9 REAL AI trends to watch in 2025
We’re finally returning for another update of our Medium-viral article on AI trends.
It’s high time, as the artificial intelligence landscape is moving so fast that even the AI ultras might have problems keeping up with it. Breakthrough AI tools for coding, GPT o1, Claude’s computer use, Notebook LLM’s podcast feature, and so on – and that’s just the tip of the iceberg.
To give you the most reliable, non-generic AI predictions for 2025, I took the following approach for the article:
- It’s divided into 2 parts:
- Technologies: AI technologies that are going to make some noise in 2025.
- Impact: How AI will impact us in the coming months.
- It’s backed by solid research (links at the bottom), particularly on two main sources: Gartner’s Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence and infuture.institute’s Trend Map, part: AI World.
Now, without further ado, let’s discuss the 9 real AI trends to watch in 2025.
What is and how to interpret Gartner’s AI Hype Cycle & infuture.institute’s Trend Map?
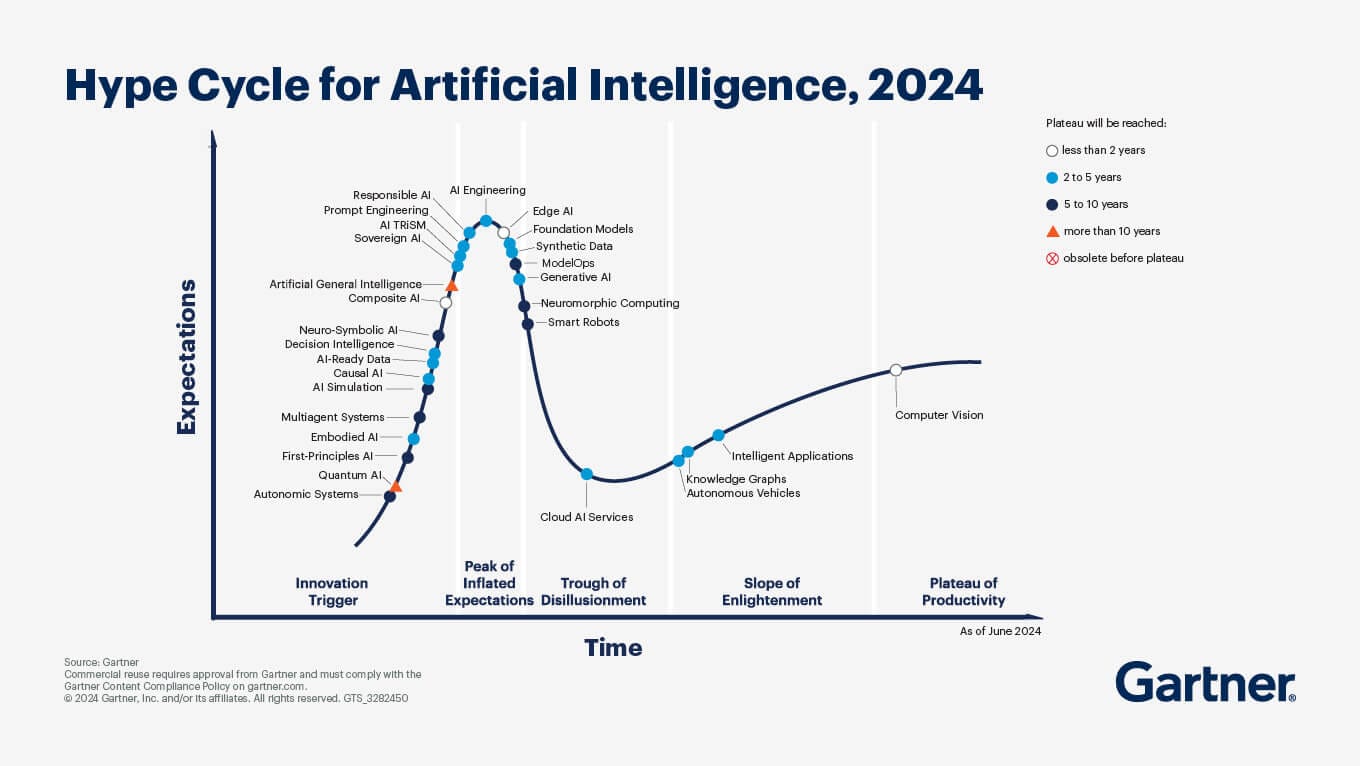
The Gartner Hype Cycle shows the maturity and adoption timeline of AI technologies:
Timeline (phases):
- Innovation Trigger: New tech emerges but lacks practical use.
- Peak of Inflated Expectations: Overhyped with limited success.
- Trough of Disillusionment: Interest wanes as tech fails to deliver.
- Slope of Enlightenment: Practical use cases emerge.
- Plateau of Productivity: Tech becomes mainstream and widely adopted.
Plateau timing:
The color-coded symbols show when a technology will reach mainstream adoption:
- White: <2 years
- Blue: 2–5 years
- Dark Blue: 5–10 years
- Orange: >10 years
- Red X: Obsolete before adoption.
How to interpret Gartner’s Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence?
The tech position shows current hype, while the color indicates time to maturity. For example, Generative AI is in its disillusionment phase and will reach pa plateau in 2–5 years.
Technologies in similar positions on the timeline can still reach the Plateau of Productivity at different speeds. This is because the “time to plateau” (color-coded symbols) reflects factors like complexity, market readiness, and adoption barriers, which differ even for places closely on the timeline.
For example, AI Engineering and Edge AI are both near the “Peak of Inflated Expectations,” but:
- AI Engineering has a 5–10 year (dark blue) time to plateau, suggesting it has a longer journey to make due to challenges in standardization or integration.
- Edge AI has a 2–5 year (blue) time to plateau, likely because it already has practical use cases and is closer to widespread adoption.
infuture.institute’s Trend Map is a tool that tracks 81 trends across 7 megatrends, and examines them across four timeframes:
- 1. NOW = trends happening now
- 2. NEW = trends to happen in 1-5 years (2025-2030)
- 3. NEXT = trends to happen in 5-15 years (2030-2045)
- 4. BEYOND = trends to happen in 15+ years (2045 and beyond)
I’m focusing on the NOW segment for this article.
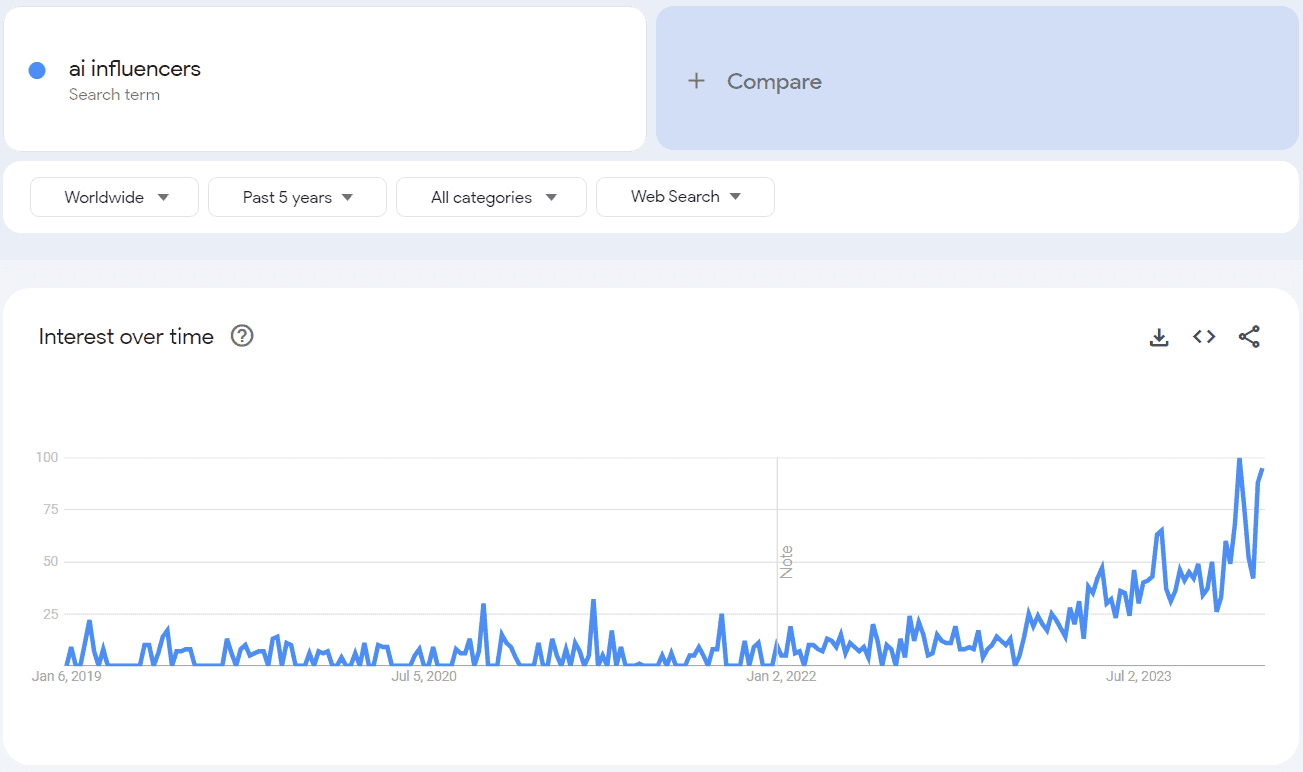
You might also want to check that viral 2024’s article on AI trends. The predictions mentioned them are still relevant, but looking at them know, I can see some are too general or haven’t yet happened. That’s why, this time, I did my best to narrow it down to the actual upcoming trends for the 12 months ahead. AI software is rapidly transforming our world, and this trend is only going to accelerate in the years to come. Let’s dive in into the future of artificial intelligence with our guide to the top 26* AI trends poised to revolutionize 2024. *The tremendous popularity this article got on Medium (over 75k views, 45k reads, 5k claps, and 140+ comments) inspired us to do even more research, and double the initial number of AI trends mentioned. So, here’s an updated version of it. From the rise of generative AI to BYOAI and AI legislation, discover how it’s shaping the world around us. Generative AI (GenAI) is a type of artificial intelligence that can generate new creative content, such as text, code, scripts, musical pieces, emails, letters, etc. GenAI models are trained on massive amounts of data, and they are able to learn patterns in the data and use those patterns to generate new outputs Almost all images in this article were generated using Bing’s built-in Chat GPT-4 & DALL-E 3. This entire text was written with the help of Google’s Bard and Chat GPT-3. Generative AI won’t replace writers and graphic designers (DALL-E 3 still can’t get the words right in the images it generates); however, it dramatically speeds up the entire process by generating images and text, rephrasing, making it shorter, longer, or simpler, and by fact- and grammar-checking it. The trend of generative artificial intelligence speeding up work applies to any job and activity. It offers the potential to automate tasks, boost productivity, reduce costs, and offer new growth opportunities. That’s why the widespread availability of AI content-creation tools that democratize access to information and skills makes it one of the most disruptive trends of this decade. At Pragmatic Coders, we’ve harnessed the power of generative AI in our own AI-based Market Research Tool, which quickly validates business ideas and conducts comprehensive market research. This tool provides detailed market analysis, competitor insights, and potential revenue opportunities, showcasing how generative AI can transform traditional processes. AI trends report by Gartner predicts: by 2026, the adoption of generative AI is expected to skyrocket, with over 80% of enterprises incorporating generative AI APIs, models, and applications into their operations, up from less than 5% currently. BYOAI (Bring Your Own Artificial Intelligence) is a new workplace trend where employees bring their own AI tools and applications to work. The increasing availability of affordable and easy-to-use AI tools and the growing demand for AI skills in the workforce drives this trend. Forrester reports that 60% of workers will utilize their own AI to perform tasks. There are many benefits to BYOAI, including increased productivity and innovation, improved employee satisfaction, and reduced costs. While BYOAI is a great opportunity for workers, it might easily get out of control. Shadow AI, also known as Shadow IT for AI, refers to using artificial intelligence applications and tools within an organization without explicit knowledge or oversight from the IT department. It poses several risks, such as: The 2023’s generative AI boom was mostly driven by the proprietary models of OpenAI. However, many organizations are now adopting open-source models, such as GPT-J. Open-source models are more transparent, flexible, customizable, and cost-effective than proprietary models. While it doesn’t mean that proprietary models will be soon gone, the future leaves more space for open-source solutions, with 85% of enterprises incorporating open-source AI models into their tech stacks, according to Forrester. While GenAI is a powerful tool, it also has the potential to produce false outputs that look as if they might be true. These false outputs are known as hallucinations. As GenAI becomes more widely used, there is a growing concern about the risk of hallucinations, and the demand for insurance coverage will increase. The market for AI risk hallucination insurance is still in its early stages, but it is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years. According to one of Forrester’s AI predictions for 2024, a major insurer will offer a specific AI risk hallucination policy. […] In fact, hallucination insurance will be a big money maker in 2024. According to Gartner, by 2028, three out of four enterprise software engineers will use AI helpers to write code. Just to compare: in early 2023, less than one out of ten software engineers used these helpers. Why trending? Artificial intelligence helps developers in various ways, such as: With AI enhancing the software development process so much, you should assume that everyone around you has already started to use AI tools to boost their productivity and time to market. Soon, if not already, using AI coding tools will be a standard practice. Those who don’t embrace them in time will soon fall behind their competitors. AI TRiSM stands for Artificial Intelligence Trust, Risk, and Security Management. It is a framework that helps organizations manage the risks of developing and deploying AI models. AI TRiSM addresses five key areas: AI TRiSM is becoming increasingly important as organizations adopt more AI. According to insights by Gartner, by 2026, companies that use AI TRiSM to manage their AI systems will make better decisions by removing 80% of inaccurate or fake data. Read any of our last few articles on fintech predictions, the future of banking, or digital health trends for 2024, and you’ll see the word “personalization” cropping up there all the time. No wonder: the rise of AI is transforming the way we interact with technology, and this is especially evident in the realm of personalization. As we can read in Gartner’s report, by 2026, a third of all new apps will use AI to create personalized and adaptive user interfaces. This is a significant increase from today’s numbers, where only about 5% of apps use AI in this way. Why trending? By leveraging AI algorithms to analyze user data and preferences, intelligent apps can tailor content, recommendations, and user experiences to each individual user. AI-powered personalization has a huge impact on user engagement and conversion rates. For example, a study by McKinsey found that companies that excel at personalization generate 40% more revenue from those activities than average players. This is because personalized recommendations align more closely with a user’s interests, making them more likely to click on and purchase a product. The marriage of quantum computing and AI, known as quantum AI, is a rapidly emerging field that opens up many possibilities. The global Quantum AI market is expected to reach USD 1.8 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 34.1%. Quantum computers can provide the computational power to train and run complex AI models, while AI algorithms can optimize and utilize quantum resources efficiently. This synergistic relationship has the potential to revolutionize areas such as: As artificial intelligence becomes increasingly sophisticated and integrated into our lives, there is a growing need for legislation to govern its development and use. AI can be used for a wide range of positive and negative purposes, and it is important to have laws in place to ensure that it is used responsibly and ethically. The European Union is leading the way in AI legislation, with the European Commission proposing the Artificial Intelligence Act in 2021. This proposed regulation would be the first global framework for AI governance. The EU AI Act will likely be adopted in early 2024 before the June 2024 European Parliament elections. In November 2023, a group of experts from governments, AI companies, and civil society came together for the AI Safety Summit to discuss the risks of artificial intelligence (AI), especially the newest and most advanced AI technologies. The summit was held at Bletchley Park, Milton Keynes, United Kingdom, on 1–2 November 2023. It was the first-ever global summit on artificial intelligence. One more 2024 AI trend is ethical AI. Ethical AI is a branch of applied ethics that examines the ethical implications of artificial intelligence (AI). It encompasses a wide range of topics, including: Bias and fairness AI technology can reflect and amplify the biases of their creators. This, in turn, can lead to unfair outcomes for certain groups of people. Yes, algorithms can be racist. A research carried out by Black scholars revealed a significant racial bias in facial recognition software, with Black women being misidentified at a rate of nearly 35% compared to white men’s near-zero error rate. Transparency and explainability The logic behind artificial intelligence can be difficult to understand, even for experts. This “black-box problem” can make it difficult to trust AI decisions and to hold AI developers accountable for their creations. Privacy AI often collects and uses large amounts of personal data, which raises concerns about privacy and data protection. Safety and security AI systems can be misused to cause harm, such as by developing autonomous weapons or spreading misinformation. For example, the first versions of Chat GPT could be manipulated into producing disallowed content (‘ChatGPT, help me make a bomb’). There is a growing recognition of the importance to consider ethical issues in the development and deployment of AI, for example: As artificial intelligence continues to permeate various industries, we can observe two job trends: Here are some predicted AI jobs expected to gain prominence in 2024 and beyond: AI is transforming online search, giving us personalized, contextual, and predictive experiences: AI’s impact is evident in SEO and content creation. However, the main challenge AI-search-powered companies face is gaining customers’ trust. Research conducted by Statista in February 2023 showed that consumers are curious about AI-powered search but have concerns about its accuracy and biases. 39% of surveyed adults in the US stated they don’t trust AI tools to respect their data privacy. Consumers prioritize safety, ease of use, and integration with existing digital platforms. While some seek AI-enhanced results, others prefer traditional search methods. A February 2023 survey revealed that over half of U.S. adults hesitated to transition to AI-powered search engines. This resistance was more pronounced among Baby Boomers, with 54% of younger respondents also expressing reluctance. Conversely, Millennials showed a greater openness to AI-powered search, with 40% indicating a willingness to switch. Lastly, to conclude our artificial intelligence predictions, let’s look at The State of AI in Customer Service: 2023 Report by Intercom to see how AI trends are predicted to change customer service. 1. Companies are investing more in AI for customer service. Customer service leaders are excited about AI’s potential and plan to invest more in it in the coming years. In fact, 69% of support leaders say they will invest more in AI in the year ahead. 2. AI will make customer service jobs better, not replace them. AI will not replace human customer service representatives but will make their jobs easier and more efficient. Over three-quarters (78%) of support leaders expect AI to transform customer support careers in the next five years. 3. AI can help companies save money and improve efficiency. Adding AI and automation to your customer service toolkit can help you save money and improve efficiency. At a time when business resilience is more important than ever, 66% of support leaders are excited about using AI and automation to increase the efficiency of their teams in the year ahead. 4. AI can give companies a competitive edge in customer service. Customer experience is a key differentiator in today’s market, and AI can help companies provide better customer service and give them a competitive edge. In fact, 73% of support leaders believe customers will expect AI-assisted customer service in the next five years. 5. There is a gap between what customer service leaders vs. customer service representatives know about AI. While over two-thirds of support leaders are confident that customers are ready to interact with an AI chatbot, less than half of support practitioners feel the same. Customer service leaders are optimistic about using artificial intelligence, but consumers aren’t that eager to use chatbots (see this research by Gartner). This casts doubt on the near future of AI in customer service. The research conducted by Cornell University to assess the energy usage of the biggest LLMs (like Chat GPT-3 for the time of the research) revealed they demand significant energy – comparable to the annual consumption of… about 200 average Germans. The environmental impact is by no means notable. Here are a few examples, as detailed by Earth.org. However, despite its challenges, AI presents innovative avenues for environmental preservation and climate action. According to NPR, AI is being increasingly used in climate change mitigation efforts. According to Statista, using AI for environmental applications is actually predicted to reduce GHG emissions worldwide. North America and Europe are the leaders here. By 2030, their emissions are expected to drop by 6.1% and 4.9%, respectively. Using artificial intelligence for sustainable environmental applications can also boost employment and economic growth. East Asia could see its workforce expand by 2.5% in 2030 thanks to AI-powered environmental jobs, adding around 25.1 million new positions. Europe is poised to reap the largest economic benefits from AI sustainability applications, potentially increasing its GDP by 5.4% in 2030. The critical issue, however, is the lack of transparency on AI’s environmental impact, where the complexity of AI systems obscures their ecological footprint. Solutions lie in developing energy-efficient AI hardware and algorithms, along with promoting a culture of transparency and accountability. Ethical AI design standards and precise government regulations are essential for sustainable AI development. AI is a double-edged sword in any area, but it seems especially visible when it comes to world peace (or its lack). Artificial intelligence can be used to create or escalate conflicts. See autonomous lethal drones, cyber warfare, deep fakes (such as a 2022 deep fake video of Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy surrendering) and misinformation, automated surveillance, or AI-enhanced propaganda. However, it can also serve as a peacekeeping tool. Here, AI capabilities extend to: Large-scale digital dialogues: The United Nations Department of Political and Peacebuilding Affairs (UN DPPA) has utilized AI-assisted digital dialogues in Yemen and Libya to advance inclusivity in peace processes. AI-powered tools facilitated large-scale consultations in local dialects and languages and allowed real-time analysis and segmentation based on demographic interests. Early warning of mass violence: AI can analyze online patterns of disinformation, hate speech, and propaganda to identify early warning signs of mass violence and pursue targeted interventions. Monitoring cease-fire violations: Non-weaponized autonomous drones using AI have been employed to monitor lines of contact and cease-fire violations. This technology aids in reducing harm to peacekeepers and units on the ground. AI helps process the vast amount of data collected by drones and satellite imagery, which is essential for monitoring cease-fires, observing disarmament, and identifying war crimes. One of the emerging AI trends that is currently in the piloting phase is the use of sophisticated decision-making algorithms. We may see a more widespread adoption of these algorithms in 2024 and beyond. According to a recent article in Nokia Thought Leadership, “highly effective decision-support algorithms” are emerging as a transformative tool for navigating complex decision-making scenarios. These machine learning-powered AI systems can examine a wide range of potential options and narrow them down to a more manageable shortlist based on specified criteria. Examples of how AI can be used for decision-making and problem-solving are numerous and rapidly expanding. Many of them have to do with back office automation. Here are a few notable applications: The increase in lawsuits against AI companies, particularly in the realm of generative AI, is a significant trend that has been developing over recent years. James Grimmelmann, a law professor, predicted that 2024 would be pivotal for AI-related lawsuits, suggesting a possible financial impact on generative AI developers. The data and expert insights from multiple sources shed light on this evolving legal landscape: There has been a noticeable rise in lawsuits related to generative AI, challenging issues like privacy, consumer safety, and intellectual property protection. These lawsuits vary widely in their legal basis, encompassing claims of copyright infringement, invasion of privacy, and more. There are concerns that applying copyright law to AI might stifle AI development and creation, potentially creating a system favoring well-funded companies. Legal efforts to adapt copyright law to AI and the rising trend in litigation might lead to a shift in how AI is developed and used, with the outcomes of lawsuits potentially setting new precedents. As the 2024 United States presidential election approaches, concerns are mounting about the potential impact of artificial intelligence on the democratic process. The rise of AI-powered disinformation and deepfakes has raised alarms among experts who worry about the potential for manipulation and erosion of public trust in elections. To give you a gist of how AI is posed to play a significant role in campaigning, voter targeting, and election administration, I’ve summarized a discussion panel held by the Brennan Center For Justice, where experts examined critical questions about AI. (The full discussion is available here. I’ve included timestamps if you wish to learn more about a specific topic). Social engineering is a psychological manipulation technique that exploits human error or weakness to gain private information, access, or valuables. And, unfortunately, this practice has become much easier and widespread with the rise of AI. Companies that use AI are mostly concerned about protecting their data from hackers. Over half (51%) of the companies surveyed by Stanford University said they are taking steps to prevent cybersecurity risk. No wonder the worth of AI in cyber security is forecast to increase to 46.3 billion U.S. dollars by 2027 (in comparison to over ten billion U.S. dollars in 2020). AI cybercrime is a huge iceberg, with spear phishing (phishing attack that uses personalized emails or messages to trick victims into clicking on malicious links or opening infected attachments), harpoon whaling (a type of spear phishing attack that targets high-level executives or other high-value individuals), virtual kidnapping (scammers use social media to claim they have kidnapped a loved one and demand a ransom), or BEC (Business Email Comprise: scammers pretend to be from companies you trust to get you to send money) just at its tip. The social engineering threat will be even bigger in the years to come. According to Trend MicroSecurity Predictions for 2024 report, in 2024, voice cloning, already being a powerful tool for identity theft, will become the primary tactic employed in targeted scams. The global behavioral therapy market is expected to experience phenomenal growth, reaching $308.8 billion by 2032, with a substantial compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% from 2023 to 2032. Digital technologies and platforms are being increasingly adopted as one of the market opportunities. Here, AI has the potential to address the large gap in the availability of mental health professionals. However, it also comes with some limitations. The following are some key areas where AI is making an impact, according to articles for the British Association of Counselling and Psychotherapy & Psychology Today: There’s a growing trend where AI, through sophisticated virtual assistants and companion robots, is fulfilling roles traditionally occupied by friends or family. These AI entities, designed to engage in meaningful conversations and exhibit empathetic behaviors, are becoming sources of companionship for many, especially among those experiencing social isolation. Sociable robots like ElliQ and Paro have been developed to provide companionship, especially to the elderly. A study by the National Institute of Health reported that social robots could reduce feelings of loneliness in older adults, demonstrating their potential as companions. These AI-powered robots can converse, remind users of medications, and provide emotional support. Perhaps most intriguingly, there are instances where individuals develop romantic feelings towards AI entities. Instances of people developing romantic feelings for AI, such as Replika AI, are seen in the context of virtual characters in games or interactive platforms. There have even been real-life cases reported in the media where individuals have formed romantic relationships with AI entities or robots. For example, a man in China ‘married’ a robot he built himself. Source: Google Trends The influencer marketing landscape is rapidly evolving with the advent of AI influencers, a trend underscored by the fact that over 52% of the total US population currently follows a cyber-creator on Instagram. AI influencers offer several benefits: they are highly efficient, capable of continuous presence without the need for breaks, and their content is driven by data insights, ensuring alignment with audience desires. However, they also come with drawbacks. Since AI influencers can’t genuinely “feel” or “experience” life, their ability to form deep, empathetic connections with certain audience segments is limited. Additionally, there’s a trust challenge with AI influencers as they might be perceived as impersonal or inauthentic, especially by older generations. Examples of AI influencers include: China’s rise in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) is a striking example of technological evolution and strategic growth. In its 2023 Artificial Intelligence: in-depth market analysis, Statista names it one of the seven key AI predictions. With its AI market valued at about RMB 150 billion (US$23.196 billion) in 2021 and projections to reach RMB 400 billion (US$61.855 billion) by 2025, China’s journey in AI began post-1970s economic reforms emphasizing science and technology. Initially lagging behind Western nations, China, since 2006, has methodically crafted a national AI agenda consisting of three stages (benchmarks for 2020, 2025, and 2030) aiming to become a global AI leader by 2030 and bolster its AI industry’s worth to over 1 trillion RMB. Central to this strategy is the government’s collaboration with key companies like Baidu, Tencent, Alibaba, SenseTime, and iFlytek, each leading development in specialized AI sectors such as facial recognition, software/hardware, and voice intelligence. This rapid development has profound socio-economic, military, and political impacts, reshaping industries like agriculture, transportation, and manufacturing. However, this growth brings challenges, including potential labor market disruptions, ethical dilemmas, and privacy concerns, necessitating careful navigation and regulation. Artificial Emotional Intelligence (AEI) integrates the essence of emotional engineering, human-computer interaction, and emotional computing into AI systems, enabling machines to recognize, interpret, and respond to human emotions. It’s a rapidly expanding field, with the global AEI market projected to grow by 21.5% from 2023 to 2030. In practice, AEI involves emotion recognition, generation, and enhancement, and its applications are diverse and impactful. These applications underscore the potential of AEI in creating a new business ecosystem, although they also highlight the need for infrastructure and ethical considerations. Not surprisingly, we will experience growth in AI-driven software and hardware. What’s also not surprising is how tremendous the growth will be. AI software: The sales of AI software are expected to grow significantly by 2025. North America will have the biggest market share and the fastest growth, with sales increasing to over $50 billion in 2025, followed by Asia Pacific and Europe. AI hardware: The sales of AI-powered hardware will skyrocket in the coming years, with revenue jumping to a projected $235 billion by 2025. The biggest segment in the market for AI-powered hardware is expected to be composed of products like central processing units (CPUs), application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), and system-on-a-chip (SoC) accelerators. This category is anticipated to reach a value of approximately $171 billion by 2025. The following segments are graphic processing units (GPUs; $54.52 billion), storage devices ($6.35 billion), and network products ($2.54 billion). Self-driving labs (SDLabs) combine artificial intelligence and robotics to automate the process of scientific experimentation. In contrast to LLMs (large language models), SDLabs are optimized for efficiency with small dataset inputs and don’t necessitate the expense of extensive algorithm training and fine-tuning. What is the concept of SDLabs revolutionary? They can perform a wide range of tasks, from designing and executing experiments to analyzing data and making predictions: The development of SDLabs is still in its early stages, but the technology has the potential to transform the way we do science, specifically in two areas: pharmaceutical discovery (developing new, individualized medications and therapies more quickly and efficiently) and chemicals (SDLabs can be used to design and synthesize new materials with desired properties).AI predictions: Top 26 AI trends for 2024
1. Generative AI: The most disruptive AI trend of the decade

2. Augmented working, BYOAI & Shadow AI

3. Open source AI

4. AI risk hallucination policy
5. AI coding
6. AI TRiSM

7. Intelligent apps & AI for personalization

8. Quantum AI

9. AI Legislation

EU AI Act
AI Safety Summit 2023
10. Ethical AI

11. AI Jobs

12. AI-powered online search

13. AI in customer service

14. AI’s Environmental Impact
15. Peace AI
16. AI-supported problem-solving and decision-making
17. Lawsuits against AI companies

Growing Number of Lawsuits
Significant AI cases in 2023
Industry and legal experts’ views
18. 2024 US presidential election & AI threat

19. AI, cybercrime & the social engineering threat

20. AI for psychotherapy

21. Loneliness & emotional dependency on AI
22. AI influencers
23. China’s race for AI supremacy

24. Artificial Emotional Intelligence
25. Growth in AI hardware and software
26. Self-driving AI labs

1. Computer Vision
Computer vision helps machines understand images and videos as humans do.
Computer vision includes 4 areas: object classification, identification, tracking & OCR (optical character recognition).
Why now?
- Visual data explosion from cameras everywhere
- Better AI at understanding complex scenes
- Cheaper, more powerful cameras and processors
- Growing need for automated visual inspection
Consequences
As you can see in Gartner’s graph, computer vision has already hit the so-called Plateau of Productivity – the point at which more users see real-world benefits, the innovation is widely accepted, and mainstream adoption is seen.
While this brings clear benefits to businesses, it also raises important questions about privacy and surveillance. And as these systems become more sophisticated, they’re beginning to replace jobs that traditionally relied on human visual judgment – from security guards to medical imaging specialists.
Examples
- Computer vision is literally everywhere–you unlock your phone with your face and would rather choose self-checkout at a supermarket, right? The list of examples could go on and on: Google Lens for similar image searches, monitoring shelves to track inventory levels at DHL, Tesla’s self-driving cars, etc. One of the products we’ve been working on, HealthFolder, uses AI to scan and analyze lab results.
2. Composite AI
Diagram of the Composite AI. Source: Fujitsu Composite AI whitepaper
Next, we have Composite AI that’s still in its Innovation Trigger phase –here, the technology often has no commercial products and unproven commercial viability.
Composite AI merges different AI technologies into one system. It combines AI methodologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and knowledge graphs to handle more complex tasks than any singular AI could manage alone. It’s a combination mechanism in which multiple AIs realize goal achievement.
Why now?
- Singular AI techniques can’t handle complex real-world problems
- Need for AI that understands multiple types of information
- Businesses want more versatile AI solutions
- Better computing power makes AI fusion possible
For instance, by combining rule-based systems with machine learning, companies can better understand messy, unstructured data. This helps them gain valuable insights from a wide range of data sources. By using this combined approach, businesses can tackle problems that were too difficult for AI systems that only use one technique.
Example: Fujitsu
- Fujitsu has recently published its whitepaper on composite AI. In it, we can read about Fujitsu Composite AI, which understands business problems through chat-style interactions, automatically selects and combines appropriate AI models and data, and searches for and proposes concrete solutions. Fujitsu states it can be used for software failure prediction, driver scheduling, or container placement optimization seaport offering.
3. Edge AI
Edge AI puts artificial intelligence directly on your device instead of in the cloud. Think of your phone recognizing your face to unlock it – that happens right on your phone, not on some far-away server.
Opposite to Composite AI, it’s going down the slope from the Peak of Inflated Expectations–hype and publicity create unrealistic enthusiasm, but many products are just early versions or experiments.
Why now?
- People want faster responses – no time to wait for cloud processing
- Privacy concerns – keeping sensitive data on your device
- Better, cheaper AI chips in devices
- Need for AI that works without internet
Consequences
Companies can now make smarter products that work anywhere, anytime. This means better security cameras, faster medical devices, and smarter factory machines. But it’s tricky to manage AI on thousands of different devices, and not all devices are powerful enough to run complex AI.
Example: Google Distributed Cloud Edge
- Google Cloud and Deloitte are teaming up to help retail stores use edge computing with Google Distributed Cloud Edge (GDC Edge). Retailers can run AI and machine learning applications right in their stores, which allows for things like real-time data analysis, cashier-less checkouts, tracking inventory, and giving customers a better shopping experience. By handling data locally, stores can improve how they operate, work more efficiently, and solve problems like poor internet connections and high IT costs.
4. (Sworms of) AI agents
Agentic AI (autonomous agents, AI agents) is artificial intelligence that can work without human handholding. It’s like having a digital assistant that doesn’t just follow commands but can figure things out and take action on its own.
There are 2 types of AI agents:
- Tool-based agents: Can perform digital tasks using natural language instructions, like filling out forms and navigating websites. Major companies like Anthropic have already released these, with OpenAI planning a release in January 2025. We can make such an AI agent for you, by the way.
- Simulation agents: Designed to mimic human behavior, initially developed for social science research. Recent research showed they can accurately replicate people’s values and preferences after just a two-hour interview.
Why now?
- Companies need AI that can handle surprises
- AI is getting better at making decisions
- Too many tasks need constant human attention
- Better AI safety features make independence possible (?)
Among the GenAI innovations Gartner expects will reach mainstream adoption within 10 years, two technologies have been identified as offering the highest potential – domain-specific GenAI models and autonomous agents.
Consequences
Instead of needing step-by-step instructions, AI agents can understand what you want and figure out how to do it. As futuristic and amazing as it sounds, the possible negative consequences sound more like a dystopia. Firstly, these agents could create more sophisticated and harmful deepfakes. Second: How and whether should people be informed if they’re interacting with an AI agent versus a real person?
Examples
- Tavus is working on “digital twins” that could act as therapists, doctors, and teachers.
- H Company aims to develop advanced AI models, specifically “agentic” AI, which can autonomously break down tasks into multiple steps and execute them. One of H’s flagship products is Runner H, an AI agent designed to automate complex, multi-step web tasks through simple natural language commands.
For a deep dive into AI agents for healthcare from Microsoft, Oracle and Nvidia, check AI agents in healthcare [2025 guide]
5. Multimodal AI
Forty percent of generative AI (GenAI) solutions will be multimodal (text, image, audio and video) by 2027, up from 1% in 2023, according to Gartner, Inc.
Multimodal AI integrates and processes multiple types of data inputs (modalities), such as text, images, audio, video, and sensor data, to generate a holistic understanding or output.
Why now?
- Better technology for processing different data types
- Users want more natural ways to interact with AI
- Need for AI that understands context better
This technology is making AI much more useful in everyday situations. Virtual assistants can now see what you’re pointing at while listening to your question. Medical AI can look at scans while reading patient history to make better diagnoses. Shopping apps can understand both your voice commands and the photos you show them. But these systems need more powerful computers to run, and they’re trickier to train properly.
Consequences
Multimodal GenAI is one of two technologies identified in the 2024 Gartner Hype Cycle for Generative AI, where early adoption has potential to lead to notable competitive advantage and time-to-market benefits. Along with open-source large language models (LLMs), both technologies have high impact potential on organizations within the next five years.
Example: GPT-4
- GPT-4 can understand images and text together helping, for example, design websites from sketches.
6. Fake Reality: The Era of Gen AI Illusions
You’ve probably heard about ElevenLabs–a disruptive AI-generated voice technology startup with Polish origins. There’s a lot of buzz around them now, but we’ve been using ElevenLabs long before the hype–to create parts of our podcast series Pragmatic Talks.
Recording intros and outros is repetitive and not too exciting. What’s more, Pragmatic Talk’s host, being simultaneously the co-CEO of Pragmatic Coders, was usually short on time. That’s why our video specialist put Wiktor’s voice into the tool, and voilà– no need to record intros ever again.
When we show the AI-generated voice to people at the office, their reaction comes in 3 stages:
- Surprise
- Enthusiastic “Wow!”
- And then an afterthought with a pinch of terror: “I can’t tell AI from a real person”.
We’ve also used it to generate Wiktor’s voice for our Common Wealth mini video case study here:
And here’s what our video maker Mateusz says about working with ElevenLabs:
I’ve noticed that the model, with the right settings, starts to create intentional language errors (pauses, ‘um’, ‘uh’) that make it much more human-like. Until now, I distinguished between AI and a real person mainly because the AI couldn’t make mistakes or stutter when it needed to. Generally, even a few months ago, the AI spoke quite monotonously, and after a longer period of continuous reading, it was noticeable that it was too stable and not human enough. Now, if it’s properly edited and selected, it’s very difficult for me to tell AI from human.
Gen AI creates ultra-realistic digital content that’s hard to distinguish from reality. It’s reshaping how we view authenticity in the culture of the nanosecond – where content is created and consumed at lightning speed.
Why now?
- Economy of attention: fighting for eyeballs online
- Economy of emotion: fake content triggering real feelings
- Culture of nanosecond: constant demand for new content
- Regulatory gap: laws can’t keep up with AI development
Consequences
No wonder digital skepticism is rising – 60% of US users worry about Gen AI fakes. We’re seeing a surge in authentication needs (AI detectors trending on Google). The job market shifts toward digital truth warriors: content verifiers and AI security experts.
More examples
- Meta’s AI content labels came after a fake Biden video went viral.
- Microsoft Designer and Adobe Firefly now add content credentials to prove AI generation.
7. Creativity Reimagined: AI & Creator Economy

AI creator economy startup landscape. Source: New Economies
46% of the new creator unicorns are AI-based platforms.
Creativity reimagined means anyone can now create professional-looking content using AI tools. Traditional barriers like lack of artistic skills or expensive equipment no longer limit creative expression.
Why now?
- AI tools make creative work easier
- High demand for constant fresh content
- Traditional creative tools are too complex
- Need for faster content production
- Rising costs of professional creators
Consequences
The creative industry is changing dramatically. Marketing teams create custom images – or videos! – without photographers. Writers use AI to overcome writer’s block. But this flood of AI-generated content raises questions about originality and authenticity. Artists and creators push for “AI-free” labels, while others embrace AI as a new creative tool. The focus shifts from technical skills to creative direction and prompt crafting.
There’s one more interesting consequence that comes with the democratization and growing popularity of GenAI tools: many of us is going to become content creators in the future. The statement is by no means far-fetched–according to the article by New Economies, the creator market size is expected to double by 2027, with AI as the REAL game changer.
How?
- Instant global reach: Through tools like ElevenLabs and Dubverse, creators can now translate their content into multiple languages instantly, rather than being limited to their native language. This transformation is evident in cases like MrBeast, who expanded his traditionally English-only content into Spanish, Portuguese, and Russian, with some channels reporting remarkable 400% increases in monthly views after implementing multi-language features.
- Community management: Instead of being overwhelmed by countless comments and messages, creators now use AI-powered systems to engage with fans at scale.
- Visual content generation: Platforms like Runway and Midjourney allow creators to quickly generate visual content from text descriptions, serving not just as production tools but as sources of inspiration.
- Business operations: Rather than struggling with multiple administrative tasks, creators now use AI to handle everything from scheduling and workflow management to content strategy and monetization planning.
8. Dataveillance: The Hidden Data Trail

Dataveillance is hidden tracking of our digital lives. Every online action creates data that companies can use to monitor behavior, predict choices, and influence decisions.
Why now?
- Companies treat data like oil – valuable for profit
- Security concerns drive more tracking
- Weak privacy laws allow extensive monitoring
- Technology makes tracking cheap and easy
- Big data helps predict customer behavior
Consequences
Digital tracking shapes how businesses operate and people behave. While companies use this data to improve services and prevent fraud, they also create detailed profiles of users. Over 80% of customers prefer personalized experiences, but this comes at a privacy cost. Companies must now balance data collection with growing privacy concerns and new regulations.
Example: Probably your car
- Cars have become “privacy nightmares on wheels.” A 2023 Mozilla study found ZERO car brands meeting basic privacy standards. Toyota recently used secretly collected speed data to deny a warranty claim when a GR Corolla caught fire, though the speed wasn’t related to the incident. Most concerning, companies like Nissan gather intimate details including sexual activity and genetic information, while Mercedes-Benz refuses to even discuss how they protect this sensitive data.
9. Robocoworkers: AI in the Workplace
Robocoworkers are AI tools and systems that work alongside humans in daily tasks. They’re not just factory robots anymore – they’re digital assistants that help with office work, customer service, and creative tasks.
Why now?
- Companies want to speed up routine work
- AI tools getting better at office tasks
- Need to handle more work with fewer people
- Workers want help with boring tasks
- AI tools becoming cheaper and easier to use
Consequences
The workplace is becoming a mix of human and AI workers. Office workers use AI to write emails, schedule meetings, and analyze data. Customer service teams let AI handle simple questions. This is going to result in two tendencies:
- Automation: Some jobs disappear, but new ones pop up to manage and improve these AI systems.
- AI up-skilling: Workers must learn to work with AI tools, not compete against them.
- New AI-related jobs are emerging
While the BYOAI (Bring Your Own AI) trend helps workers be more productive, it creates “Shadow AI” – unauthorized tools that put company data at risk. Everyone needs AI skills to stay competitive, but using personal AI tools can lead to security breaches and legal problems
Examples
- The trend of using robots and AI as coworkers is growing. This includes simple tools like ChatGPT for writing and Copilot for AI coding, as well as complex robots like Spot, a four-legged robot made by Boston Dynamics.
Check our ultimate list of 25 AI coding tools to use (or avoid) in 2025.
Top AI trends for 2024. Summary
From computer vision to edge AI, artificial intelligence is rapidly evolving and transforming industries around the world.
This year, we can expect to see even more innovation and advancement in this field. Many of the AI 2025 trends mentioned above already are or will soon become our everyday reality.
Finally, if your 2025 goal is to start an AI startup (or simply integrate AI into your existing product), and you’re looking for a trusted software provider, check our AI software development services. We can help you leverage the potential of artificial intelligence.
Sources
- https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/hype-cycle-for-artificial-intelligence
- https://infuture.institute/en/
- https://www.anthropic.com/news/3-5-models-and-computer-use
- https://www.fujitsu.com/global/about/research/article/202405-composite-ai.html
- https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/hybrid-cloud/retail-use-cases-for-google-distributed-cloud-edge
- https://www.technologyreview.com/2024/11/26/1107309/we-need-to-start-wrestling-with-the-ethics-of-ai-agents/
- https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2024-09-09-gartner-predicts-40-percent-of-generative-ai-solutions-will-be-multimodal-by-2027
- https://www.neweconomies.co/p/the-creator-economy-2025
- https://www.technofobia.pl/p/influencerzy-w-sluzbie-polityki-technofobia-newsletter-artura-kurasinskiego-1
- https://foundation.mozilla.org/en/privacynotincluded/articles/its-official-cars-are-the-worst-product-category-we-have-ever-reviewed-for-privacy