleek, agile, and innovative insurance machine ready to take on the challenges of the 21st century. So, buckle up, dear readers, and let’s dive into the guide to insurance software development.
Here are our other guides – even more knowledge awaits!
Who is this guide for, and why read it?
This guide is for insurance business (InsurtTch startup) founders and insurance companies seeking to build robust custom insurance software solutions.
Inside, you’ll find valuable insights and strategies for navigating the world of insurance software development, whether for B2B or B2C insurance products (apps) or internal insurance operations.
What will you get from it?
- A general overview of the insurance software industry, including the most popular types of insurance software and features,
- A walk-through of the insurance market trends for 2024 and beyond,
- A step-by-step guide on building an insurance app from ideation to MVP development.
Introduction to insurance & insurance software
Before we dive into industry regulations, market trends, and insurance software development process intricacies, let’s start with defining the basics.
Insurance: definitions
Insurance | financial protection against unforeseen events |
Insurance policy | legally binding contract for financial protection |
Insurance claim | formal request for reimbursement |
Insurance quote | estimated cost of an insurance policy |
Premium | regular payment for insurance coverage |
Insurance policyholder | purchaser of insurance coverage |
Gross written premium (GWP) | total revenue from insurance sales |
Insurance software | A suite of comprehensive tools that automate and optimize various aspects of insurance operations. It connects all stakeholders and streamlines the insurance process from underwriting to billing.
|
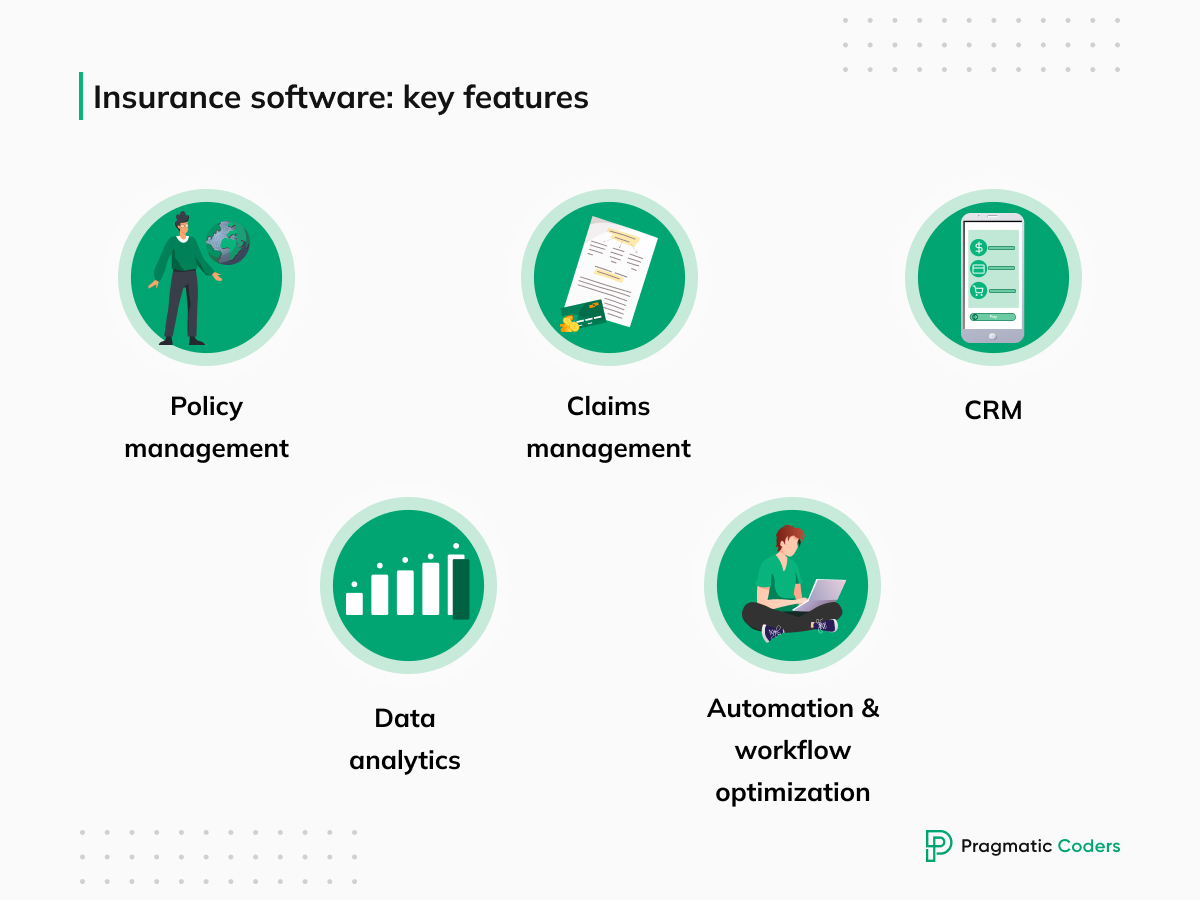
Insurance software key features
Key features of insurance software include:
- Policy management: Automates policy creation, issuance, and renewal.
- Claims management: Streamlines claims processing, adjudication, and payment, reducing processing times.
- Customer Relationship Management (insurance CRM): Provides a unified platform for customer interactions and data management.
- Data analytics: Extracts valuable insights from vast data sets. With data analytics, making informed decisions and assessing risk is much easier.
- Automation and workflow optimization: Minimizes manual tasks and automates repetitive processes.
Types of insurance software
Insurance software encompasses a wide range of specialized solutions tailored to different areas of the industry. Let’s examine some of them.
Core insurance software
- Generating Quotes: Core insurance software streamlines the process of generating quotes for potential policyholders. This involves gathering customer information, assessing risk factors, and applying appropriate rates to determine the premium.
- Processing Claims: When policyholders file claims, core insurance software facilitates the claims processing workflow – receiving claims documents, verifying information, assigning claims to adjusters, and processing payments.
- Tracking customer interactions: Core insurance software keeps track of customer interactions across various channels, such as phone calls, emails, chat sessions, and social media interactions.
Risk management software
- Analyzing historical data: Risk management software analyzes historical data, such as claims history, loss trends, and weather patterns, to assess the potential risks associated with different types of insurance policies.
- Setting premiums: Premiums are the regular payments that insurance customers make to keep their coverage active and protect themselves from financial losses, and risk management software plays a crucial role in setting them right. It considers various factors, such as risk assessment, competitive market rates, and regulatory requirements, to determine fair and appropriate premiums.
- Predicting future losses: Analyzing historical data and considering current market conditions help insurers predict potential losses and adjust premiums accordingly.
Fraud detection software
- Analyzing claim data: Insurance fraud detection software carefully checks claims for signs of cheating. This includes reviewing the details of claims, verifying supporting documents, and checking the timing of claims.
- Identifying suspicious claims: The software flags suspicious claims for further investigation, allowing insurers to check them more closely and determine their validity.
- Preventing fraudulent claims.
Agent and broker management software
- Tracking commission payments: Agent and broker management software tracks how much money agents and brokers receive from the insurance company for bringing in business. This makes sure agents and brokers get paid fairly for their work.
- Managing customer data: The software helps agents and brokers manage customer information, like contact details, policy information, and past transactions.
- Providing training materials: Agent and broker management software can provide agents and brokers access to training materials, such as product information, sales techniques, and compliance requirements.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software
- Connecting core processes: Just like putting all your puzzle pieces together, ERP software connects all the major parts of insurance operations into one system. This eliminates data silos and provides a holistic view of the business.
- Enhancing efficiency: It automates repetitive tasks, reduces the need for manual data entry, and makes it easier for people to share information. Less time wasted on paperwork and more time spent helping customers.
- Improving decision-making: ERP software gathers information from all parts of the business and stores it in one place to give a clear and up-to-date view of a company’s operations.
Benefits of implementing insurance software
In the fast-paced insurance world, embracing insurance software can transform your entire operation from a tangled mess of paperwork and manual processes into a sleek, efficient machine.
Imagine automated tasks handling repetitive tasks, errors disappearing, and every process running like clockwork. This newfound efficiency translates into a seamless customer experience with personalized service and faster claim resolutions.
With better data analytics, you unlock valuable insights that guide smarter decisions and risk assessments. And as you streamline and optimize, costs plummet, giving you a competitive edge.
Insurance market in 2024 and beyond: analysis
The insurance industry is amid an exciting transformation. A whirlwind of change, driven by various factors, reshapes how insurance works and its role in our lives. In today’s world, marked by climate shifts, tech advances, evolving work dynamics, and ever-changing customer expectations, insurers are on a mission for more than just profits – they’re aiming for relevance and purpose. Here’s what the global insurance market will look like in 2024 and the years to come, according to Deloitte and Statista.
Insurance market overview
According to Statista’s research, the global insurance market was worth around US$9 trillion in 2023. Non-life insurance was the largest segment, accounting for over half of the market. The average person spent around US$1,180 on insurance each year. The United States is the biggest market for insurance, with a total premium of US$4.5 trillion. The insurance market is expected to grow at a steady pace of 2.2% per year, reaching a value of US$10 trillion by 2028.
Insurance market structure
We can divide the insurance market into two types of insurance: life and non-life insurance. The other includes legal, general liability, property, motor vehicle, and health insurance.
Life insurance market
5 life insurance market trends (Statista)
- Digitalization: Life insurance is going digital, with online platforms and data analytics revolutionizing how policies are accessed and managed.
- Customization: Personalized life insurance plans are the new norm, catering to individual needs and risk profiles.
- Long-term care and retirement: As the population ages, insurers are developing solutions to support retirees and their needs.
- Sustainability and ESG: Life insurance embraces sustainability, offering ESG-focused policies that align with ethical values and social impact.
- Regulatory compliance: Life insurers must stay on top of evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maintain trust.
Non-life insurance market
5 non-life insurance market trends (Statista)
- Cybersecurity protection: More and more non-life insurers offer cybersecurity coverage to protect businesses and individuals from cyber threats, such as data breaches and ransomware attacks.
- Climate resilience: With rising climate risks, specialized insurance for floods, wildfires, and extreme weather events is gaining popularity.
- Parametric insurance: Parametric insurance is gaining traction. It’s a type of insurance that pays out based on predefined parameters, such as specific weather conditions or seismic activity, rather than assessing actual losses. Payouts are automatically triggered once these parameters exceed predetermined thresholds, eliminating the need for lengthy damage assessments. For instance, a parametric insurance policy for farmers could payout based on rainfall levels, ensuring rapid financial assistance when drought or excessive rainfall affects their crops.
- Data-driven auto insurance: Telematics (using sensors and data to track vehicle behavior and assess a driver’s risk profile) and usage-based insurance (charging premiums based on the number of miles driven) are transforming auto insurance, tailoring premiums to driving behavior and rewarding safer driving.
- Liability coverage for emerging risks: Non-life insurers are adapting liability insurance to cover new risks like autonomous vehicles and drone operations.
5 more insurance market trends for 2024 and beyond
Making a real impact
One big driver of this transformation is insurers’ newfound awareness of their potential to make a significant impact on society. Traditionally, insurers have been society’s financial safety net.. But now, they realize they can do more by actively preventing risks, minimizing losses, and addressing global protection gaps.
These challenges are pushing insurers to rethink their role. Instead of just covering losses after disasters, they’re finding new ways to prevent and reduce risks.
Digital transformation: AI to change the insurance industry
In this ever-changing landscape, technology is playing a pivotal role. Artificial Intelligence (AI), advanced analytics, automation, and core transformations reshape how insurance works.
Outdated systems, multiple platforms, integration headaches, and data flow issues are common hurdles. To make a real impact, insurers can level up their digital game using AI and advanced analytics to enhance customer interactions.
So, how can insurance companies leverage AI? This cutting-edge technology isn’t just about efficient operations. AI can:
- Boost productivity and cut costs,
- Help clients prevent or reduce risks before they happen,
- Provide personalized coverage, improve customer service, and reach underserved groups.
- Offer real-time insights into customer behavior and needs, ensuring insurers provide what customers want when they want it. (Take HDFC ERGO, for instance, an Indian insurer that uses artificial intelligence to offer hyper-personalized customer experience from onboarding to claims resolution.)
Check: AI predictions: Top 13 AI trends for 2024, trend 4. AI risk hallucination policy
AI and IoT: A dynamic duo for risk management
But the tech revolution doesn’t stop at AI and analytics. Insurers also embrace the Internet of Things (IoT) and AI to manage risks. By analyzing data from IoT devices, insurers can predict potential disasters and prompt policyholders to take preventive actions. For example, Hartford Steam Boiler uses hardware sensors to detect changes in temperature and water presence, sending alerts through a remote app to prevent losses.
Generative AI is another tool insurers are using to enhance efficiency and customer-centricity. It impacts various aspects of the insurance value chain, from improving employee experiences to boosting productivity. However, insurers need to balance the benefits of this technology with quality control and regulatory compliance.
Data: The key to transformation
The strength of insurers’ AI and analytics capabilities relies on their data sources. To generate faster, more accurate insights, insurers are breaking down data silos, modernizing data capabilities, and integrating both internal and external data sources.
Innovation often extends beyond an organization’s capabilities. Insurers actively collaborate with third-party vendors, from InsurTech startups to tech giants, to tap into these transformative capabilities.
Navigating regulations
Even though AI is making things easier for insurers, they still need to be careful about the rules and regulations around AI. The speed at which AI is changing can mean that the rules don’t always keep up. That’s why it’s essential that insurers collaborate with risk and compliance officers to establish ethical guidelines.
The EU is leading the way in creating rules for AI worldwide. Insurers need to make sure that their AI is not just profitable but that it also follows their ethical values and the law.
Meeting the Demands of Gen Z
Consumer expectations are evolving rapidly, and the insurance industry must adapt to these changing demands, particularly from Generation Z. This demographic shift brings unique expectations and preferences:
- Gen Z demands personalized, digital, and seamless insurance experiences. One way to provide them is through embedded insurance.
- Zoomers seek instant gratification and omnichannel access, expecting to manage their insurance policies effortlessly across multiple platforms.
- Interfaces and navigation must be simple and intuitive to meet the needs of this tech-native generation.
- Sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors are important for Gen Z. Insurance companies are incorporating sustainability principles into their underwriting and investment decisions, reflecting the growing trend of responsible and environmentally friendly practices.
The insurance industry is changing because of how society, the economy, and technology are changing. These changes are creating new risks and opportunities for insurers. To keep up, insurers must be innovative, adaptable, and customer-focused; emerging technologies can help them achieve that.

Insurance industry regulations
InsurTech companies collect and analyze a vast amount of personal data, which raises concerns about privacy and data security. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) aim to protect consumer data and give them control over how their information is used.
Examples of specific insurance technology regulations:
- The European Union’s Insurance Distribution Directive (IDD): The IDD aims to modernize the insurance distribution market and ensure that consumers receive clear and transparent information from insurance intermediaries.
- The U.S. National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) Innovation and Technology Task Force: The NAIC task force is focused on examining the impact of emerging technologies on the insurance industry and providing guidance to regulators and industry participants.
.png)
From idea to execution. The insurance software development process
Let’s delve deeper into the insurance software development process. Here’s a step-by-step walkthrough of how we at Pragmatic Coders approach it. To better visualize the process, we’ll use the example of a software development process for an insurance management app.
For a detailed explanation of an MVP app development process, check out the How to start a startup e-book.
Research
Before starting any project, the first important step is to gather information. In the case of creating software, we suggest going through these types of studies:
- Market research
- Competitor analysis
- User experience (UX) research
Market Research
Market research means studying the insurance market to make smart business decisions. For your insurance app, you should look at trends in the insurance industry. You want to know what people are looking for in insurance apps and how many people might use your app in the future.
To assist with this, our AI-based Market Research Tool can be incredibly valuable. It delivers in-depth market insights, analyzes competitor strengths and weaknesses, and projects potential revenue streams, all within moments. This tool will help you stay ahead of the curve and fine-tune your app to meet market demands effectively.
Competitor analysis
With competitor analysis, you study the existing insurance market. You want to see what your competitors are good at and where you can outcompete them. This will help you find a unique angle for your app. You should also compare the features, pricing, and marketing strategies of your competitors to see how you can stand out.
UX research
UX research means talking to potential users to understand their needs. UX researchers interview people to find out what they find frustrating about insurance apps and what features they would like to see.
Discovery & definition
Once you have gathered all this information, it’s time to plan your insurance app.
Solution discovery
Based on your research, you should come up with different ideas to solve the problems you’ve identified. For example, if you find that users want better ways to compare insurance plans, your solution could be to create a tool that makes this easier.
Solution definition
In this step, you test your ideas to find the best one. You create designs and prototypes of your insurance app to see how it might work. You want to make sure your solution meets users’ needs and can be built quickly (because the sooner the MVP is ready, the sooner can you validate it with your target audience).
A word about product discovery
The discovery process doesn’t end here; it evolves into a phase known as continuous product discovery. This ongoing cycle plays a crucial role in ensuring that your insurance app remains relevant, valuable, and aligned with your users’ changing needs and preferences over time.
Business & development planning
Now, let’s talk about the business side of creating an insurance app.
Lean Canvas
A Lean Canvas is a one-page plan for your insurance app. It covers things like the problem you’re solving, who your customers are, how you’ll make money, and more.
Business model
Your business model is how you’ll make money with your insurance app. You might offer a free version with basic features and then charge for extra features. You could also make money from ads or partnerships with other insurance companies.
Pitch deck
If you’re looking for investors to support your insurance app, you’ll need a pitch deck. This is a short presentation that explains your app, its benefits, how it makes money, and other important details.
MVP roadmap
An MVP roadmap is a plan for creating and launching the first version of your insurance app. It outlines the steps you’ll take to bring your app to life.
Research, discovery & definition, and business & development planning – we can assist you in all or some aspects of your app creation during a tailored Product Discovery Workshop session.
To learn more about workshops, read this article: Product Discovery Workshop: Everything you need to know
How to choose the right insurance software provider? 3 key steps
With the business side of your endeavor established, you’re ready to start your insurance MVP development. By partnering with an experienced custom insurance software development company, you’ll be ready to launch it in 3 months. But how do you choose the right one?
Check three steps and make an informed decision that meets your needs and budget.
1. Define your requirements
Before embarking on your search, take a step back and clearly define your requirements. What specific functionalities do you need to streamline your insurance development processes? What challenges are you trying to address? What exact requirements should the insurance software development company meet to make you want to work with them?
Having a clear understanding of your goals will help you narrow down the options and evaluate potential providers effectively.
2. Research potential companies & evaluate their expertise
Armed with your defined requirements, research the potential insurance software providers. Referrals are the best way to find your development partner. However, if you are new to the industry, you can utilize online directories like Clutch or Pangea to find and review them.
3. Evaluate their approach toward building (insurance) digital products
There’s a huge difference between hiring a product development and software development company. The first will simply build your software, the second will take care of the business side of it. In the end, you don’t want to create an insurance app just for the sake of doing it right? You want it to address users’ needs and be useful, so that it can generate revenue and real value. Here, a well-defined and experienced product management team plays a crucial role in the success of an insurance software solution.
Remember, choosing the right insurance software provider is a strategic decision. It can significantly impact your business operations, customer satisfaction, and overall success in the competitive insurance landscape, so you don’t want to rush with it.
Insurance software development guide. Summary
Let’s sum up. What is insurance software going to be like in 2024 and beyond?
- The insurance market is expected to grow at a steady pace of 2.2% per year, reaching US$10 trillion by 2028.
- The future of insurance technology will be all about AI, IoT, data science, personalization, omnichannel experience, sustainability, and inclusion.
Find a partner that can provide you with a perfectly tailored insurance software development service, embrace technology, and emphasize innovation. Building a great insurance software product is at your fingertips.
Contents
Would you like to talk about your project?
We are here to help! We take care of the entire product development process. Your success will make us successful.

.jpg)
